|
Kost Hordiienko
Kost Hordiienko (; unknown – 15 May 1733) was a Zaporozhian Cossack Kish otaman. After 1709 he allied with Ivan Mazepa, and co-authored the Constitution of Pylyp Orlyk. Hordiienko was born in the Poltava region, Hetmanate. He studied at the Kyiv Mohyla Academy. Later he joined the Zaporizhian Sich, headed the Cossack troops (1702–1706, 1707–1709, 1710–1728). As an ally of Mazepa, he fought in the Battle of Poltava. On 6 May 2019, the 57th Motorized Brigade of the Ukrainian Army received the honorary name of ''Kost Hordiienko''. Origin Dmytro Yavornytskyi, a Ukrainian specialist in the history of the Ukrainian Cossacks, believed that Hordiienko came from the Poltava region, while Apollon Skalkowski, a researcher of Polish origin, assumed that he was from Volhynia, from the Ukrainian noble family of the . In favor of the first option, the fact that it was customary to attach the surname to the father's name was in Left-bank Ukraine, but not in Volhynia. Biography Hor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary ethnic groups, second largest ethno-linguistic community. At around 46 million worldwide, Ukrainians are the second largest Slavs, Slavic ethnic group after Russians. Ukrainians have been Endonym and exonym, given various names by foreign rulers, which have included Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Habsburg monarchy, the Austrian Empire, and then Austria-Hungary. The East Slavic population inhabiting the territories of modern-day Ukraine were known as Ruthenians, referring to the territory of Ruthenia; the Ukrainians living under the Russian Empire were known as Little Russians, named after the territory of Little Russia. The ethnonym Ukrainian, which was associated with the Cossack Hetmanate, was adopted following the Ukrainian natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ukrainian Army
The Ukrainian Ground Forces (SVZSU, ), also referred to as the Ukrainian army, is a land force, and one of the eight Military branch, branches of the Armed Forces of Ukraine. It was formed from Ukrainian units of the Soviet Army after Declaration of Independence of Ukraine, Ukrainian independence, and its ancestry is traced back to the 1917–22 army of the Ukrainian People's Republic. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, Ukraine retained its Soviet-era army equipment. The Armed Forces were systematically downsized and underinvested in after 1991. As a result, the Ukrainian army had very little of its Soviet equipment in working order by July 2014, and most systems had become antiquated. Personnel numbers had shrunk and training, command, and support functions needed improvement.In the Army Now: Answering Many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chortomlyk Sich
The Chortomlyk Sich (also Old Sich) was a sich founded by Cossacks led by kish otaman Fedir Lutay in the summer of 1652 on the right bank of the Chortomlyk distributary of the Dnieper near the current village of Kapulivka. The Sich lasted until May 25, 1709, when it was destroyed by Moscow's punitive expedition undertaken in response to the support of Hetman Ivan Mazepa by Zaporozhian Cossacks. History During the Khmelnytsky Uprising, Chortomlyk Sich guarded the then southern borders of Ukraine. Cossacks of the Sich took part in Bohdan Khmelnytskyi's campaigns, excelling in the battles of Zhvanets (1653), Horodok (1655), during the second siege of Lviv (1655), etc. The national recognition of the Chortomlyk Sich spread during the time of kish otaman Ivan Sirko (1659—1680), who lived exclusively in the sich for 17 years and was elected a kish otaman more than 15 times, favoring his military merits. In particular, he became famous for the defeat of the 60,000-strong Ottoman-Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Samara (Dnieper)
The Samara () is a river in Ukraine, a left tributary of the Dnieper. The city of Dnipro is located near the confluence of the Dnieper and the Samara. The river has a length of 320 km and a drainage basin of 22,600 km². From its source, near the village of Mar'ivka in the suburbs of Kramatorsk in Donetsk Oblast, the river flows through the oblasts of Kharkiv (briefly) and Dnipropetrovsk (for most of its length). As it approaches the Dnieper, it goes through Samara Bay (formerly Lenin Lake), an artificial lake 10km long and 3km wide, formed as a result of the hydroelectric dam on the Dnieper. The Samara is mostly used for irrigation and fish farming. The water quantities are variable, mainly because the river is fed by snowmelt from the spring thaw. The width of the river varies between 40 and 60 meters, with 300 m being the maximum. The most important tributaries of the Samara are the Vovcha The Vovcha () is a river in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, Dnipropetrovsk a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Peter The Great
Peter I (, ; – ), better known as Peter the Great, was the Sovereign, Tsar and Grand Prince of all Russia, Tsar of all Russia from 1682 and the first Emperor of Russia, Emperor of all Russia from 1721 until his death in 1725. He reigned jointly with his half-brother Ivan V of Russia, Ivan V until 1696. From this year, Peter was an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch, an autocrat who remained the ultimate authority and organized a well-ordered police state. Much of Peter's reign was consumed by lengthy wars against the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman and Swedish Empire, Swedish empires. His Azov campaigns were followed by the foundation of the Imperial Russian Navy, Russian Navy; after his victory in the Great Northern War, Russia annexed a Treaty of Nystad, significant portion of the eastern Baltic Sea, Baltic coastline and was officially renamed from a Tsardom of Russia, tsardom to an Russian Empire, empire. Peter led a cultural revolution that replaced some of the traditionalist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Territorial Evolution Of Russia
The borders of Russia changed through military conquests and by ideological and political unions from the 16th century. Tsarist Russia The formal end to Tatars, Tatar rule over Russia was the defeat of the Tatars at the Great Stand on the Ugra River in 1480. Ivan III of Russia, Ivan III () and Vasili III of Russia, Vasili III () had consolidated the centralized Russian state following the annexations of the Novgorod Republic in 1478, Principality of Tver, Tver in 1485, the Pskov Republic in 1510, Volokolamsk in 1513, Principality of Ryazan, Ryazan in 1521, and Principality of Novgorod-Seversk, Novgorod-Seversk in 1522. After a period of political instability between 1598 and 1613, which became known as the Time of Troubles, the Romanovs came to power in 1613 and the expansion-colonization process of the tsardom continued. While Western Europe European colonization of the Americas, colonized the New World, the Tsardom of Russia expanded overland – principally to the east, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Zaporozhian Sich
The Zaporozhian Sich (, , ; also ) was a semi-autonomous polity and proto-state of Zaporozhian Cossacks that existed between the 16th to 18th centuries, for the latter part of that period as an autonomous stratocratic state within the Cossack Hetmanate. The lands of Zaporozhian Sich were centred around the Great Meadow region of Ukraine, spanning the lower Dnieper river. In different periods the area came under the sovereignty of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Ottoman Empire, the Tsardom of Russia, and the Russian Empire. The establishment of Zaporozhian Sich was an important factor in defense of Ukraine and Russia from Crimean-Nogai raids. In 1650, its total population consisted of 100,000. In 1657–1687, Zaporizhian Sich was practically independent, possessing its own administration and armed forces consisting of 12,000–20,000 Cossacks. It was reliant on population growth, mainly consisting of Ukrainian refugees from devastated lands. In 1775, shortly af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kurin
Kurin () has two definitions: a military and administrative unit of the Zaporozhian Cossacks, Black Sea Cossack Host, and others; and of a type of housing (see below). In the administrative definition, a kurin usually consisted of a few hundred Cossacks, with their own land, treasury and flag, and around a hundred houses. The number of kurins was not permanent, and varied throughout time: during the 16th century, there were 8 kurins in the Zaporozhian Sich and 38 during the first half of the 18th century. All Cossacks had to be part of a kurin and were listed on the so-called "kurin komput" (a register of Cossacks in the kurin), and were subject to the kurin otaman. In the other definition, a kurin is a type of housing, sometimes temporary, which can vary in size and purpose: from a small tent made of leaves, to a large wooden house for permanent occupation. Administrative unit The kurin was the lowest administrative division in the Cossack Hetmanate. According to a Ukraini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cossack Host
A Cossack host (; , ''kazachye voysko''), sometimes translated as Cossack army, was an administrative subdivision of Cossacks in the Russian Empire. Earlier the term ''voysko'' ( host, in a sense as a doublet of ''guest'') referred to Cossack organizations in their historical territories, most notable being the Zaporozhian Host of Zaporozhian Cossacks. Russian Empire Each Cossack host consisted of a certain territory with Cossack settlements that had to provide military regiments for service in the Imperial Russian Army and for border patrol operations. Usually the hosts were named after the regions of their location. The ''stanitsa'', or village, formed the primary unit of this organization. In the Russian Empire (1721-1917), the Cossacks constituted twelve separate hosts, settled along the frontiers: * the Don Cossack Host * the Bug Cossacks * the Kuban Cossack Host * the Terek Cossack Host * the Astrakhan Cossack Host * the Ural Cossack Host * the Orenburg Cos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
National University Of Kyiv-Mohyla Academy
The National University of Kyiv-Mohyla Academy ( NaUKMA, ), colloquially known as Mohylianka (), is a highly ranked national state-sponsored research university located in a historic section of Kyiv, Ukraine. The university is bilingual in Ukrainian and English and is one of Ukraine's few universities with internationally recognized diplomas. NaUKMA takes part in numerous international university collaborations, such as the European University Association. With around 4000 students, NaUKMA is one of the smallest universities in Ukraine. The university takes its name from the institution cited as its main predecessor, the Kyiv-Mohyla Academy established in 1615 and operating until 1819. The NaUKMA is located on that Academy's grounds in the ancient Podil neighborhood. In 1991, the modern university was organized, and teaching began the following year. Alumni of the Kyiv-Mohyla Academy played a formative role in the intellectual and church life of Ukraine and Russia in 17th a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Left-bank Ukraine
The Left-bank Ukraine is a historic name of the part of Ukraine on the left (east) bank of the Dnieper River, comprising the modern-day oblasts of Chernihiv, Poltava and Sumy as well as the eastern parts of Kyiv and Cherkasy. Left-bank Ukraine is bordered by the historical regions of Right-bank Ukraine to the southwest, Zaporizhzhia to the southeast, Sloboda Ukraine to the east, and Polesia and White Ruthenia to the north. History Since the Middle Ages, the region formed part of the Khazar Khanate, Kievan Rus', Mongol Empire, Golden Horde, Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland. The term appeared in 1663 with the election of Ivan Bryukhovetsky as the hetman of Ukraine in opposition to Pavlo Teteria. Bryukhovetsky was the first known "left-bank Ukraine" hetman over the area, that was under the Russian influence. Up until the mid-17th century, the area had belonged to the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Treaty of Pereyaslav of 1654 saw the region tent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
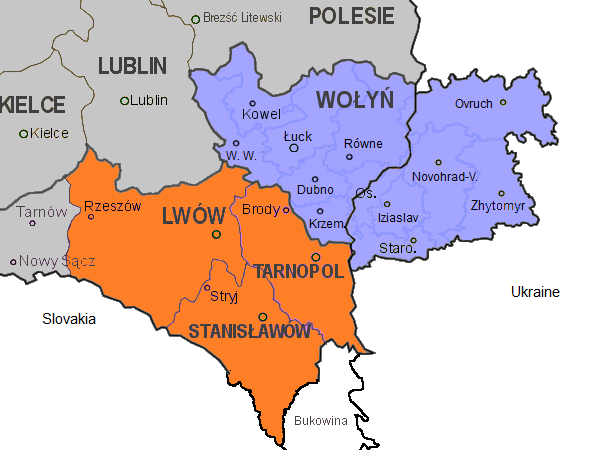
Volhynia
Volhynia or Volynia ( ; see #Names and etymology, below) is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between southeastern Poland, southwestern Belarus, and northwestern Ukraine. The borders of the region are not clearly defined, but in Ukraine it is roughly equivalent to Volyn Oblast, Volyn and Rivne Oblasts; the territory that still carries the name is Volyn Oblast. Volhynia has changed hands numerous times throughout history and been divided among competing powers. For centuries it was part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. After the Russian annexation during the Partitions of Poland, all of Volhynia was made part of the Pale of Settlement on the southwestern border of the Russian Empire. Important cities include Rivne, Lutsk, Zviahel, and Volodymyr (city), Volodymyr. Names and etymology *, ; * ; *, ; * or ; *; * ; *; *; * or (both ); Volhynian German: , , or (all ); *, or . The alternative name for the region is Lodomeria after the city of Volodymyr (city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |