|
Klecka's Tau
Klecka's tau (''τ'') is a statistic which is used to test whether a given classification analysis improves one's classification to groups over a random allocation to the various groups under consideration.Klecka, WR (1980) Discriminant analysis. Sage Publications, Beverly Hills The maximum value of ''τ'' is 1.0 indicating no errors in the prediction. A value of zero indicates no improvement over a random assignment. The distribution of ''τ'' is not presently known and it is used as a descriptive rather than as an analytic statistic. Rationale for use Klecka's ''τ'' was developed for use with discriminant analysis. The raw accuracy of discriminant analysis the sum of correct predictions divided by the total number of cases. Klecka noted that although the percentage of cases predicted accurately is the most intuitive measure of discrimination, the magnitude of this percentage should be judged in relation to the expected percentage of correct classifications made by random assign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Classification
In statistics, classification is the problem of identifying which of a set of categories (sub-populations) an observation (or observations) belongs to. Examples are assigning a given email to the "spam" or "non-spam" class, and assigning a diagnosis to a given patient based on observed characteristics of the patient (sex, blood pressure, presence or absence of certain symptoms, etc.). Often, the individual observations are analyzed into a set of quantifiable properties, known variously as explanatory variables or ''features''. These properties may variously be categorical (e.g. "A", "B", "AB" or "O", for blood type), ordinal (e.g. "large", "medium" or "small"), integer-valued (e.g. the number of occurrences of a particular word in an email) or real-valued (e.g. a measurement of blood pressure). Other classifiers work by comparing observations to previous observations by means of a similarity or distance function. An algorithm that implements classification, especially in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
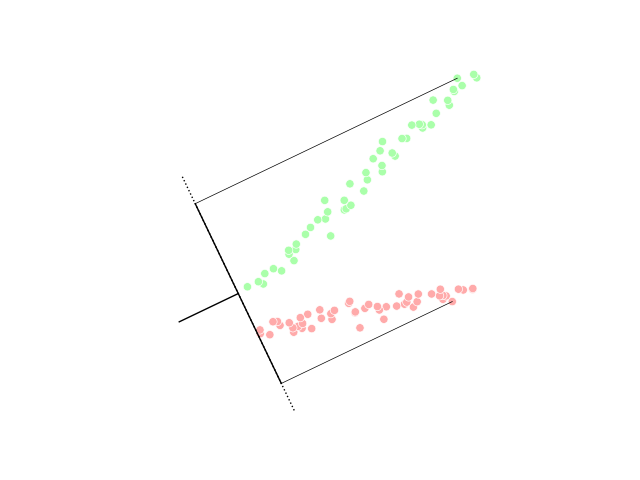
Discriminant Analysis
Linear discriminant analysis (LDA), normal discriminant analysis (NDA), or discriminant function analysis is a generalization of Fisher's linear discriminant, a method used in statistics and other fields, to find a linear combination of features that characterizes or separates two or more classes of objects or events. The resulting combination may be used as a linear classifier, or, more commonly, for dimensionality reduction before later classification. LDA is closely related to analysis of variance (ANOVA) and regression analysis, which also attempt to express one dependent variable as a linear combination of other features or measurements. However, ANOVA uses categorical independent variables and a continuous dependent variable, whereas discriminant analysis has continuous independent variables and a categorical dependent variable (''i.e.'' the class label). Logistic regression and probit regression are more similar to LDA than ANOVA is, as they also explain a categorical va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Regression
In statistical modeling, regression analysis is a set of statistical processes for estimating the relationships between a dependent variable (often called the 'outcome' or 'response' variable, or a 'label' in machine learning parlance) and one or more independent variables (often called 'predictors', 'covariates', 'explanatory variables' or 'features'). The most common form of regression analysis is linear regression, in which one finds the line (or a more complex linear combination) that most closely fits the data according to a specific mathematical criterion. For example, the method of ordinary least squares computes the unique line (or hyperplane) that minimizes the sum of squared differences between the true data and that line (or hyperplane). For specific mathematical reasons (see linear regression), this allows the researcher to estimate the conditional expectation (or population average value) of the dependent variable when the independent variables take on a given set of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probit Regression
In statistics, a probit model is a type of regression where the dependent variable can take only two values, for example married or not married. The word is a portmanteau, coming from ''probability'' + ''unit''. The purpose of the model is to estimate the probability that an observation with particular characteristics will fall into a specific one of the categories; moreover, classifying observations based on their predicted probabilities is a type of binary classification model. A probit model is a popular specification for a binary response model. As such it treats the same set of problems as does logistic regression using similar techniques. When viewed in the generalized linear model framework, the probit model employs a probit link function. It is most often estimated using the maximum likelihood procedure, such an estimation being called a probit regression. Conceptual framework Suppose a response variable ''Y'' is ''binary'', that is it can have only two possible ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logistic Regression
In statistics, the logistic model (or logit model) is a statistical model that models the probability of an event taking place by having the log-odds for the event be a linear function (calculus), linear combination of one or more independent variables. In regression analysis, logistic regression (or logit regression) is estimation theory, estimating the parameters of a logistic model (the coefficients in the linear combination). Formally, in binary logistic regression there is a single binary variable, binary dependent variable, coded by an indicator variable, where the two values are labeled "0" and "1", while the independent variables can each be a binary variable (two classes, coded by an indicator variable) or a continuous variable (any real value). The corresponding probability of the value labeled "1" can vary between 0 (certainly the value "0") and 1 (certainly the value "1"), hence the labeling; the function that converts log-odds to probability is the logistic function, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Analysis
Image analysis or imagery analysis is the extraction of meaningful information from images; mainly from digital images by means of digital image processing techniques. Image analysis tasks can be as simple as reading bar coded tags or as sophisticated as identifying a person from their face. Computers are indispensable for the analysis of large amounts of data, for tasks that require complex computation, or for the extraction of quantitative information. On the other hand, the human visual cortex is an excellent image analysis apparatus, especially for extracting higher-level information, and for many applications — including medicine, security, and remote sensing — human analysts still cannot be replaced by computers. For this reason, many important image analysis tools such as edge detectors and neural networks are inspired by human visual perception models. Digital Digital Image Analysis or Computer Image Analysis is when a computer or electrical device au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |