|
Klaipėda Region
The Klaipėda Region () or Memel Territory ( or ''Memelgebiet'') was defined by the 1919 Treaty of Versailles in 1920 and refers to the northernmost part of the German province of East Prussia, when, as Memelland, it was put under the administration of the Entente's Council of Ambassadors. The Memel Territory, together with other areas severed from Germany (the Saar and Danzig), was to remain under the control of the League of Nations until a future date, when the people of those regions would be allowed to vote on whether or not the land would return to Germany. Today, the former Memel Territory is controlled by Lithuania as part of Klaipėda and Tauragė counties. Historical overview In 1226, Duke Konrad I of Masovia requested assistance against the Prussians and other Baltic tribes, including the Skalvians who lived along the Neman (Memel) River. In March 1226, Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II issued the Golden Bull of Rimini, which provided that the Teutonic Knight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Prussia
East Prussia was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1772 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 1871); following World War I it formed part of the Weimar Republic's Free State of Prussia, until 1945. Its capital city was Königsberg (present-day Kaliningrad). East Prussia was the main part of the Prussia (region), region of Prussia along the southeastern Baltic Sea, Baltic Coast. The bulk of the ancestral lands of the Baltic Old Prussians were enclosed within East Prussia. During the 13th century, the native Prussians were conquered by the crusading Teutonic Knights. After the Northern Crusades, conquest the indigenous Balts were gradually converted to Christianity. Because of Germanization and colonisation over the following centuries, Germans became the dominant ethnic group, while Polish people, Poles and Lithuanians formed sizeable minorities. From the 13th century, the region of Prussia was part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Ambassadors
A council is a group of people who come together to consult, deliberate, or make decisions. A council may function as a legislature, especially at a town, city or county/shire level, but most legislative bodies at the state/provincial or national level are not considered councils. At such levels, there may be no separate executive branch, and the council may effectively represent the entire government. A board of directors might also be denoted as a council. A committee might also be denoted as a council, though a committee is generally a subordinate body composed of members of a larger body, while a council may not be. Because many schools have a student council, the council is the form of governance with which many people are likely to have their first experience as electors or participants. A member of a council may be referred to as a councillor or councilperson, or by the gender-specific titles of councilman and councilwoman. In politics Notable examples of types of counc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian Uprisings
The Prussian uprisings were two major and three smaller uprisings by the Old Prussians, one of the Baltic tribes, against the Teutonic Knights that took place in the 13th century during the Prussian Crusade. The crusading military order, supported by the Popes and Christian Europe, sought to conquer and convert the pagan Prussians. In the first ten years of the crusade, five of the seven major Prussian clans fell under the control of the less numerous Teutonic Knights. However, the Prussians rose against their conquerors on five occasions. The first uprising was supported by Duke Swietopelk II, Duke of Pomerania. The Prussians were successful at first, reducing the Knights to only five of their strongest castles. The duke then suffered a series of military defeats and was eventually forced to make peace with the Teutonic Knights. With Duke Swietopelk's support for the Prussians broken, a prelate of Pope Innocent IV negotiated a peace treaty between the Prussians and the Knigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teutonic Order
The Teutonic Order is a religious order (Catholic), Catholic religious institution founded as a military order (religious society), military society in Acre, Israel, Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to the Holy Land and to establish hospitals. Its members have commonly been known as the Teutonic Knights, having historically served as a crusades, crusading military order for supporting Catholic rule in the Holy Land and the Northern Crusades during the Middle Ages, as well as supplying military protection for Catholics in Eastern Europe. Purely religious since 1810, the Teutonic Order still confers limited honorary knighthoods. The Bailiwick of Utrecht of the Teutonic Order, a Protestant order of chivalry, chivalric order, is descended from the same medieval military order and also continues to award knighthoods and perform charitable work. Name The name of the Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Bull Of Rimini
The Golden Bull of Rimini was a decree issued by Emperor Frederick II in Rimini in March 1226 that granted and confirmed the privilege of territorial conquest and acquisition for the Teutonic Order in Prussia. According to historian Tomasz Jasiński, the bull was backdated and had actually been issued in 1235. It represents the first of a series of three documents, that include the Treaty of Kruschwitz of 1230 and the Papal Golden Bull of Rieti of 1234. Background The Piast duke Konrad I of Masovia had since 1209 engaged in several military campaigns against the pagan Old Prussians. In 1217 Pope Honorius III authorized bishop Christian of Oliva to designate these conquests as the Prussian Crusade. In 1222/23 Konrad attempted to subdue the Prussian territories of the Culmer Land east of the Vistula River. Backed by his Polish cousins Leszek I the White and Henry I the Bearded, he initially was successful, but was eventually confronted with relentless Prussian counter attack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick II (, , , ; 26 December 1194 – 13 December 1250) was King of Sicily from 1198, King of Germany from 1212, King of Italy and Holy Roman Emperor from 1220 and King of Jerusalem from 1225. He was the son of Emperor Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Henry VI of the Hohenstaufen dynasty (the second son of Emperor Frederick Barbarossa) and Queen Constance I of Sicily of the Hauteville dynasty. Frederick was one of the most powerful figures of the Middle Ages and ruled a vast area, beginning with Sicily and stretching through Italy all the way north to Germany. Viewing himself as a direct successor to the Roman emperors of antiquity, he was Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of the Romans from his papal coronation in 1220 until his death; he was also a claimant to the title of King of the Romans from 1212 and unopposed holder of that monarchy from 1215. As such, he was King of Germany, King of Italy, of Italy, and King of Burgundy, of Burgundy. At the age of three, he was crowned King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neman River
Neman, Nemunas or Niemen is a river in Europe that rises in central Belarus and flows through Lithuania then forms Lithuania–Russia border, the northern border of Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia's western exclave, which specifically follows its southern channel. It drains into the Curonian Lagoon, narrowly connected to the Baltic Sea. The long Neman is a major Eastern European river. It flows generally west to Grodno within of the Polish border, north to Kaunas, then westward again to the sea. The largest river in Lithuania, and the third-largest in Belarus, it is navigable for most of its length. It starts from two small headwaters merging about southwest of the town of Uzda – about southwest of capital city Minsk. Only , an eastward meander, contributes to the Belarus–Lithuania border. Thereafter the river includes notable loops along a minor tectonic fault. Its drainage basin settled in the late Quaternary to be roughly along the edge of the last glacial sheet so d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skalvians
The Scalovians (; ), also known as the Skalvians, ''Schalwen'' and ''Schalmen'', were a Baltic tribe related to the Prussians. According to the '' Chronicon terrae Prussiae'' of Peter of Dusburg, the now extinct Scalovians inhabited the land of Scalovia south of the Curonians and Samogitians, by the lower Neman River ca. 1240. Geography This region is located at both sides of the river Memel north of Nadruvians and south of Samogitia. In the North-East it stretched to rivers Šešupė, Ežeruona and Jūra. In the East it bordered on Sudovia, in the North-West on river Minija, in the West on the Curonian Lagoon and in the South-West on river Gilija. The center were the towns of Rusnė, Ragainė and Tilžė. Name The meaning is uncertain: ''skalwa'' "splinter (living split off)" or ''skalauti'' "between waters". According to Prussian legends, the tribe's name is derived from one of the sons of King Widewuto named Schalauo. History The inhabitants can be traced back to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples (, ) are a group of peoples inhabiting the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea who speak Baltic languages. Among the Baltic peoples are modern-day Lithuanians (including Samogitians) and Latvians (including Latgalians (modern), Latgalians) — all East Balts — as well as the Old Prussians, Curonians, Sudovians, Skalvians, Yotvingians and Galindians — the West Balts — whose languages and cultures are now extinct, but made a large influence on the living branches, especially on literary Lithuanian language. The Balts are descended from a group of Proto-Indo-Europeans, Proto-Indo-European tribes who settled the area between the lower Vistula and southeast shore of the Baltic Sea and upper Daugava and Dnieper rivers, and which over time became differentiated into West and East Balts. In the fifth century CE, parts of the eastern Baltic coast began to be settled by the ancestors of the Western Balts, whereas the East Balts lived in modern-day Belarus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
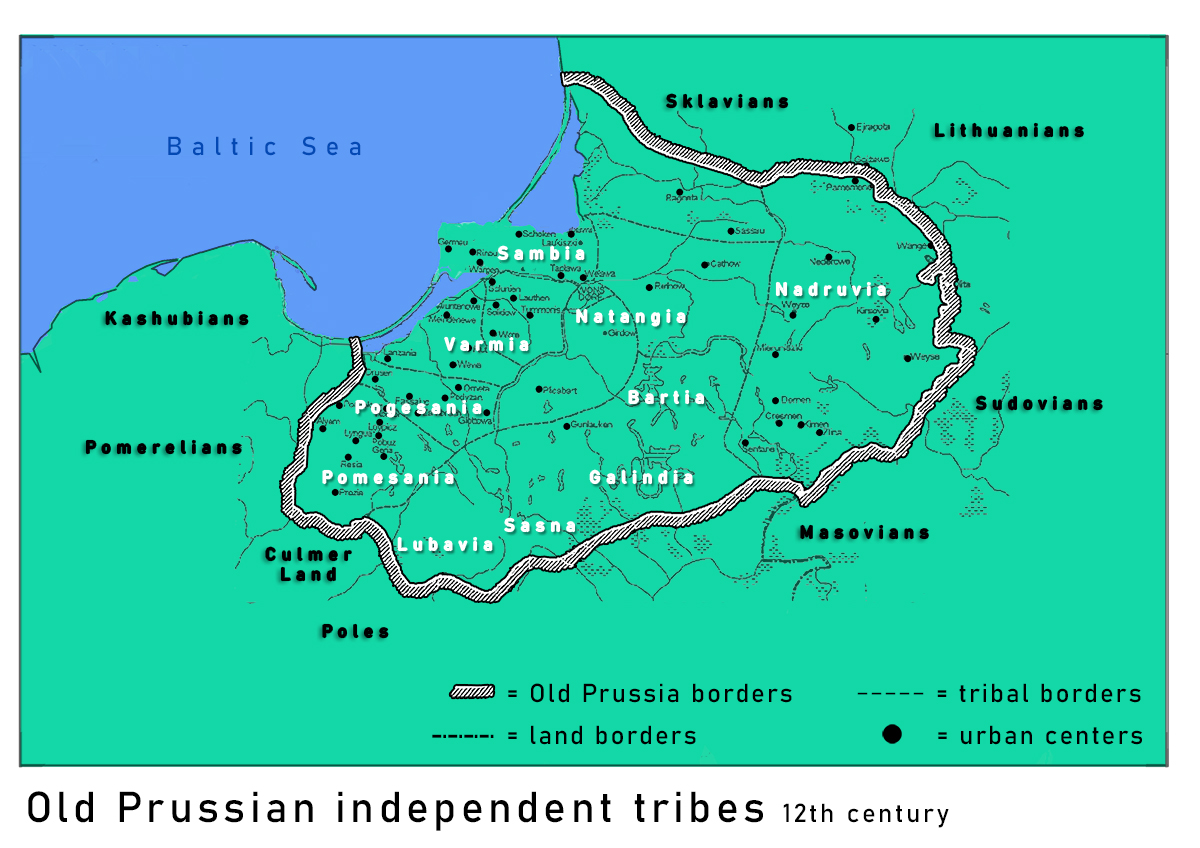
Old Prussians
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians were a Balts, Baltic people that inhabited the Prussia (region), region of Prussia, on the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea between the Vistula Lagoon to the west and the Curonian Lagoon to the east. As Balts, they spoke an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language of the Baltic languages, Baltic branch now known as Old Prussian language, Old Prussian and worshipped pre-Christian Prussian mythology, deities. Their ethnonym was later adopted by predominantly Low German language, Low German-speaking inhabitants of the region. The duchy of the Duchy of Poland (c. 960–1025), Polans under Mieszko I, which was the predecessor of the Kingdom of Poland (1025–1385), Kingdom of Poland, first attempted to conquer and baptize the Baltic tribes during the 10th century, but repeatedly encountered strong resistance. Not until the 13th century were the Old Prussians subjugated and their lands conquered by the State of the Teuton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konrad I Of Masovia
Konrad I of Masovia (ca. 1187/88 – 31 August 1247), from the Polish Piast dynasty, was the sixth Duke of Masovia and Kuyavia from 1194 until his death as well as High Duke of Poland from 1229 to 1232 and again from 1241 to 1243. Life Konrad was the youngest son of High Duke Casimir II the Just of Poland and Helen of Znojmo, daughter of the Přemyslid duke Conrad II of Znojmo (ruler of the Znojmo Appanage in southern Moravia, part of Duchy of Bohemia). His maternal grandmother was Maria of Serbia, apparently a daughter of the pre- Nemanjić ''župan'' Uroš I of Rascia. After his father's death in 1194, Konrad was brought up by his mother, who acted as regent of Masovia. In 1199, he received Masovia and in 1205 the adjacent lands of Kuyavia as well. In 1205, he and his brother, Duke Leszek I the White of Sandomierz, had their greatest military victory at Battle of Zawichost against Prince Roman the Great of Galicia–Volhynia. The Ruthenian army was crushed and R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tauragė County
Tauragė County (Lithuanian language, Lithuanian: ''Tauragės apskritis'') is one of ten counties of Lithuania, counties in Lithuania. It is in the west of the country, and its capital is Tauragė. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Tauragė County remains as a territorial and statistical unit. Famous landmarks include Tauragė Castle and Panemunė Castle. Municipalities Cities #Tauragė #Jurbarkas #Šilalė #Pagėgiai #Skaudvilė #Smalininkai #Panemunė Population by municipality Gallery 2. Šilalės bažnyčia.JPG, St. Francis church in Šilalė Lithuania Raudone Castle.jpg, Raudonė Castle Veliuonos dvaras - panoramio (1).jpg, Veliuona Manor La katolika kirko de Jurbarkas (Georgenburg) c.jpg, Holy Trinity church in Jurbarkas Panemune Castle Aerial.jpg, Panemunė Castle References External links Social and demographic characteristics of Tauragė CountyEconomy of Tauragė CountyEnvironment of Tauragė County {{DEFA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |