|
Korfantów
Korfantów (, ), formerly known in Polish as Fryląd, is a town in the Opole Voivodeship of southwestern Poland, with 1,808 inhabitants (2019). In 1946 the town was renamed in honour of politician and activist Wojciech Korfanty, however, the previous name ''Fryląd'' is still in use. Geography Korfantów is located in the Niemodlin Plain (''Równina Niemodlińska''), in the historical region of Silesia. The total area inside the town's boundary is . Etymology The former name of the settlement was ''Hurtlanth'' or ''Hurthland''. Other documents refer to the town as: ''Fredland'', ''Fredelant'', ''Fredlandt'', ''Fridland'', ''Freijland'', and ''Friedland''. The locality's Polish name was based on the German name, and had various forms: ''Ferląd'', ''Ferlondt'', ''Frydląd'', ''Fyrląd'', and ''Fryląd'', officially adopted in 1945. In 1946, in the aftermath of World War II, due to the German origin of the name, the town was renamed after Wojciech Korfanty. History Until 1532 the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gmina Korfantów
__NOTOC__ Gmina Korfantów is an urban-rural gmina (administrative district) in Nysa County, Opole Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. Its seat is the town of Korfantów, which lies approximately east of Nysa and south-west of the regional capital Opole. The gmina covers an area of , and as of 2019 its total population is 8,803. Villages Apart from the town of Korfantów, Gmina Korfantów contains the villages and settlements of Borek, Gryżów, Jegielnica, Kuropas, Kuźnica Ligocka, Myszowice, Niesiebędowice, Piechocice, Pleśnica, Przechód, Przydroże Małe, Przydroże Wielkie, Puszyna, Rączka, Rynarcice, Rzymkowice, Ścinawa Mała, Ścinawa Nyska, Stara Jamka, Węża, Wielkie Łąki, Włodary and Włostowa. Neighbouring gminas Gmina Korfantów is bordered by the gminas of Biała, Łambinowice, Nysa, Prószków, Prudnik and Tułowice. Twin towns – sister cities Gmina Korfantów is twinned with: * Boulleret, France * Debrzno, Poland * Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nysa County
__NOTOC__ Nysa County () is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Opole Voivodeship, south-western Poland, on the Czech border. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Nysa, which lies south-west of the regional capital Opole. The county contains four other towns: Głuchołazy, south of Nysa, Paczków, west of Nysa, Otmuchów, west of Nysa, and Korfantów, east of Nysa. The county covers an area of . As of 2019 its total population is 136,393. The most populated towns are Nysa with 43,849 inhabitants, Głuchołazy with 13,534 inhabitants, and Paczków with 7,460 inhabitants. Neighbouring counties Nysa County is bordered by Ząbkowice Śląskie County to the west, Strzelin County and Brzeg County to the north, Opole County to the north-east, and Prudnik County to the south-east. It also borders the Czech Republic to the south-west. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wojciech Korfanty
Wojciech Korfanty (; born Adalbert Korfanty; 20 April 1873 – 17 August 1939) was a Polish activist, journalist and politician, who served as a member of the German parliaments, the Reichstag and the Prussian Landtag, and later, in the Polish ''Sejm''. Briefly, he also was a paramilitary leader, known for organizing the Polish Silesian Uprisings in Upper Silesia, which after World War I was contested by Germany and Poland. Korfanty fought to protect Poles from discrimination and the policies of Germanisation in Upper Silesia before the war and sought to join Silesia to Poland after Poland regained its independence. Early life He was born the son of a coal miner in Sadzawka, part of Siemianowice (at the time ''Laurahütte''), in Prussian Silesia, then part of the German Empire. From 1895 until 1901, he studied philosophy, law, and economics, first at the Technische Hochschule in Charlottenburg (Berlin) (1895) and then at the University of Breslau, where the Marxist Wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opole Voivodeship
Opole Voivodeship ( , , ), is the smallest and least populated voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship (province) of Poland. The province's name derives from that of the region's capital and largest city, Opole. It is part of Silesia. A relatively large Germans, German minority lives in the voivodeship, and the German language is co-official in 28 communes. Opole Voivodeship is bordered by Lower Silesian Voivodeship to the west, Greater Poland Voivodeship, Greater Poland and Łódź Voivodeships to the north, Silesian Voivodeship to the east, and the Czech Republic (Olomouc Region and Moravian-Silesian Region) to the south. Opole Province's geographic location, economic potential, and its population's level of education make it an attractive business partner for other Polish regions (especially Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Lower Silesian and Silesian Voivodeships) and for foreign investors. Formed in 1997, the Euroregion Praděd, Praděd/Pradziad Euroregion with its headquarter in Prud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polenlager
The ''Polenlager'' (, ''Polish Camps'') was a system of forced labor camps in Silesia that held Poles during the World War II Nazi German occupation of Poland. The prisoners, originally destined for deportation across the border to the new semi-colonial General Government district, were sent to the ''Polenlager'' between 1942 and 1945, once the other locations became too overcrowded to accommodate the prisoners. There were over 30 ''Polenlager'' camps, mostly in Silesia. History All ''Polenlager'' camps were classified by the Germans as "labour reformatories". They were built near major military work-sites for the steady supply of slave labor. The camps had permanent German staff, augmented by captives and volunteers from other Eastern European countries (known as Hiwis). The Poles were delivered to ''Polenlagers'' by trainloads from German temporary transit camps, after they had been evicted from their homes to make way for new settlers (see: Action Saybusch). Some of the Sile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia (), sometimes referenced in English literature as the Czech Kingdom, was a History of the Czech lands in the High Middle Ages, medieval and History of the Czech lands, early modern monarchy in Central Europe. It was the predecessor state of the modern Czech Republic. The Kingdom of Bohemia was an Imperial State in the Holy Roman Empire. The List of Bohemian monarchs, Bohemian king was a prince-elector of the empire. The kings of Bohemia, besides the region of Bohemia itself, also ruled other Lands of the Bohemian Crown, lands belonging to the Bohemian Crown, which at various times included Moravia, Silesia, Lusatia, and parts of Saxony, Brandenburg, and Bavaria. The kingdom was established by the Přemyslid dynasty in the 12th century by the Duchy of Bohemia, later ruled by the House of Luxembourg, the Jagiellonian dynasty, and from 1526 the House of Habsburg and its successor, the House of Habsburg-Lorraine. Numerous kings of Bohemia were also elected Hol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is also referred to as the Austrian monarchy, the Austrian Empire () or the Danubian monarchy. The history of the Habsburg monarchy can be traced back to the election of Rudolf I of Germany, Rudolf I as King of the Romans, King of Germany in 1273 and his acquisition of the Duchy of Austria for the Habsburgs in 1282. In 1482, Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, Maximilian I acquired the Habsburg Netherlands, Netherlands through marriage. Both realms passed to his grandson and successor, Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V, who also inherited the Monarchy of Spain, Spanish throne and Spanish Empire, its colonial possessions, and thus came to rule the Habsburg empire at its greatest territorial extent. The abdication of Charles V in 1556 led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Vasa
The House of Vasa or Wasa was a Dynasty, royal house that was founded in 1523 in Sweden. Its members ruled the Kingdom of Sweden from 1523 to 1654 and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1587 to 1668. Its agnatic line became extinct with the death of King John II Casimir Vasa in 1672. The Vasa dynasty descended from a 14th-century Swedish noble family, tracing agnatic kinship to Nils Kettilsson (Vasa) (), the of Tre Kronor (castle), ''Tre Kronor'' Castle in Stockholm. Several members held high offices during the 15th century. In 1523, after the Stockholm Bloodbath, Stockholm bloodbath and the abolition of the Kalmar Union, Gustav Eriksson (Vasa) became King Gustav I of Sweden and the royal house was founded. His reign is sometimes referred to as the beginning of the modern Swedish state, which included the King's break with the Catholic Church during the Protestant Reformation and the foundation of the Church of Sweden. However, his eldest son and successor Erik XIV of Sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a significant role in the unification of Germany in 1871 and was a major constituent of the German Empire until its German Revolution of 1918–1919, dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the Prussia (region), region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. The list of monarchs of Prussia, kings of Prussia were from the House of Hohenzollern. The polity of Brandenburg-Prussia, predecessor of the kingdom, became a military power under Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, known as "The Great Elector". As a kingdom, Prussia continued its rise to power, especially during the reign of Frederick the Great, Frederick II "the Great".Horn, D. B. "The Youth of Frederick the Great 1712–30." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
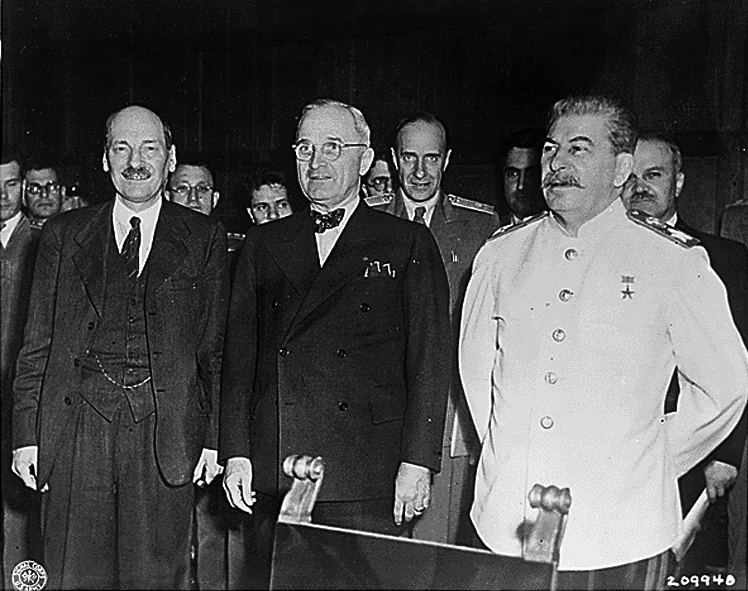
Potsdam Agreement
The Potsdam Agreement () was the agreement among three of the Allies of World War II: the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union after the war ended in Europe that was signed on 1 August 1945 and published the following day. A product of the Potsdam Conference, it concerned the military occupation and reconstruction of Germany, its border, and the entire European Theatre of War territory. It also addressed Germany's demilitarisation, reparations, the prosecution of war criminals and the mass expulsion of ethnic Germans from various parts of Europe. France was not invited to the conference but formally remained one of the powers occupying Germany. Executed as a communiqué, the agreement was not a peace treaty according to international law, although it created accomplished facts. It was superseded by the Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany signed on 12 September 1990. As De Gaulle had not been invited to the Conference, the French resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |