|
Kofun
are megalithic tombs or tumulus, tumuli in Northeast Asia. ''Kofun'' were mainly constructed in the Japanese archipelago between the middle of the 3rd century to the early 7th century AD.岡田裕之「前方後円墳」『日本古代史大辞典』大和書房、2006年。 The term is the origin of the name of the Kofun period, which indicates the middle 3rd century to early–middle 6th century. Many ''kofun'' have distinctive keyhole-shaped mounds (). The Mozu kofungun, Mozu-Furuichi kofungun, Furuichi kofungun or tumulus clusters were inscribed on the World Heritage Sites in Japan, UNESCO World Heritage List in 2019, while Ishibutai Kofun is one of a number in Asuka-Fujiwara residing on the World Heritage Sites in Japan#Tentative List, Tentative List. Overview The ''kofun tumuli'' have assumed various shapes throughout history. The most common type of ''kofun'' is known as a , which is shaped like a keyhole, having one square end and one circular end, when viewed from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daisen Kofun
The are a group of ''kofun'' ()—megalithic tombs—in Sakai, Osaka, Sakai, Osaka Prefecture, Japan. Originally consisting of more than 100 tombs, fewer than 50% of the key-hole, round, and rectangular tombs remain. The , the largest ''kofun'' in Japan, is believed to have been constructed over a period of 20 years in the mid 5th century during the Kofun Period. While it cannot be accurately confirmed, it is commonly accepted that the tomb was built for the late Emperor Nintoku. The Imperial Household Agency of Japan treats it as such. Location The Mozu Kofun Cluster is located in the city of Sakai, Osaka, Sakai which is within Osaka Prefecture. The tumuli are built on a plateau overlooking Osaka Bay near the ancient coastline and are distributed in a range of about four kilometers from east-to-west and north-to-south.The Furuichi Kofun Cluster is located in nearby Habikino, Osaka, Habikino and Fujiidera, Osaka, Fujiidera cities. History In the Japanese archipelago, more th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mozu Kofungun
The are a group of ''kofun'' ()—megalithic tombs—in Sakai, Osaka Prefecture, Japan. Originally consisting of more than 100 tombs, fewer than 50% of the key-hole, round, and rectangular tombs remain. The , the largest ''kofun'' in Japan, is believed to have been constructed over a period of 20 years in the mid 5th century during the Kofun Period. While it cannot be accurately confirmed, it is commonly accepted that the tomb was built for the late Emperor Nintoku. The Imperial Household Agency of Japan treats it as such. Location The Mozu Kofun Cluster is located in the city of Sakai which is within Osaka Prefecture. The tumuli are built on a plateau overlooking Osaka Bay near the ancient coastline and are distributed in a range of about four kilometers from east-to-west and north-to-south.The Furuichi Kofun Cluster is located in nearby Habikino and Fujiidera cities. History In the Japanese archipelago, more than 20,000 tumuli (''kofun''), which are mounds of earth and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Furuichi Kofungun
is a group of Kofun period burial mounds located in the cities of Fujiidera and Habikino, Osaka Prefecture, Japan. Twelve of the tumuli in this group were individually designated a National Historic Site of Japan in 1956, with an additional 14 collectively added to the designation in 2001, and the area under protection expanded in 2018. Overview The Furuichi Kofun Cluster extends over an area of 2.5 kilometers north-to-south by four kilometers east-to-west, covering plateaus and hill with an average elevation of 24 meters above sea level. These tumuli were built between the late 4th and the mid-sixth century AD. Twenty-seven, including many of the larger tumuli, are under the control of the Imperial Household Agency and are classified as "imperial tombs", for which archaeological excavation has been prohibited. In 2010 the Furuichi kofungun cluster of tumuli, along with those of Mozu kofungun, were proposed for inscription on the UNESCO World Heritage List. On 6 July 2019, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zempō-kōen Fun
Zenpokoenfun is an architectural model of Japanese ancient tombs (Kofun), which consists of a square front part (, Zenpō-bu) and a circular back part (, Kōen-bu). The part connecting the two is called the middle part (, Kubire-bu), which looks like a keyhole when viewed from above. Therefore, they are also called keyhole-shaped mounds in English, and in Korean, they are called long drum tombs (, Janggobun) due to their resemblance to Janggu, and it is also a form of the Kofun that appeared earlier in the Kofun period along with the . Generally, large Kofun are front and rear circular tombs, widely distributed in Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu with Gokishichidō as the center. Among them, the largest front and rear circular tomb in Japan are the Mozu Tombs with a total length of 525 meters. In addition to Japan, there are also the front and rear circular tombs in South Korea, as well as the front and rear circular tombs in Chosan County Ancient Tomb Group and Chasong County Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kofun Period
The is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD (the date of the introduction of Buddhism), following the Yayoi period. The Kofun and the subsequent Asuka periods are sometimes collectively called the Yamato period. This period is the earliest era of recorded history in Japan, but studies depend heavily on archaeology since the chronology of historical sources tends to be distorted. ''Kofun'' is Japanese for the type of tumulus, burial mound dating from this era. It was a period of cultural import. Continuing from the Yayoi period, the Kofun period is characterized by influence from China and the Korean Peninsula; archaeologists consider it a shared culture across the southern Korean Peninsula, Kyūshū and Honshū. On the other hand, the most prosperous keyhole-shaped burial mounds in Japan during this period were approximately 5,000 in Japan from the middle of the 3rd century in the Yayoi period to the 7th century in the Asuka period, and many of them had huge tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishibutai Kofun
is a Kofun period burial mound, located in the village of Asuka, Nara in the Kansai region of Japan. The tumulus was designated a National Historic Site of Japan in 1935. In 1954 the designation was elevated to a , The ''kofun'' is also known as the Kofun. Overview The Ishibutai Kofun occupies an area of , and is the largest known megalithic structure in Japan. It is located 5 km from Tanzan Shrine. It was originally covered by a mound made of piled up earth, but the earth has disappeared, exposing a horizontal stone burial chamber made of huge stones. Name The name of the ''kofun'' in Japanese is a combination of two words, the first, , meaning "stone", and the second, , meaning "stage". The name of the ''kofun'' therefore originates in its resemblance to a large stone stage. The Ishibutai ''kofun'' has been known by this name at least as early as the Tokugawa period, as evidenced by its entry in the ''Saigoku sanjūsansho meisho zue'', a large guide to Buddhist pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asuka-Fujiwara
Asuka-Fujiwara: Archaeological sites of Japan's Ancient Capitals and Related Properties is a cluster of archaeological sites from in and around the late sixth- to early eighth-century Capital of Japan, capitals of Asuka, Yamato, Asuka and Fujiwara-kyō, Nara Prefecture, Japan. In 2007, twenty-eight sites were submitted jointly for future inscription on the UNESCO World Heritage List under criteria World Heritage Site#Cultural criteria, ii, iii, iv, v, and vi. As of 28 January 2025, the number of component sites in the nominated property has been reduced to nineteen. Currently, the submission is included on the World Heritage Site#Nominating process, Tentative List. The Japanese government is aiming for inscription in 2026. Since 2011, the Cultural Landscape of the Asuka Hinterland has been Cultural Properties of Japan, protected as one of the Cultural Landscapes of Japan. An area of 60 Hectare, ha is also National Government Parks, protected within the Asuka Historical National Gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Special Places Of Scenic Beauty, Special Historic Sites And Special Natural Monuments
To protect Japan's cultural heritage, the country's government selects through the Agency for Cultural Affairs important items and designates them as Cultural Properties of Japan, Cultural Properties under the Law for the Protection of Cultural Properties. Designated items are classified in a number of categories, one of which is . This category includes historic locations such as Midden, shell mounds, ancient tombs, sites of palaces, sites of forts or Japanese castle, castles, monumental dwelling houses and other sites of high historical or scientific value; gardens, bridges, gorges, mountains, and other places of great scenic beauty; and natural features such as animals, plants, and geological or mineral formations of high scientific value. The government further designates "significant" monuments classifying them in three categories: , , and . Items of particularly high significance receive higher classifications: , , and respectively. As of October 24, 2023 there are 1,040 Natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haniwa
The are terracotta clay figures that were made for ritual use and buried with the dead as funerary objects during the Kofun period (3rd to 6th centuries AD) of the history of Japan. ''Haniwa'' were created according to the ''wazumi'' technique, in which mounds of coiled clay were built up to shape the figure, layer by layer. ''Haniwa'' can also refer to offering cylinders, not the clay sculptures on top of them as well as the "wooden haniwa" found in Kofun tumulus, tumuli. Terracotta ''Haniwa'' were made with water-based clay and dried into a coarse and absorbent material that stood the test of time. Their name means "circle of clay", referring to how they were arranged in a circle above the tomb. The protruding parts of the figures were made separately and then attached, while a few things were carved into them. They were smoothed out by a wooden paddle. Terraces were arranged to place them with a cylindrical base into the ground, where the earth would hold them in place. Dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
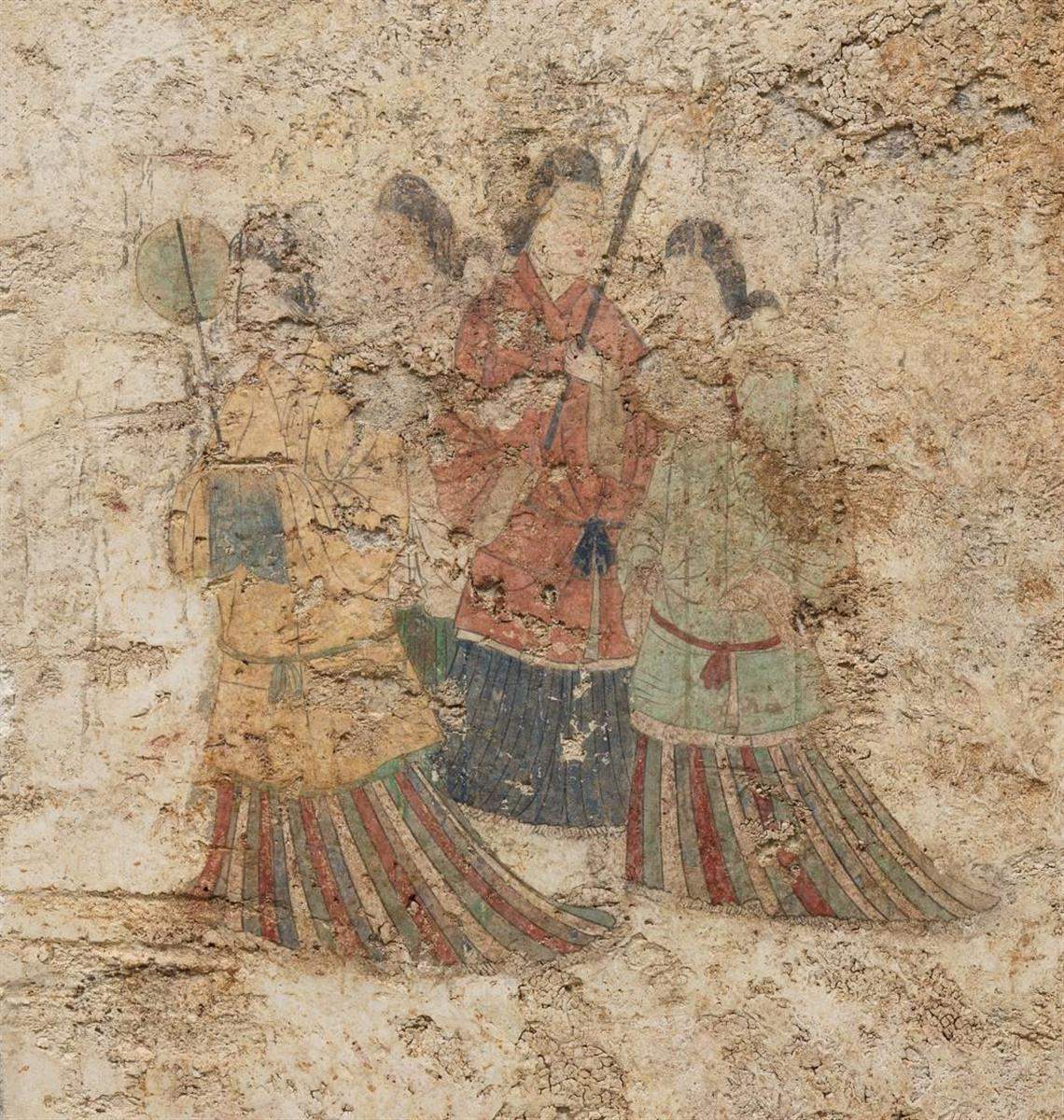
Takamatsuzuka Tomb
The is an Asuka period burial mound, located in the village of Asuka, Nara in the Kansai region of Japan. The tumulus was designated a National Historic Site of Japan in 1972. History The tumulus was discovered October 1970 when villagers dug a hole to store ginger and found old cut stones. The Nara Prefectural Kashihara Archaeological Institute began archaeological excavations from March 1972 together with researchers and students from Kansai University and Ryukoku University. Due to its small size and lack of historical documentation, the tumulus was regarded as unimportant until the horizontal entry stone burial chamber was opened, at which time it was realized that this was a decorated kofun. The tumulus was designated a Special Historic Site on April 23rd, 1973, and the vividly colored murals were designated a National Treasure on April 17th, 1974. The tumulus had been looted during the Kamakura period, and looting holes had been opened in the south wall of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
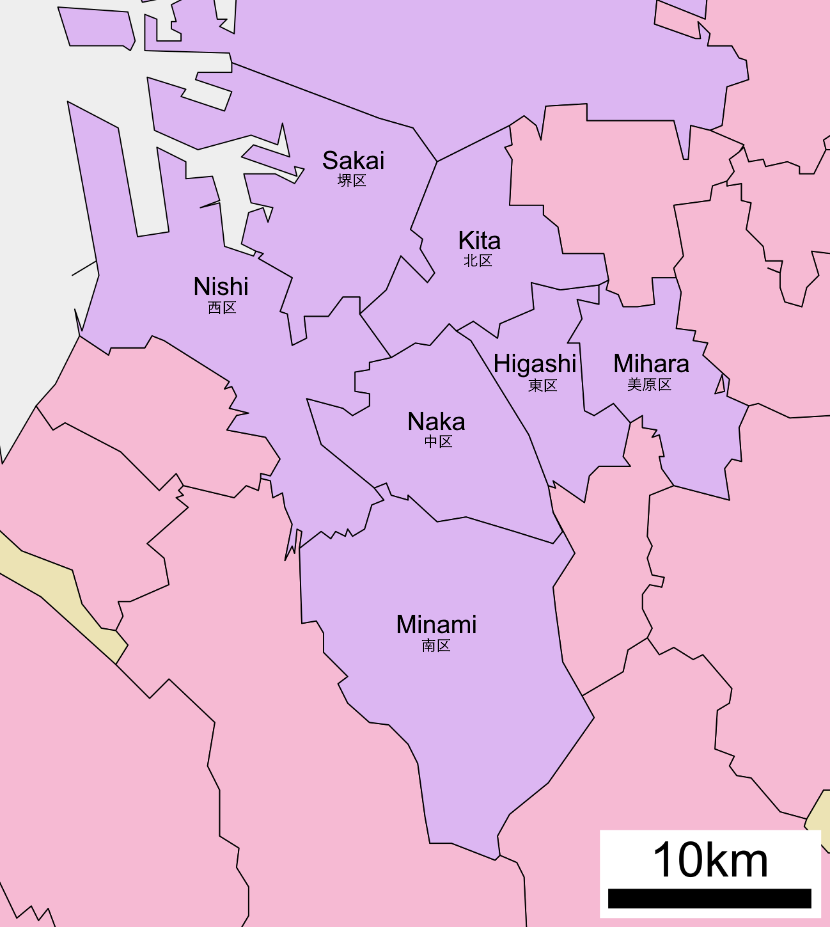
Sakai, Osaka
is a city located in Osaka Prefecture, Japan. It has been one of the largest and most important seaports of Japan since the medieval era. Sakai is known for its ''kofun'', keyhole-shaped burial mounds dating from the fifth century. The ''kofun'' in Sakai include the largest grave in the world by area, Mozu Tombs, Daisen Kofun. Once known for Katana, swords, Sakai is now famous for the quality of its Japanese kitchen knife, cutlery. , the city had an estimated population of 819,965, making it the fourteenth most populous city in Japan (excluding Tokyo). Geography Sakai is located in southern Osaka Prefecture, on the edge of Osaka Bay and directly south of the city of Osaka. Neighboring municipalities Osaka Prefecture *Habikino, Osaka, Habikino *Izumi, Osaka, Izumi *Kawachinagano, Osaka, Kawachinagano *Matsubara, Osaka, Matsubara *Osaka *Ōsakasayama, Osaka, Ōsakasayama *Takaishi, Osaka, Takaishi Climate Sakai has a Humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |