|
Konstal 105N Poznań RB4
Alstom Konstal is a company based in Chorzów, Poland producing rail vehicles, in particular metro cars and trams, as well as components for trains. In 1864, the plant was founded as part of the Royal Steelworks in Chorzów and in 1917, it was excluded from its structures as a separate enterprise. During World War II, the factory belonged to the ''Reichswerke Hermann Göring'' produced for the needs of the army of the Third Reich, while during the Communist Period, as the Chorzów Steel Structures Factory Konstal, it was the main supplier of trams for Poland. In 1995, the company's shares were transferred to the National Investment Funds, after which the plant began cooperation with the Linke-Hofmann-Busch factory belonging to the French Alstom concern. In 1997, the company was bought out by Alstom, and a year later, simultaneously with the change of its name to Alstom, the Polish factory adopted its current name. History Origins and beginnings of activity In 1864, the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
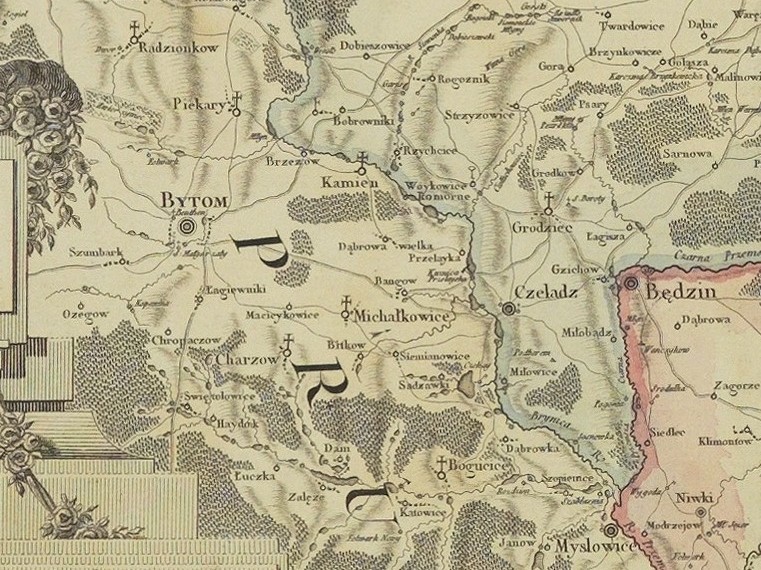
Chorzów
Chorzów ( ; ; ) is a city in the Silesia region of southern Poland, near Katowice. Chorzów is one of the central cities of the Metropolis GZM – a metropolis with a population of 2 million. It is located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Rawa River (a tributary of the Vistula River, Vistula). Administratively, Chorzów is in the Silesian Voivodeship since 1999, previously Katowice Voivodeship, and before then, the Silesian Voivodeship (1920–1939), Silesian Voivodeship. Chorzów is one of the cities of the 2.7 million conurbation – the Katowice urban area and within a greater Katowice-Ostrava metropolitan area with a population of about 5,294,000 people. The population within the city limits is 105,628 as of December 2021. Chorzów is particularly known as the location of the Silesian Stadium, one of the largest and historically most important stadiums in Poland. Ruch Chorzów, one of the most accomplished Polish football clubs, is based in the city. History City name The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alstom Metropolis 98B
Alstom Metropolis 98B is an electric multiple unit produced by the France, French conglomerate Alstom and operated by the Warsaw Metro as their third-generation of rolling stock. Between 2000 and 2002, and again between 2004 and 2005, a total of 108 carriages were constructed at the manufacturer’s plants in Barcelona and Chorzów, forming 18 six-car trains. History Origins On 7 April 1995, the first section of the Warsaw Metro, M1 (Warsaw), M1, was opened. The long route connecting the Kabaty metro station with the Politechnika metro station was initially served by 14 three-car sets of the Russian Metrovagonmash 81-717/81-714. This rolling stock allowed trains to run at 5-minute intervals during peak hours and 7-minute intervals off-peak, with an eventual plan for five-car trains running at 90-second intervals. In November 1997, a batch of 18 cars ordered from Russia arrived in Warsaw, allowing for the extension of trains to four cars and the assembly of a fifteenth set. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstal 105Na
The Konstal 105Na are a class of Polish trams manufactured from 1979 to 1992 in workshops Konstal Chorzów, Poland. The Metre-gauge railway, metre-gauge version is designated as 805Na. As of 2016 they were still the most common trams in Poland. Construction 105Na is unidirectional motor tramcar, equipped with four doors. It is a development of the earlier Konstal 105N. The main changes being a shift in the location of the electrical equipment from under the steps to the back wall of the driver's cabin, the introduction of a separate cabin for the driver, as well as the removal of the small windows under the front and side windscreens. The most important change was the introduction of motor grouping, which reduced the energy consumption by 12%. During initial acceleration, the four motors are connected in series, whilst at higher speeds, two groups of motors are connected in parallel. While in service, the 105Na vehicles were the subject of various modifications and upgrades (inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstal 805Nm
Konstal 805NM is the name of a tram, that was modernized in 2003 by the company PESA for ''MZK Bydgoszcz'' which operates trams in Bydgoszcz Bydgoszcz is a city in northern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Kuyavia. Straddling the confluence of the Vistula River and its bank (geography), left-bank tributary, the Brda (river), Brda, the strategic location of Byd .... Only one set of 805Na wagons was modernized. Changes regarding 805Na were both in the exterior and the equipment of the vehicle. External links *Technical data from the producer Tram vehicles of Poland PESA trams {{Europe-tram-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstal 105NWr
Konstal 105NWr is a Polish tram resulting from the modernization of the tram Konstal 105Na by Protram plants. Building In the process of modernization many things were upgraded for example the tram received new doors and new front and rear plastic walls with rectangular headlights. Currently, in Wrocław Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ..., there are 64 trams of this type. Design The tram is not far different from its predecessor Konstal 105Na. The overall exterior design is changed, including the removal of one of the doors in each carriage. The interior differs from tram to tram because the seats were chosen by price and quantity available. The rear car has more seating than the front due to the lack of a driver's cabin. Today, the tram is often mistaken as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstal 105N
Konstal 105N is a family of electric trams designed by Konstal, a Poland, Polish company based in Chorzów, produced between 1973 and 1979. Konstal 105N 105N is a single module, unidirectional tramcar with four doors on the right side. The design came about as a result of modernisation of Konstal's earlier Konstal 13N, 13N model. All the electrical systems from the 13N remained unchanged, but the 105N abandoned the streamlined appearance of its predecessor for a more angular look. The side windows were enlarged, and smaller windows were added on the front and sides, leading to its being nicknamed ''aquarium''. These changes made the 105N significantly (approximately 1200 kg) lighter than the 13N and decreased the amount of raw materials used in production. The first models lacked the ability to be connected to one another, and the placement of the electrical system caused problems with humidity. The tram was equipped with electromagnetic brake, electromagnetic, drum brake, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstal 102N
Konstal 102N was an electric tram built by Konstal in Chorzów between 1969 and 1970, replacing the Konstal 13N. History Konstal 102N was directly descended from the older 13N produced by Konstal between 1959 and 1969, but, unlike 13N, it was an articulated tram - basically two 13N cars connected by a pivot. Most of the electrical equipment remained unchanged; the body of the tram is where the most dramatic changes were visible. The streamlined design of 13N was replaced by a more boxy shape which made for excellent visibility - unfortunately in daytime only. The large windscreen was tilted in such a way that at night-time it reflected light directly into the driver's eyes making the 102N difficult to drive after dark. This issue was ultimately to prove the downfall of the 102N, as after producing just 42 units the company decided to abandon the 102N project, and in 1970 reverted to the 13N look for the newer 102Na model. Konstal 802N While most of the tram networks in Pola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstal 13N
The Konstal 13N was an electric tram built by Konstal in Chorzów between 1959 and 1969 and used in Warsaw until 2012. The design borrowed heavily from the PCC-derived ČKD Tatra T1. History After 1945, the tram networks in most Polish cities relied on small, slow, and outdated Konstal N trams. The N-class trams were intended as a temporary measure to improve the disastrous state of public transport in the aftermath of World War II, and were in fact based on a wartime German design, but all attempts at designing a better tram in Poland ended in failure. In 1955, two Tatra T1 trams were bought by the Warsaw Transport Authority. In 1956, these were sent to the Konstal works in Chorzów for analysis, and formed the basis for the first Konstal prototype called ''11N''. The prototype was then modernized with a redesigned interior, Belgian ACEC electrical equipment, different wheels, and transmission. In 1959, the prototype was put into production as the ''13N''. Passenger servic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstal N
Konstal N was a tram model based on the German ''Kriegsstraßenbahnwagen'' concept, manufactured between 1948 and 1956 by the companies Konstal in Chorzów, Gdańsk Shipyard no. 3 and Sanok Railcar Factory "Sanowag". The narrow-gauge version (Konstal 2N) was built from 1950 to 1956. Trailers (tram units with no engine) were marked ND or 2ND. The ''N'' was the first tram manufactured in Poland after the Second World War. Specifications The ''N'' was a bidirectional motor tramcar, equipped with four sliding doors. In post-war Poland, many cities struggled with significant shortages of rolling stock, and therefore it was necessary to develop a tram with simple construction and easy assembly. It was decided to copy the construction of the German tram ''Kriegsstraßenbahnwagen'' (KSW), developed during the Second World War to satisfy the demand of local tram transport companies. Due to the lack of motors, initially the ND trailers for Upper Silesia were built. The successor of Kon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
113 Silesian Interurbans, Citadis Car, Bytom
113 may refer to: *113 (number), a natural number * AD 113, a year * 113 BC, a year * 113 (band), a French hip hop group * 113 (MBTA bus), Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority bus route * 113 (New Jersey bus), Ironbound Garage in Newark and run to and from the Port Authority bus route *113 Amalthea 113 Amalthea () is a stony Florian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately in diameter. It was discovered on 12 March 1871, by German astronomer Robert Luther at the Bilk Observatory in Düsseldorf, Germany. The elo ..., a main-belt asteroid See also * 11/3 (other) * Nihonium, synthetic chemical element with atomic number 113 {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |