|
Kinetic Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. Types of friction include dry, fluid, lubricated, skin, and internal -- an incomplete list. The study of the processes involved is called tribology, and has a history of more than 2000 years. Friction can have dramatic consequences, as illustrated by the use of friction created by rubbing pieces of wood together to start a fire. Another important consequence of many types of friction can be wear, which may lead to performance degradation or damage to components. It is known that frictional energy losses account for about 20% of the total energy expenditure of the world. As briefly discussed later, there are many different contributors to the retarding force in friction, ranging from asperity deformation to the generation of charges and changes in local structure. When two bodies in contact move relative to each other, due to these various ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
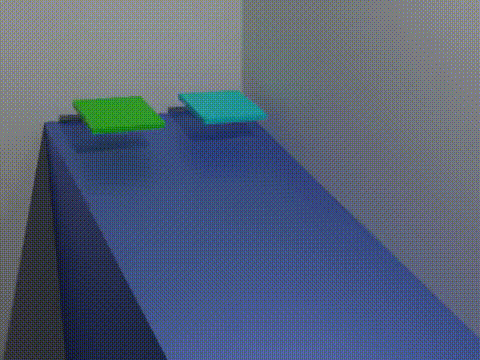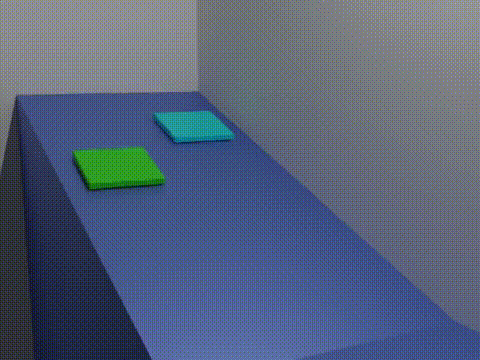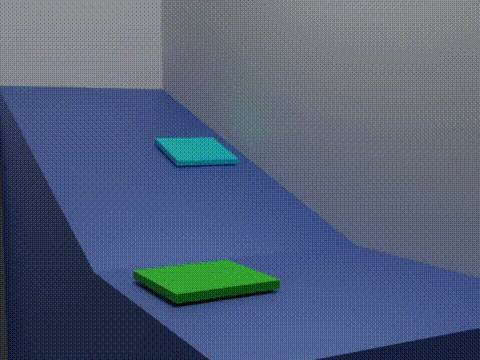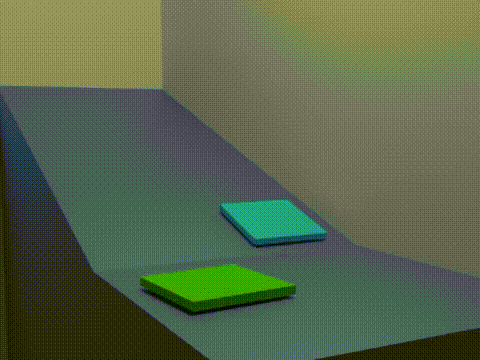
Friction Animation 2 Blocks
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding (motion), sliding against each other. Types of friction include dry, fluid, lubricated, skin, and internal -- an incomplete list. The study of the processes involved is called tribology, and has a history of more than 2000 years. Friction can have dramatic consequences, as illustrated by the use of friction created by Fire making#Friction, rubbing pieces of wood together to start a fire. Another important consequence of many types of friction can be wear, which may lead to performance degradation or damage to components. It is known that frictional energy losses account for about 20% of the total energy expenditure of the world. As briefly discussed later, there are many different contributors to the retarding force in friction, ranging from Asperity (materials science), asperity deformation to the generation of Triboelectric effect, charges and changes in Micros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asperities
In materials science, asperity, defined as "unevenness of surface, roughness, ruggedness" (from the Latin ''asper''—"rough"), has implications (for example) in physics and seismology. Smooth surfaces, even those polished to a mirror finish, are not truly smooth on a microscopic scale. They are rough, with sharp, rough, or rugged projections, termed "asperities". Surface asperities exist across multiple scales, often in a self-affine or fractal geometry. The fractal dimension of these structures has been correlated with the contact mechanics exhibited at an interface in terms of friction and contact stiffness. An understanding of the concept of asperities is required for any understanding of the field of Tribology, or the scientific study of friction, wear, and lubrication. Expanding on the linkage between asperities and seismology, asperities are critical in the understanding of geophysical faults via elastic deformation. These faults, such as the San Andreas fault line, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonhard Euler
Leonhard Euler ( ; ; ; 15 April 170718 September 1783) was a Swiss polymath who was active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, logician, geographer, and engineer. He founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made influential discoveries in many other branches of mathematics, such as analytic number theory, complex analysis, and infinitesimal calculus. He also introduced much of modern mathematical terminology and Mathematical notation, notation, including the notion of a mathematical function. He is known for his work in mechanics, fluid dynamics, optics, astronomy, and music theory. Euler has been called a "universal genius" who "was fully equipped with almost unlimited powers of imagination, intellectual gifts and extraordinary memory". He spent most of his adult life in Saint Petersburg, Russia, and in Berlin, then the capital of Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia. Euler is credited for popularizing the Greek letter \pi (lowercase Pi (letter), pi) to denote Pi, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German (, ) is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. It is the majority and Official language, official (or co-official) language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. It is also an official language of Luxembourg, German-speaking Community of Belgium, Belgium and the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. There are also notable German-speaking communities in other parts of Europe, including: Poland (Upper Silesia), the Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Denmark (South Jutland County, North Schleswig), Slovakia (Krahule), Germans of Romania, Romania, Hungary (Sopron), and France (European Collectivity of Alsace, Alsace). Overseas, sizeable communities of German-speakers are found in the Americas. German is one of the global language system, major languages of the world, with nearly 80 million native speakers and over 130 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Forest De Bélidor
Bernard Forest de Bélidor (1698, Catalonia, Spain – 8 September 1761, Paris, France) was a French engineer, significant to the development of the science of hydraulics and ballistics. He was the son of Jean Baptiste Foret de Belidor, an officer of dragoons, and his wife, Marie Héber but was orphaned at five months old and brought up by the family of his godfather, an artillery officer named de Fossiébourg. Bélidor enlisted in the army at a young age. After leaving the army, he developed an interest in science and engineering, and became professor at the school of artillery of La Fère in Aisne. For a while he worked on measuring the Circle, arc of the earth. In the years to come he published several works of great importance, on a wide range of subjects, including hydraulics, mathematics, and civil engineering, civil and military engineering. His most famous book is ''L'architecture hydraulique'' (published in four volumes from 1737 to 1753). Here, integral calculus is used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guillaume Amontons
Guillaume Amontons (31 August 1663 – 11 October 1705) was a French scientific instrument inventor and physicist. He was one of the pioneers in studying the problem of friction, which is the resistance to motion when bodies make contact. He is also known for his work on thermodynamics, the concept of absolute zero, and early engine design. Life Guillaume was born in Paris, France. His father was a lawyer from Normandy who had moved to the French capital. While still young, Guillaume lost his hearing and became mostly deaf. According to one biographer, Fontenelle, while studying perpetual motion, he became convinced of the importance of studying machines from a mathematical perspective. He never attended a university, but was able to study mathematics, the physical sciences, and celestial mechanics. He also spent time studying the skills of drawing, surveying, and architecture. He died in Paris, France. Work He was supported in his research career by the government, and was e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonardo Da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 1452 - 2 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested on his achievements as a painter, he has also become known for #Journals and notes, his notebooks, in which he made drawings and notes on a variety of subjects, including anatomy, astronomy, botany, cartography, painting, and palaeontology. Leonardo is widely regarded to have been a genius who epitomised the Renaissance humanism, Renaissance humanist ideal, and his List of works by Leonardo da Vinci, collective works comprise a contribution to later generations of artists matched only by that of his younger contemporary Michelangelo. Born out of wedlock to a successful notary and a lower-class woman in, or near, Vinci, Tuscany, Vinci, he was educated in Florence by the Italian painter and sculptor Andrea del Verrocchio. He began his career ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Themistius
Themistius ( ; 317 – c. 388 AD), nicknamed Euphrades (, "''eloquent''"), was a statesman, rhetorician and philosopher. He flourished in the reigns of Constantius II, Julian, Jovian, Valens, Gratian and Theodosius I, and he enjoyed the favour of all those emperors, notwithstanding their many differences and the fact that he himself was not a Christian. He was admitted to the senate by Constantius in 355, and he was prefect of Constantinople in 384 on the nomination of Theodosius. Of his many works, thirty-three orations of his have come down to us, as well as various commentaries and epitomes of the works of Aristotle. Early life Themistius was born in Paphlagonia and taught at the Colchian Academy in Phasis. Several of his orations mention his father Eugenius, a distinguished philosopher from whom he received supplemental training. Themistius devoted himself chiefly to Aristotle, though he also studied Pythagoreanism and Platonism. His early commentaries on Aristotle w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic (''Natural History''), a comprehensive thirty-seven-volume work covering a vast array of topics on human knowledge and the natural world, which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is Lost literary work, no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus, and Suetonius. Tacitus may have used ''Bella Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitruvius
Vitruvius ( ; ; –70 BC – after ) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work titled . As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissance as the first book on architectural theory, as well as a major source on the canon of classical architecture. It is not clear to what extent his contemporaries regarded his book as original or important. He states that all buildings should have three attributes: , , and ("strength", "utility", and "beauty"), principles reflected in much Ancient Roman architecture. His discussion of perfect proportion in architecture and the human body led to the famous Renaissance drawing of the ''Vitruvian Man'' by Leonardo da Vinci. Little is known about Vitruvius' life, but by his own descriptionDe Arch. Book 1, preface. section 2. he served as an artilleryman, the third class of arms in the Roman military offices. He probably served as a senior of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, and the arts. As the founder of the Peripatetic school of philosophy in the Lyceum (classical), Lyceum in Athens, he began the wider Aristotelianism, Aristotelian tradition that followed, which set the groundwork for the development of modern science. Little is known about Aristotle's life. He was born in the city of Stagira (ancient city), Stagira in northern Greece during the Classical Greece, Classical period. His father, Nicomachus (father of Aristotle), Nicomachus, died when Aristotle was a child, and he was brought up by a guardian. At around eighteen years old, he joined Plato's Platonic Academy, Academy in Athens and remained there until the age of thirty seven (). Shortly after Plato died, Aristotle left Athens and, at the request ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deformation (mechanics)
In physics and continuum mechanics, deformation is the change in the shape (geometry), shape or size of an object. It has dimension (physics), dimension of length with SI unit of metre (m). It is quantified as the residual displacement (geometry), displacement of particles in a non-rigid body, from an configuration to a configuration, excluding the body's average translation (physics), translation and rotation (its rigid transformation). A ''configuration'' is a set containing the position (geometry), positions of all particles of the body. A deformation can occur because of structural load, external loads, intrinsic activity (e.g. muscle contraction), body forces (such as gravity or electromagnetic forces), or changes in temperature, moisture content, or chemical reactions, etc. In a continuous body, a ''deformation field'' results from a Stress (physics), stress field due to applied forces or because of some changes in the conditions of the body. The relation between stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |