|
Kowale Pańskie
Kowale Pańskie () is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Kawęczyn, within Turek County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. It lies approximately north of Kawęczyn, south of Turek, and south-east of the regional capital Poznań. The village has a population of 190. History Village Kowale existed already in the 13th century. Bought by Archbishop Jakub Świnka around 1280 it remained the property of the Gniezno Archdiocese until the 18th century. The name Kowale appeared in the 17th century, in reference to a community of blacksmiths (''kowale'' in Polish) servicing local market. The church, founded by Antoni Czarnecki, was built in 1847; the church's parish included 12 villages. In mid 19th century, during the Partitions of Poland, the population of Kowale Pańskie (and the adjacent Wola Kowalska) was only 323 people, half of whom lived and worked around the local historic manor (built in 1750), owned by industrialist Robert Schultz who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of the First World War. The Second Republic ceased to exist in 1939, when Poland was invaded by Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union and the Slovak Republic, marking the beginning of the European theatre of the Second World War. In 1938, the Second Republic was the sixth largest country in Europe. According to the 1921 census, the number of inhabitants was 27.2 million. By 1939, just before the outbreak of World War II, this had grown to an estimated 35.1 million. Almost a third of the population came from minority groups: 13.9% Ruthenians; 10% Ashkenazi Jews; 3.1% Belarusians; 2.3% Germans and 3.4% Czechs and Lithuanians. At the same time, a significant number of ethnic Poles lived outside the country's borders. When, after several regional conflicts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Gas Van
A gas van or gas wagon (russian: душегубка, ''dushegubka'', literally "soul killer"; german: Gaswagen) was a truck reequipped as a mobile gas chamber. During the World War II Holocaust, Nazi Germany developed and used gas vans on a large scale as an extermination method to murder inmates of asylums, Poles, Romani people, Jews, and prisoners in occupied Poland, Belarus, Yugoslavia, the Soviet Union, and other regions of German-occupied Europe. One case of usage of gas van by Soviet NKVD during the Great Purge was documented. Nazi Germany The use of gas vans by the Germans to murder Jews, Poles, Romani people, mentally ill people, and prisoners in occupied territories during World War II originated with the Nazi Euthanasia Program in 1939. Ordered to find a suitable method of killing, the ''Technical Institute for the Detection of Crime'' ("Kriminaltechnisches Institut der Sicherheitspolizei", abbreviated KTI) of the Reichssicherheitshauptamt (RSHA) decided to gas victim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chełmno Extermination Camp
Chełmno or Kulmhof was the first of Nazi Germany's extermination camps and was situated north of Łódź, near the village of Chełmno nad Nerem. Following the invasion of Poland in 1939, Germany annexed the area into the new territory of Reichsgau Wartheland. The camp, which was specifically intended for no other purpose than mass murder, operated from , to , parallel to Operation Reinhard during the deadliest phase of the Holocaust, and again from , to , during the Soviet counter-offensive. In 1943, modifications were made to the camp's killing methods as the reception building had already been dismantled. At the very minimum, 152,000 people were murdered in the camp, which would make it the fifth deadliest extermination camp, after Auschwitz, Treblinka, Bełżec, and Sobibór. However, the West German prosecution, citing Nazi figures during the Chełmno trials of 1962–65, laid charges for at least 180,000 victims. The Polish official estimates, in the early postwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Lange
Herbert Lange (29 September 1909 – 20 April 1945) was an '' SS-Sturmbannführer'' and the commandant of Chełmno death camp until April 1942; leader of the ''SS Special Detachment Lange'' conducting the murder of Jews from the Łódź Ghetto. He was responsible for numerous crimes against humanity including the murder of mental patients in Poland and in Germany during the ''Aktion T4'' "euthanasia" programme and becoming one of the key originators of the Holocaust. Biography Lange studied law, but failed to obtain a degree and he subsequently joined the NSDAP (Nazi Party) on 1 May 1932. He enlisted in the ''Sturmabteilung'' (SA) three months later, and the following year, he joined the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS). He subsequently joined the police force, becoming a deputy commissioner in 1935. Crimes against humanity Lange entered Poland with ''Einsatzgruppe'' Naumann ( EG VI) during the September campaign. On 9 November 1939, following a Nazi German victory, Lange was pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judenrat
A ''Judenrat'' (, "Jewish council") was a World War II administrative agency imposed by Nazi Germany on Jewish communities across occupied Europe, principally within the Nazi ghettos. The Germans required Jews to form a ''Judenrat'' in every community across the occupied territories. The ''Judenrat'' constituted a form of self-enforcing intermediary, used by the Nazi administration to control larger Jewish communities. In some ghettos, such as the Łódź Ghetto, and in Theresienstadt, the Germans called the councils "Jewish Council of Elders" (''Jüdischer Ältestenrat'' or ''Ältestenrat der Juden''). Jewish communities themselves had established councils for self-government as early as the Middle Ages. The Jewish community used the Hebrew term ''Kahal'' (קהל) or ''Kehillah'' (קהילה), whereas the German authorities generally used the term ''Judenräte''. The Judenräte are notorious today for their collaboration with the Nazi regime, almost always under extrem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windmill
A windmill is a structure that converts wind power into rotational energy using vanes called sails or blades, specifically to mill grain (gristmills), but the term is also extended to windpumps, wind turbines, and other applications, in some parts of the English speaking world. The term wind engine is sometimes used to describe such devices. Windmills were used throughout the high medieval and early modern periods; the horizontal or panemone windmill first appeared in Persia during the 9th century, and the vertical windmill first appeared in northwestern Europe in the 12th century. Regarded as an icon of Dutch culture, there are approximately 1,000 windmills in the Netherlands today. Forerunners Wind-powered machines may have been known earlier, but there is no clear evidence of windmills before the 9th century. Hero of Alexandria (Heron) in first-century Roman Egypt described what appears to be a wind-driven wheel to power a machine.Dietrich Lohrmann, "Von der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nowy Czachulec
Nowy Czachulec is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Kawęczyn __NOTOC__ Gmina Kawęczyn is a rural gmina (administrative district) in Turek County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. Its seat is the village of Kawęczyn, Turek County, Kawęczyn, which lies approximately south of Turek, Polan ..., within Turek County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. References Nowy Czachulec {{Turek-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yad Vashem
Yad Vashem ( he, יָד וַשֵׁם; literally, "a memorial and a name") is Israel's official memorial to the victims of the Holocaust. It is dedicated to preserving the memory of the Jews who were murdered; honoring Jews who fought against their Nazi oppressors and Gentiles who selflessly aided Jews in need; and researching the phenomenon of the Holocaust in particular and genocide in general, with the aim of avoiding such events in the future. Established in 1953, Yad Vashem is located on the western slope of Mount Herzl, also known as the Mount of Remembrance, a height in western Jerusalem, above sea level and adjacent to the Jerusalem Forest. The memorial consists of a complex containing two types of facilities: some dedicated to the scientific study of the Holocaust and genocide in general, and memorials and museums catering to the needs of the larger public. Among the former there are a research institute with archives, a library, a publishing house, and an educational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghettos In Nazi-occupied Europe
Beginning with the invasion of Poland during World War II, the Nazi regime set up ghettos across German-occupied Eastern Europe in order to segregate and confine Jews, and sometimes Romani people, into small sections of towns and cities furthering their exploitation. In German documents, and signage at ghetto entrances, the Nazis usually referred to them as ''Jüdischer Wohnbezirk'' or ''Wohngebiet der Juden'', both of which translate as the Jewish Quarter. There were several distinct types including ''open ghettos'', ''closed ghettos'', ''work'', ''transit'', and ''destruction ghettos'', as defined by the Holocaust historians. In a number of cases, they were the place of Jewish underground resistance against the German occupation, known collectively as the ghetto uprisings. Background and establishment of the ghettos The first anti-Jewish measures were enacted in Germany with the onset of Nazism; these measures did not include ghettoizing German Jews: such plans were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
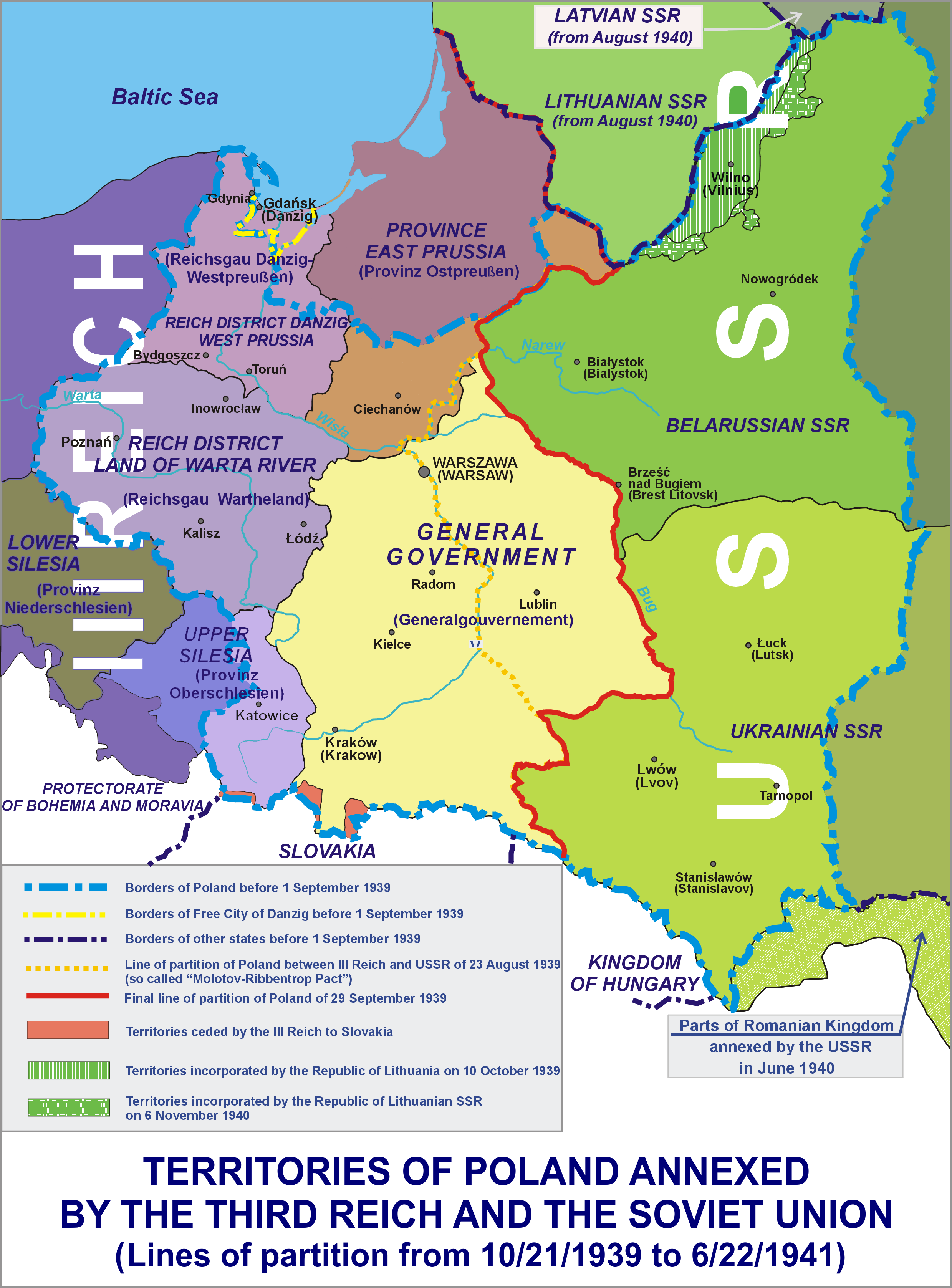
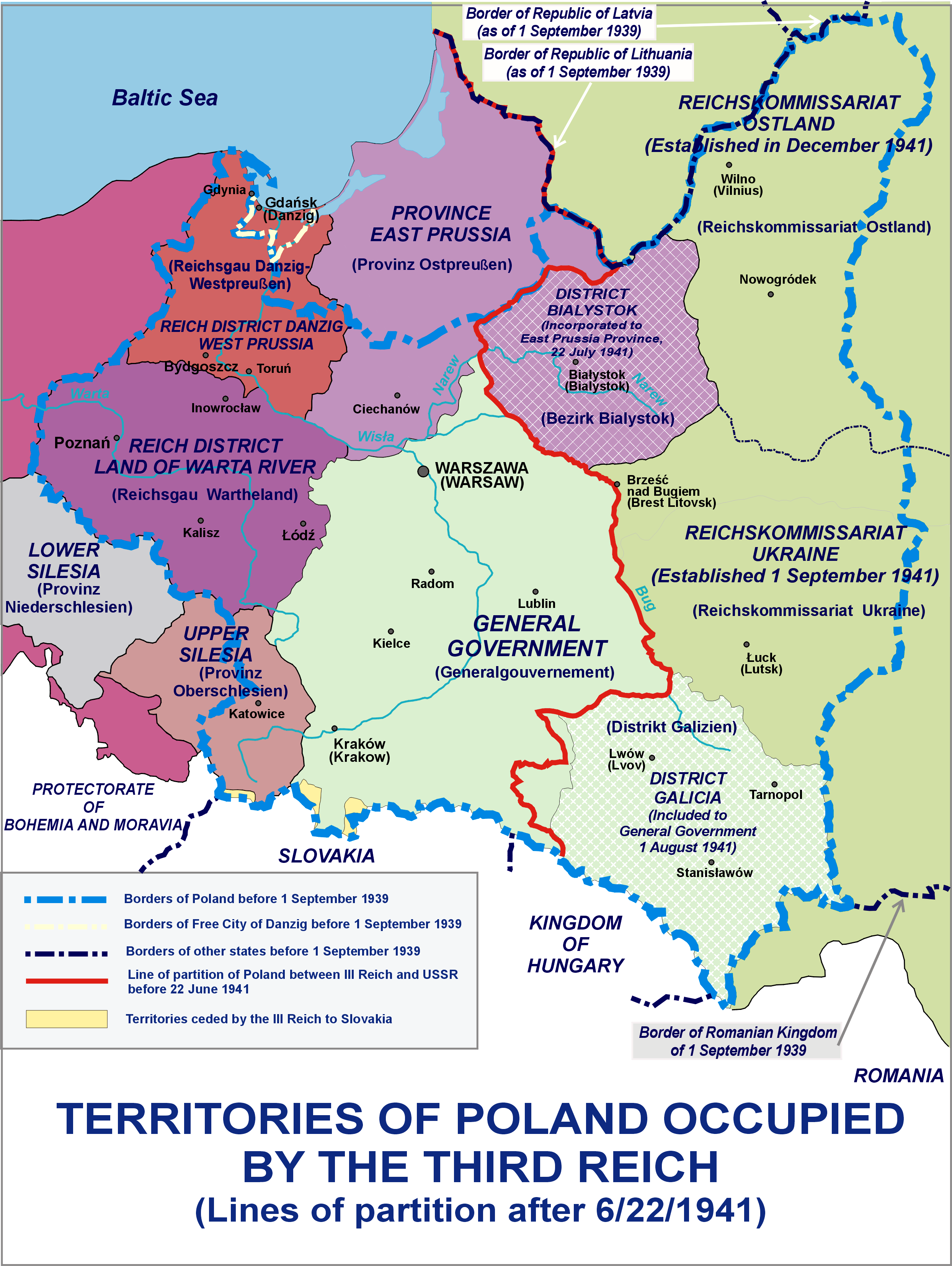
Polish Areas Annexed By Nazi Germany
Following the Invasion of Poland at the beginning of World War II, nearly a quarter of the entire territory of the Second Polish Republic was annexed by Nazi Germany and placed directly under the German civil administration. The rest of Nazi-occupied Poland was renamed as the General Government district. The annexation was part of the "fourth partition of Poland" by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union, outlined months before the invasion, in the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact.Maly Rocznik Statystyczny (wrzesien 1939 – czerwiec 1941), Ministerstwo Informacji i Documentacji, London 1941, p.5, as cited in Piotr Eberhardt, Political Migrations in Poland, 1939–1948, Warsaw 2006, p.4 Some smaller territories were incorporated directly into the existing Gaue East Prussia and Silesia, while the bulk of the land was used to create new '' Reichsgaue'' Danzig-West Prussia and Wartheland. Of those, Reichsgau Wartheland was the largest and the only one comprising solely the annexed terr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichsgau Wartheland
The ''Reichsgau Wartheland'' (initially ''Reichsgau Posen'', also: ''Warthegau'') was a Nazi German '' Reichsgau'' formed from parts of Polish territory annexed in 1939 during World War II. It comprised the region of Greater Poland and adjacent areas. Parts of ''Warthegau'' matched the similarly named pre-Versailles Prussian province of Posen. The name was initially derived from the capital city, Posen (Poznań), and later from the main river, Warthe (Warta). During the Partitions of Poland from 1793, the bulk of the area had been annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia until 1807 as South Prussia. From 1815 to 1849, the territory was within the autonomous Grand Duchy of Posen, which was the Province of Posen until Poland was re-established in 1918–1919 following World War I. The area is currently the Greater Poland Voivodeship. Invasion and occupation of Poland After the invasion of Poland, the conquered territory of Greater Poland was split between four '' Reichsgaue'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)