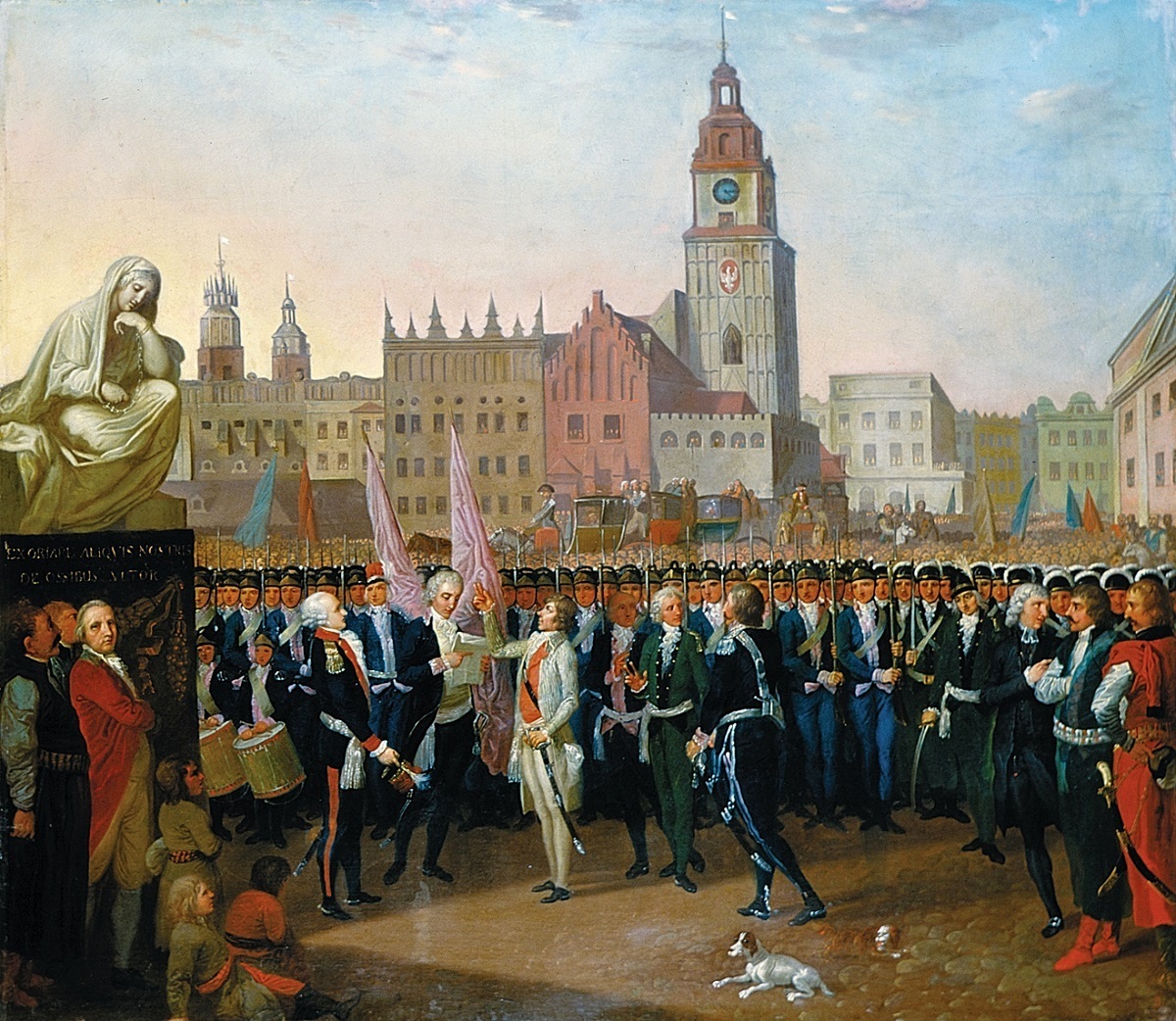|
Ko┼Ťci├│┼é ┼Ťw. Anny
St. Anne's Church () is a Roman Catholic church in the historic center of Warsaw, Poland, adjacent to the Castle Square, at '' Krakowskie Przedmie┼Ťcie 68''. It is one of Poland's most notable churches with a Neoclassical facade. The church ranks among Warsaw's oldest buildings. Over time, it has seen many reconstructions, resulting in its present-day appearance, unchanged since 1788. Currently it is the main church parish of the academic community in Warsaw. History In 1454 Duchess of Masovia Anna FiodorownaJ. T─Ögowski, Anna i Barbara ÔÇô ksi─Ö┼╝ne mazowieckie z XV wieku. Przyczynek do genealogii Piast├│w mazowieckich, in: J. ┼Üliwi┼äski (red.), Spo┼éecze┼ästwo i polityka do XVII wieku, Olsztyn 1994 (in some old books mistakenly called Holszanska), coming from a Ruthenized Lithuanian princely house, founded this church with a cloister for the Bernardine friars (''Order of Friars Minor''). The square in front of the church was a place of solemn homages to Polish monarchs b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four Evangelists
In Christian tradition, the Four Evangelists are Matthew the Apostle, Matthew, Mark the Evangelist, Mark, Luke the Evangelist, Luke, and John the Evangelist, John, the authors attributed with the creation of the four canonical Gospel accounts. In the New Testament, they bear the following titles: the Gospel of Matthew; the Gospel of Mark; the Gospel of Luke; and the Gospel of John. Gospels The gospels of Gospel of Matthew, Matthew, Gospel of Mark, Mark, and Gospel of Luke, Luke are known as the Synoptic Gospels, because they include many of the same stories, often in the same sequence or even verbatim. While the periods to which the gospels are usually dated suggest otherwise, convention traditionally holds that the authors were two of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus, John and Matthew, as well as two "apostolic men", Mark and Luke, whom Orthodox Tradition records as members of the 70 Apostles (Luke 10): * Matthew the Evangelist, Matthew ÔÇô a former tax collector (Levi) who w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortifications
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ("strong") and ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley Civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large cyclopean stone walls fitted without mortar had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae. A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum or fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, they acted as a bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernardo Bellotto
Bernardo Bellotto (c. 1721/2 or 30 January 172117 November 1780), was an Italians, Italian urban Landscape art, landscape Painting, painter or ''vedutista'', and printmaker in etching famous for his Veduta, ''vedute'' of European cities ÔÇô Dresden, Vienna, Turin, and Warsaw. He was the student and nephew of the renowned Giovanni Antonio Canal, known as Canaletto, and sometimes used the latter's illustrious name, signing himself as Bernardo Canaletto. In Germany and Poland, Bellotto called himself by his uncle's name, Canaletto. This caused some confusion, however BellottoÔÇÖs work is more sombre in color than Canaletto's and his depiction of clouds and shadows brings him closer to Dutch painting. Bellotto's style was characterized by elaborate representation of architectural and natural vistas, and by the specific quality of each place's lighting. It is plausible that Bellotto, and other Venetian masters of ''vedute'', may have used the camera obscura in order to achieve super ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presidential Palace, Warsaw
The Presidential Palace () is the official residence of the Polish List of heads of state of Poland, head of state and president alongside the Belweder Palace, located in Warsaw, Poland. Originally constructed in 1643 as an aristocratic mansion, it was rebuilt and remodelled several times over the course of its existence by notable architects. The current neoclassical architecture, neoclassical palace was completed in 1818. Throughout its history, the palace was a venue for important historical events in Polish, European, and world history. In 1791, the facility hosted authors and advocates of the Constitution of 3 May 1791, the first modern European constitution. In 1818, the palace began its ongoing career as a governmental structure when it became the seat of the Viceroy (Namiestnik of the Kingdom of Poland, ''namiestnik'') of Congress Poland. Following Poland's resurrection after World War I, in 1918, the building was taken over by the newly reconstituted Polish authorities an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond Vault
A diamond vault is a form of vault church architecture used in the Late Gothic and Renaissance style, which is based on an elaborate system of cavernous vaults in a manner resembling diamonds. It was widely used especially in Central European countries. Diamond vaults are concave-convex ceilings so complex that, as their name suggests, they invoke the facets of a cut gemstone. First appearing in 1471 at Albrechtsburg castle in Meissen, Germany, they were employed for almost a century in locations as far apart as Gda┼äsk on the Baltic to Bechyn─Ť in Southern Bohemia (today's Czech Republic). From the historical point of view, diamond vaults show the continuing vitality of the Gothic architecture in Central Europe, at a time when the rediscovery of the classical past in Renaissance Italy was changing the course of building. Architecturally, they offer some of the most impressive examples of geometrical experimentation and versatility in both secular and sacred spaces. The desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw Uprising
The Warsaw Uprising (; ), sometimes referred to as the August Uprising (), or the Battle of Warsaw, was a major World War II operation by the Polish resistance movement in World War II, Polish underground resistance to liberate Warsaw from German occupation. It occurred in the summer of 1944, and it was led by the Polish resistance Home Army (). The uprising was timed to coincide with the retreat of the German forces from Poland ahead of the Soviet advance. While approaching the eastern suburbs of the city, the Red Army halted combat operations, enabling the Germans to regroup and defeat the Polish resistance and to Planned destruction of Warsaw, destroy the city in retaliation. The Uprising was fought for 63 days with little outside support. It was the single largest military effort taken by any European Resistance during World War II, resistance movement during World War II. The defeat of the uprising and suppression of the Home Army enabled the pro-Soviet Polish administra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
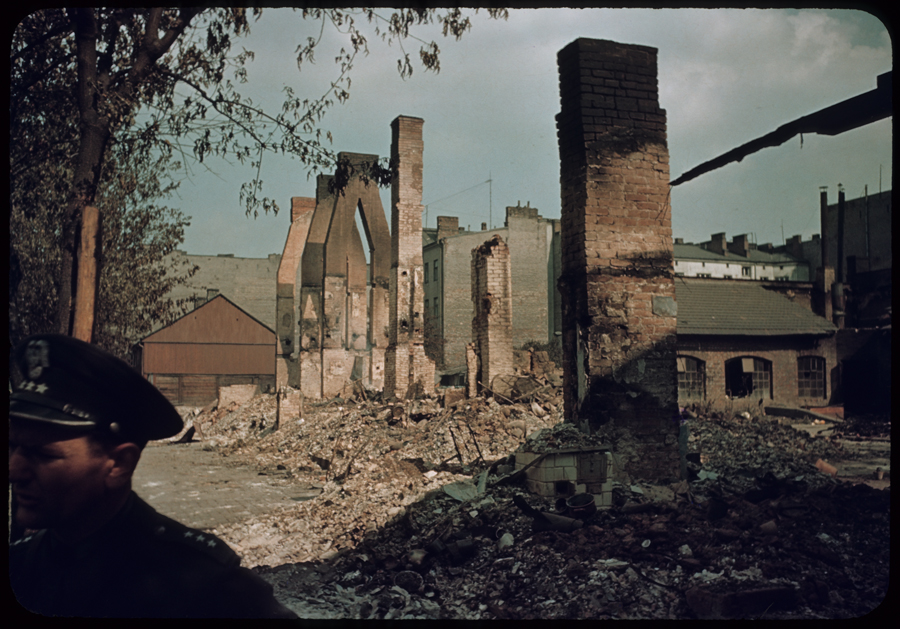
Bombing Of Warsaw In World War II
The bombing of Warsaw in World War II started with the aerial bombing campaign of Warsaw by the German Luftwaffe during the siege of Warsaw in the invasion of Poland in 1939. It also included German bombing raids during the Warsaw Uprising in 1944. During the course of the war, approximately 85% of the city was destroyed due to German mass bombings, heavy artillery fire, and a planned demolition campaign. Siege of Warsaw (1939) In 1939, the Luftwaffe opened the German attack on Poland with operation Wasserkante, an air attack on Warsaw on 1 September. This attack by four bomber groups was of limited effectiveness due to low-lying cloud cover and stout Polish resistance by the PZL P.11 fighters of the Pursuit Brigade, which claimed down 16 German aircraft for the loss of 10 of their own. However, heavy losses in Polish fighter aircraft meant that by 6 September the air defense of Warsaw was in the hands of the 40 mm (24 guns), 75 mm (72 guns) anti-aircraft guns and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J├│zef Kossakowski (bishop)
J├│zef Kazimierz Korwin Kossakowski (16 March 1738 ÔÇô 9 May 1794), of ┼Ülepowron coat of arms, was a Polish noble, bishop of Livonia from 1781, political activist, writer, and supporter of Russian Empire. Early life Brother of hetman Szymon Kossakowski, voivode Micha┼é Kossakowski and castellan Antoni Kossakowski, he took Holy orders on 17 April 1763''Hierarchia Catholica medii et recentioris aevi'', v. VI, Patavii 1958, p. 165 after having studied in Vilnius and Warsaw. His first positions in the Church were a provost in Wo┼épa and canon in Vilnius. Career On 13 March 1775 he became an aide to the bishop of Vilnius (titular bishop of Cinna), and on 17 September 1781 he became the bishop of Livonia (Polish: ''Inflanty''). At that time he also became administrator of the Courland diocese. He is known to have misappropriated vast amounts of the Church's and the public's finances. From 1787 he received a steady pension from the Russian embassy in Poland,Norman Davies, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ko┼Ťciuszko Uprising
The Ko┼Ťciuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794, Second Polish War, Polish Campaign of 1794, and the Polish Revolution of 1794, was an uprising against the Russian and Prussian influence on the PolishÔÇôLithuanian Commonwealth, led by Tadeusz Ko┼Ťciuszko in Poland-Lithuania and the Prussian partition in 1794. It was a failed attempt to liberate the PolishÔÇôLithuanian Commonwealth from external influence after the Second Partition of Poland (1793) and the creation of the Targowica Confederation. Background Decline of the Commonwealth By the early 18th century, the magnates of Poland and Lithuania controlled the state ÔÇô or rather, they managed to ensure that no reforms would be carried out that might weaken their privileged status (the " Golden Freedoms"). Through the abuse of the '' liberum veto'' rule which enabled any deputy to paralyze the Sejm (Commonwealth's parliament) proceedings, deputies bribed by magnates or foreign powers or those sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw Uprising (1794)
The Warsaw Uprising of 1794 or Warsaw Insurrection () was an armed insurrection by the people of Warsaw early in the Ko┼Ťciuszko Uprising. Supported by the Polish Army, the uprising aimed to throw off control by the Russian Empire of the PolishÔÇôLithuanian Commonwealth, Polish capital city (Warsaw). It began on 17 April 1794, soon after Tadeusz Ko┼Ťciuszko's victory at the Battle of Rac┼éawice. Although the Russian forces had more soldiers and better equipment, the Polish regular forces and militia, armed with rifles and sabres from the Warsaw Arsenal, inflicted heavy losses on the surprised enemy garrison. Russian soldiers found themselves under crossfire from all sides and from buildings, and several units broke early and suffered heavy casualties in their retreat. Ko┼Ťciuszko's envoy, Tomasz Maruszewski, and Ignacy Dzia┼éy┼äski and others had been laying the groundwork for the uprising since early 1793. They succeeded in winning popular support: the majority of Polish uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanisław August Poniatowski
Stanis┼éaw II August (born Stanis┼éaw Antoni Poniatowski; 17 January 1732 ÔÇô 12 February 1798), known also by his regnal Latin name Stanislaus II Augustus, and as Stanis┼éaw August Poniatowski (), was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1764 to 1795, and the last monarch of the PolishÔÇôLithuanian Commonwealth. Born into wealthy Polish aristocracy, Poniatowski arrived as a diplomat at the Russian imperial court in Saint Petersburg in 1755 at the age of 22 and became intimately involved with the future empress Catherine the Great. With her aid, he was elected King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania by the Sejm in September 1764 following the death of Augustus III. Contrary to expectations, Poniatowski attempted to reform and strengthen the large but ailing Commonwealth. His efforts were met with external opposition from neighbouring Prussia, Russia and Austria, all committed to keeping the Commonwealth weak. From within he was opposed by conservative interests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |