|
Kitab-ı Bahriye
The ''Kitab-ı Bahriye'' () is a navigational guide written by Piri Reis, an Ottoman Cartography, cartographer, Privateer, corsair, and captain. He compiled charts and notes from his career at sea into the most detailed Portolan chart, portolan atlas in existence. The ''Kitab-ı Bahriye'' combines information from a range of sources and Piri Reis' personal experience. The coast of North Africa relies little on outside sources. The book is also one of the few primary sources of information on Piri Reis. There are two versions of the book. The first version was composed between 1511 and 1521, and presented as a gift to the sultan Suleiman the Magnificent. The second, expanded version was produced as a commission for Ottoman Grand Vizier Pargalı İbrahim Pasha, and completed in 1526. Both versions begin with a preface and were dedicated to the sultan Suleiman. The main part of both versions is a nautical atlas to the Mediterranean Sea. Separate chapters cover different locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topkapı Palace
The Topkapı Palace (; ), or the Seraglio, is a large museum and library in the east of the Fatih List of districts of Istanbul, district of Istanbul in Turkey. From the 1460s to the completion of Dolmabahçe Palace in 1856, it served as the administrative center of the Ottoman Empire, and was the main residence of its sultans. Construction, ordered by the Sultan Mehmed the Conqueror, began in 1459, six years after the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople. Topkapı was originally called the "New Palace" ( or ) to distinguish it from the Eski Saray, Old Palace ( or ) in Beyazıt Square. It was given the name , meaning Cannon Gate, in the 19th century. The complex expanded over the centuries, with major renovations after the 1509 Constantinople earthquake, 1509 earthquake and the 1665 fire. The palace complex consists of four main courtyards and many smaller buildings. Female members of the Sultan's family lived in the harem, and leading state officials, including th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresh Water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salt (chemistry), salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mineral water, mineral-rich waters, such as chalybeate springs. Fresh water may encompass frozen water, frozen and meltwater in ice sheets, ice caps, glaciers, snowfields and icebergs, natural precipitations such as rainfall, snowfall, hail/ice pellets, sleet and graupel, and surface runoffs that form inland bodies of water such as wetlands, ponds, lakes, rivers, streams, as well as groundwater contained in aquifers, subterranea (geography), subterranean subterranean river, rivers and underground lake, lakes. Water is critical to the survival of all living organisms. Many organisms can thrive on salt water, but the great majority of vascular plants and most insects, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds need fresh water to sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman–Mamluk War (1516–1517)
The Ottoman–Mamluk War of 1516–1517 was the second major conflict between the Egypt-based Mamluk Sultanate and the Ottoman Empire, which led to the Fall of the Mamluk Sultanate and the incorporation of the Levant, Egypt, and the Hejaz as provinces of the Ottoman Empire. The war transformed the Ottoman Empire from a realm at the margins of the Islamic world, mainly located in Anatolia and the Balkans, to a huge empire encompassing much of the traditional lands of Islam, including the cities of Mecca, Cairo, Damascus, and Aleppo. Despite this expansion, the seat of the empire's political power remained in Constantinople. Background The relationship between the Ottomans and the Mamluks had been adversarial since the Fall of Constantinople to the Ottomans in 1453; both states vied for control of the spice trade, and the Ottomans aspired to eventually take control of the Holy Cities of Islam. An earlier conflict, which lasted from 1485 to 1491, had led to a stalemate. Having ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piri Reis Map
The Piri Reis map is a world map compiled in 1513 by the Ottoman admiral and cartographer Piri Reis. Approximately one third of the map survives, housed in the Topkapı Palace in Istanbul. After the empire's 1517 conquest of Egypt, Piri Reis presented the 1513 world map to Ottoman Sultan Selim I (). It is unknown how Selim used the map, if at all, as it vanished from history until its rediscovery centuries later. When rediscovered in 1929, the remaining fragment garnered international attention as it includes a partial copy of an otherwise lost map by Christopher Columbus. The map is a portolan chart with compass roses and a windrose network for navigation, rather than lines of longitude and latitude. It contains extensive notes primarily in Ottoman Turkish. The depiction of South America is detailed and accurate for its time. The northwestern coast combines features of Central America and Cuba into a single body of land. Scholars attribute the peculiar arrangement of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelibolu
Gelibolu is a town in Çanakkale Province of the Marmara Region, located in Eastern Thrace in the European part of Turkey. It is located on the southern shore of the Gallipoli, peninsula named after it on the Dardanelles strait, away from Lapseki on the other shore. It is the seat of Gelibolu District.İlçe Belediyesi Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 1 March 2023. Its population is 31,782 (2021). History  The Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonian city of Kallipolis was founded in the 5th century B.C. It has a rich history as a naval base ...
The Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonian city of Kallipolis was founded in the 5th century B.C. It has a rich history as a naval base ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Navy
The Ottoman Navy () or the Imperial Navy (), also known as the Ottoman Fleet, was the naval warfare arm of the Ottoman Empire. It was established after the Ottomans first reached the sea in 1323 by capturing Praenetos (later called Karamürsel after the founder of the Ottoman Navy), the site of the first Ottoman naval shipyard and the nucleus of the future navy. During its long existence, the Ottoman Navy was involved in many conflicts and signed a number of maritime treaties. It played a decisive role in the conquest of Constantinople and the subsequent expansion into the Mediterranean and Black Seas. At its height in the 16th century, the Navy extended to the Indian Ocean, sending an expedition to Indonesia in 1565, and by the early 17th century operated as far as the Atlantic. Commensurate with the decline and modernization of the empire in the late 18th century, the Ottoman Navy stagnated, albeit remaining among the largest in the world: with nearly 200 warships, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kemal Reis
Kemal Reis (c. 1451 – 1511) was an Ottoman privateer and admiral. He was also the paternal uncle of the famous Ottoman admiral and cartographer Piri Reis, who accompanied him in most of his important naval expeditions. Background and early career Kemal Reis was born in Manisa on the Aegean coast of the Ottoman Empire in circa 1451.Bono, Salvatore: Corsari nel Mediterraneo (Corsairs in the Mediterranean), Oscar Storia Mondadori. Perugia, 1993. His full name was Ahmed Kemaleddin (''Ahmet Kemalettin''). His ancestry is disputed; some sources claim that he was born into a Turkish family, while other sources indicate that he was born into a Greek family which converted from Christianity to Islam. He became known in Europe, particularly in Italy and Spain, with names like ''Camali'' and ''Camalicchio''. Naval mission to Spain Kemal Reis started his career as the commander of the naval fleet belonging to the ''Sanjak Bey'' (Provincial Governor) of Eğriboz (present-day Eubo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
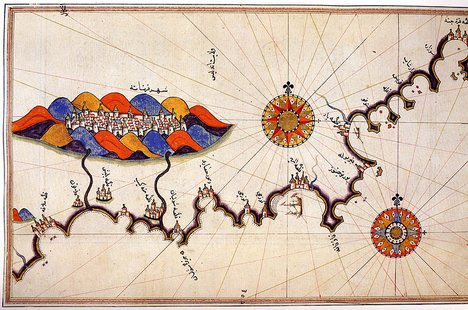
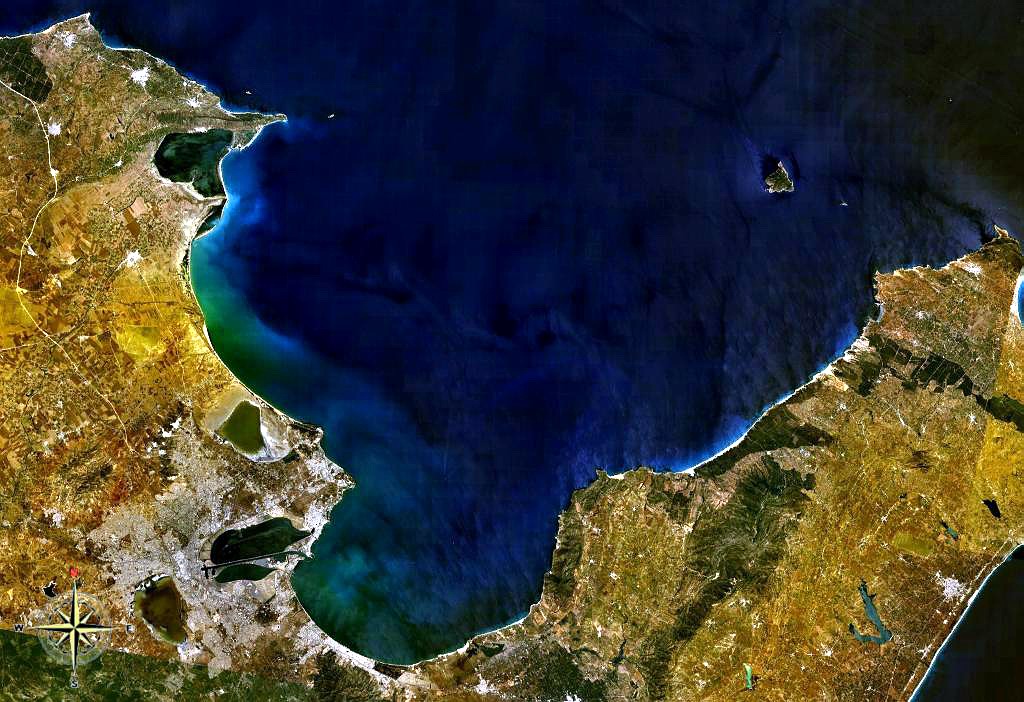
Gulf And Island Of Djerba By Piri Reis
A gulf is a large inlet from an ocean or their seas into a landmass, larger and typically (though not always) with a narrower opening than a bay. The term was used traditionally for large, highly indented navigable bodies of salt water that are enclosed by the coastline. Many gulfs are major shipping areas, such as the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Mexico, Gulf of Finland, and Gulf of Aden The Gulf of Aden (; ) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channel, the Socotra Archipelago, Puntland in Somalia and Somaliland to the south. .... See also * References External links * {{Geography-stub Bodies of water Coastal and oceanic landforms Coastal geography Oceanographical terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strait Of Hormuz
The Strait of Hormuz ( ''Tangeh-ye Hormoz'' , ''Maḍīq Hurmuz'') is a strait between the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. It provides the only sea passage from the Persian Gulf to the open ocean and is one of the world's most strategically important choke points. On the north coast lies Iran, and on the south coast lies the Musandam peninsula, shared by the United Arab Emirates and the Musandam Governorate, an exclave of Oman. The strait is about long, with a width varying from about to . A third of the world's liquefied natural gas and almost 25% of total global List of countries by oil exports, oil consumption passes through the strait, making it a highly important strategic location for international trade. It has been so for centuries; its vast hinterlands were rich in luxury trade goods with no easy access to lucrative trading ports. Babur's memoirs recount how almonds had to be carried from the distant Fergana Valley, Ferghana region to Hormuz to reach markets. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. The Indian Ocean has large marginal or regional seas, including the Andaman Sea, the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, and the Laccadive Sea. Geologically, the Indian Ocean is the youngest of the oceans, and it has distinct features such as narrow continental shelf, continental shelves. Its average depth is 3,741 m. It is the warmest ocean, with a significant impact on global climate due to its interaction with the atmosphere. Its waters are affected by the Indian Ocean Walker circulation, resulting in unique oceanic currents and upwelling patterns. The Indian Ocean is ecologically diverse, with important ecosystems such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Discovery Of The Sea Route To India
The Portuguese discovery of the sea route to India was the first recorded trip directly from Europe to the Indian subcontinent, via the Cape of Good Hope. Under the command of the Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama, it was undertaken during the reign of King Manuel I in 1497–1499. It is one of the most important events of the Age of Discovery and the Portuguese Empire, and it initiated the Portuguese maritime trade on the Malabar Coast and other parts of the Indian Ocean, the military presence and settlements of the Portuguese in Goa and Bombay. Preparations of the trip The plan for working on the Cape Route to India was charted by King John II of Portugal as a cost-saving measure in the trade with Asia and also an attempt to monopolize the spice trade. Adding to the increasingly influential Portuguese maritime presence, John II craved for trade routes and for the expansion of the Kingdom of Portugal which had already been transformed into an Empire. However, the project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
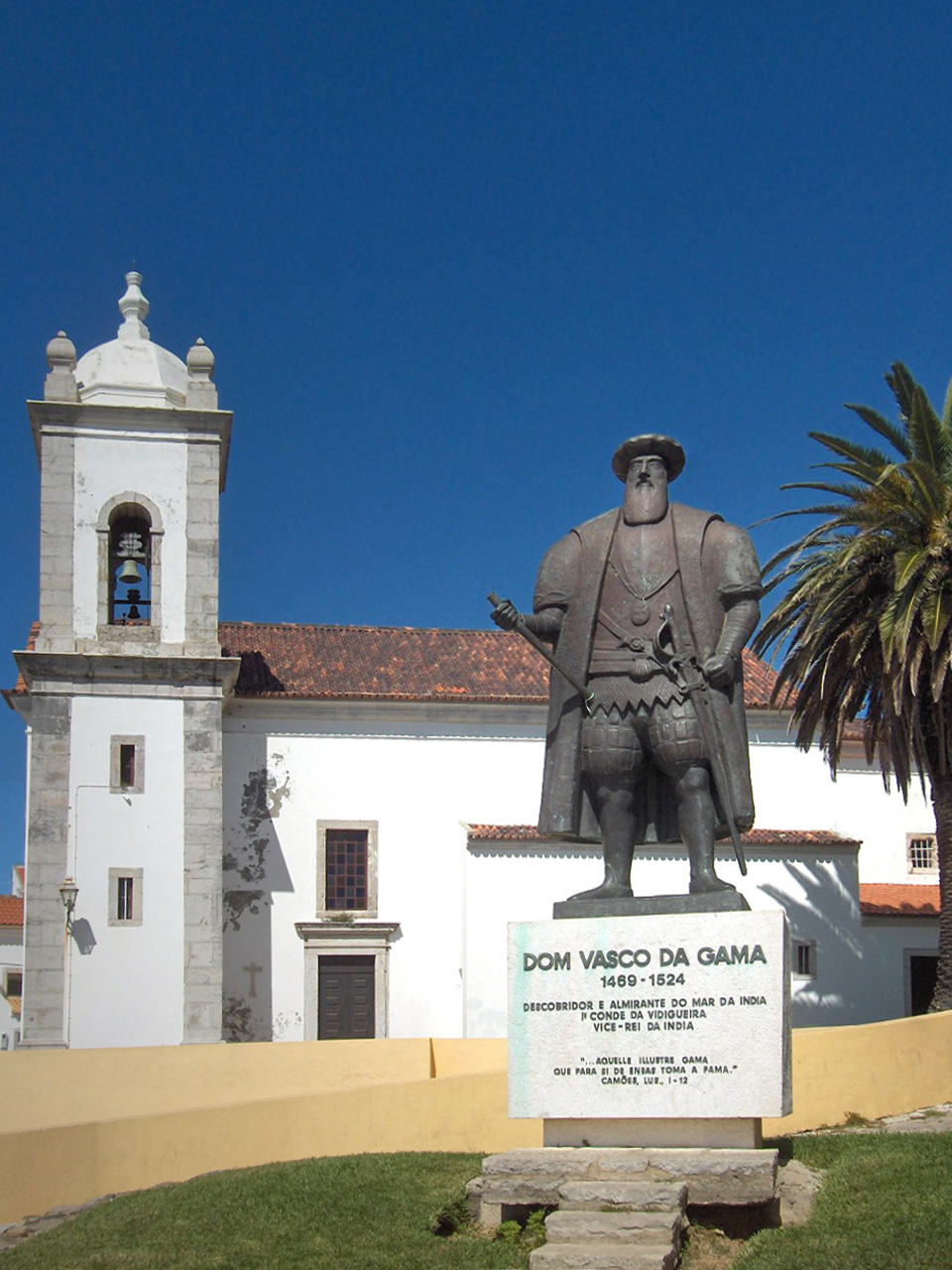
Vasco Da Gama
Vasco da Gama ( , ; – 24 December 1524), was a Portuguese explorer and nobleman who was the Portuguese discovery of the sea route to India, first European to reach India by sea. Da Gama's first voyage (1497–1499) was the first to link Europe and Asia using an Cape Route, ocean route that rounded the southern tip of Africa. This route allowed the Portuguese to avoid sailing across the highly disputed Mediterranean Sea and traversing the dangerous Arabian Peninsula, Arabian Peninsula. A milestone in Portuguese maritime exploration, this voyage marked the beginning of a sea-based phase of international trade and an age of global imperialism. The Portuguese later established a Portuguese Empire, long-lasting colonial empire along the route from Africa to Asia. The outward and return voyages constituted the longest known ocean voyages ever completed. Sailors had been trying to reach the Indies for decades, with thousands of lives and dozens of vessels lost in shipwrecks and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |