|
Kjölur
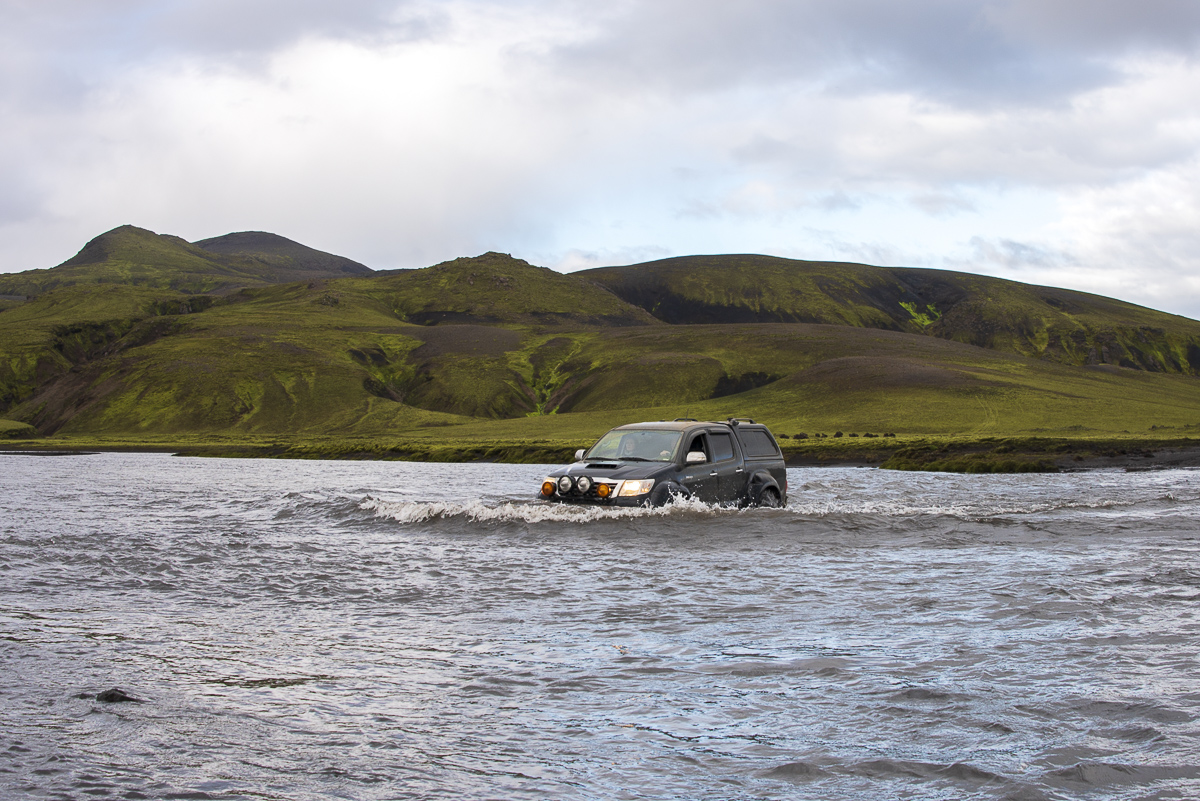
Kjölur () is a plateau in the highlands of Iceland, roughly defined as the area between the Langjökull and Hofsjökull glaciers. It lies at an elevation of about 600–700 metres. Geography At the northern end of the Kjölur road, near the headwaters of the Blanda river, the hot springs of Hveravellir provide a warm oasis. Not far from Hveravellir, the Kerlingarfjöll, a volcanic mountain range, is situated to the north-east of the Kjölur road. History Like Sprengisandur highland road, the area was probably known since the first times of Icelandic settlement and is mentioned in the Icelandic sagas. A track along Langjökull was used as a shortcut between regions during summer. This is today known as ''Kjalvegur hinn forni'' (Old Kjalvegur) and is still in use for trekking and horse-riding. Piles of stones mark the track through the highland desert. After some people had perished in a snowstorm by the end of the 18th century, the Kjölur road was forgotten for about 100 ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kjalvegur
Kjalvegur (, ) is a highland road in Iceland, crossing Kjölur from north to south. History Formerly, the name referred to a horse-track closer to Langjökull, west of the current road. This track now goes by the name ''Kjalvegur hinn forni'' (Ancient Kjalvegur), and is closed to motorized traffic. Geography The road begins in the south of Iceland near Haukadalur (Bláskógabyggð), Haukadalur and behind the Gullfoss waterfall, ending in the north near ''Blönduós''. The road traverses the interior between two glaciers, Langjökull and Hofsjökull. It is the second longest of the roads through the Highlands of Iceland. It takes about 5 hours to traverse by car, the road is generally rough, but river crossings are bridged. See also * Route 35 (Iceland) * Sprengisandsleið * Kjölur {{Iceland-transport-stub Roads in Iceland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langjökull
Langjökull (, Icelandic for "long glacier") is the second largest ice cap in Iceland (), after Vatnajökull. It is situated in the west of the Icelandic interior or Highlands of Iceland and can be seen clearly from Haukadalur. It covers the higher parts of the Langjökull volcanic system. Its volume is and the ice is up to thick. The highest point of the ice cap (at ''Baldjökull'' at the northern end of Langjökull) is about above sea level. In the past, the largest recorded surface area was in 1840. Situation and form The glacier is roughly parallel to the direction of the country's active volcanic zone: north-east to south-west. It is about long and wide, and has a slightly narrower point roughly between the lake Hvítárvatn on the Kjölur mountain road to the east and the Þrístapajökull glacier to the west, near another smaller glacier, Eiríksjökull, which is not quite connected to Langjökull. It is the nearest large glacier to Reykjavík. The area o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Route 35 (Iceland)
Route 35 is one of the interior roads of Iceland. The road is divided into two main sections. The first part is called (, ) and runs from about one kilometer northwest of Selfoss up to Gullfoss. It is a road for all cars. The second part is (, {{lit, Kjölur Road). This is a highland road which runs over the Kjölur plateau. The mountain road has the number F35. Route 35 in total is 237 km long. Biskupstungnabraut From the Ring Road (1) the road heads north-east through Árnessýsla forming the primary route to the tourist hotspots of Geysir and Gullfoss. Along the way the road meets several other routes, such as Þingvallavegur (36), Laugarvatnsvegur (37) with distinctive peninsulas and Skálholt Way (31) and Hrunamannavegur (30). Near the road are a number of tourist attractions. In addition to Geysir and Gullfoss, these include volcanic crater lake Kerið and the Faxi waterfall on the Tungufljót river. The road crosses the Alviðra. The original bridge was b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highlands Of Iceland
The Highland (Icelandic language, Icelandic: ''Hálendið)'' or The Central Highland is an area that comprises much of the interior land of Iceland. The Highland is situated above and is mostly uninhabitable. The soil is primarily volcanic ash, and the terrain consists of basalt mountains and lava fields. Snow covers the Highland from October until the beginning of June. A few oasis-like areas, such as Herðubreiðarlindir and Thórsmörk, Þórsmörk, are also found in the Highland. The area has many notable natural features and hiking trails. Natural features in the Highland The Highland encompasses various geological features, including Landmannalaugar, Torfajökull, Eldgjá, Thórsmörk, Þórsmörk, Herðubreið, Askja, Hveradalir, Laki, Lakagígar, and the Fagrifoss waterfall. Sites in the Highland are difficult to access and may be accessible only during the summer months. Most sites require all-wheel drive or all-terrain vehicles for access due to the unpaved dirt ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hveravellir
Hveravellir () is a geothermal field (high temperature field) of the Oddnýjarhnjúkur-Langjökull volcanic system - in the north of the Langjökull glacier. Description Hveravellir geothermal area is a small nature reserve and a tourist centre located at at the Kjölur mountain route between the glaciers Hofsjökull and Langjökull, in central Iceland. It is part of the Oddnýjarhnjúkur-Langjökull volcanic system. The place has been a popular resting place in highland travels since the age of settlement, 1100-1200 years ago. It is frequently mentioned in the old sagas, annals and folklore. Refuge huts have been situated there from the early beginning. The main geothermal activity is at the northern border of the large lava shield Kjalhraun . The main geothermal area covers around . The hot springs are of various types, geysers, fumaroles, solfataras, boiling pits and warm springs with lower temperatures. The currently active geysers only have small irregular eruptions. Sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerlingarfjöll
Kerlingarfjöll () is a tall volcanic massive in Iceland situated in the Highlands of Iceland near the Kjölur highland road. It is usually regarded as part of a large tuya fissure system of in the southern portion of the Hofsjökull volcanic system, although is about in diameter itself, and is between 68 and 350 thousand years old predating some of the activity in the rest of the system. The volcanic origin of these mountains is evidenced by tholeiite basalt deposits, the numerous hot springs and rivulets in the area, as well as red volcanic rhyolite stone most marked near the two caldera. Minerals that have emerged from the hot springs also color the ground yellow, red and green. The area was known formerly for its summer ski resort, but this was dismantled in 2000. Since 2000, Kerlingarfjöll has been operated as a highland resort, offering accommodation and food services to guests in the area. On March 17 in 2017 it was reported that the Kerlingarfjöll Mountains and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sprengisandur
Sprengisandur () is a highland plateau in Iceland, defined roughly as the area between the Hofsjökull and Vatnajökull glaciers. History and etymology Like Kjölur and Kaldidalur, Sprengisandur is an ancient pass - during the time of the Icelandic Free State (ca. 930–1265) it was one of the several important north–south routes that connected remote regions of the island to the Plains of the Parliament, Þingvellir, where the yearly parliament, Alþingi, was held each year at midsummer. In the sagas of Icelanders it is often called simply ''Sandr'' "Sand" or ''Sandleið'', "Sand trail". At its southern end, it was joined with another such route, Fjallabaksvegur nyrðri, running west from Landmannalaugar mountain hot springs area. Sprengisandur is only accessible during summer - like other parts of the inner desert, it is impassable in winter because of the snow, and in spring because of floods. While being the shortest way to the Alþingi for some Icelanders, for exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desert
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the land surface of the Earth is arid or Semi-arid climate, semi-arid. This includes much of the Polar regions of Earth, polar regions, where little precipitation occurs, and which are sometimes called polar deserts or "cold deserts". Deserts can be classified by the amount of precipitation that falls, by the temperature that prevails, by the causes of desertification or by their geographical location. Deserts are formed by weathering processes as large variations in temperature between day and night strain the Rock (geology), rocks, which consequently break in pieces. Although rain seldom occurs in deserts, there are occasional downpours that can result in flash floods. Rain falling on hot rocks can cause them to shatter, and the resulting frag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwestern Region (Iceland)
Northwestern Region (, ) is one of the traditional eight regions of Iceland, located in the north of the island. The largest town in the region is Sauðárkrókur, with a population of 2,609 in 2024. One of the primary attractions of the area is the basalt rock Hvítserkur, 15 meters high and resembles a dragon that throws its head to take a sip of water. References External links * {{iceland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Region (Iceland)
Southern Region ( , ) is a region of Iceland Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi .... The population of the region was 34,076 (1 January 2024). The largest town in the region is Selfoss, with a population of 9,812 as of 2024. References External links *Source {{iceland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fjalla-Eyvindur
Fjalla-Eyvindur (Icelandic language, Icelandic for "Eyvindur of the Mountains"; c. 1714–1783) was an Icelandic outlaw. He and his wife Halla are reported to have fled into the remote highlands of Iceland after 1760. They lived in the wilderness for 20 years. A hot spring named Eyvindarhver is named after him. The Icelandic playwright Jóhann Sigurjónsson dramatised his life in 1911 as ''Fjalla-Eyvindur''. This play contains the lullaby "Sofðu unga ástin mín", still used by many Icelandic parents. In 1918, the play was made into the Swedish film ''The Outlaw and His Wife'', directed by Victor Sjöström. External linksHveravellir Outlaws Icelandic criminals 18th-century Icelandic people 1710s births 1783 deaths {{Iceland-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |