|
Keogram Explainer
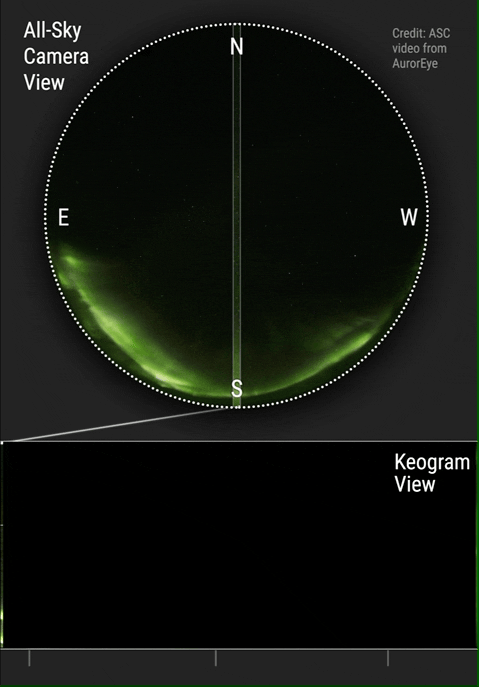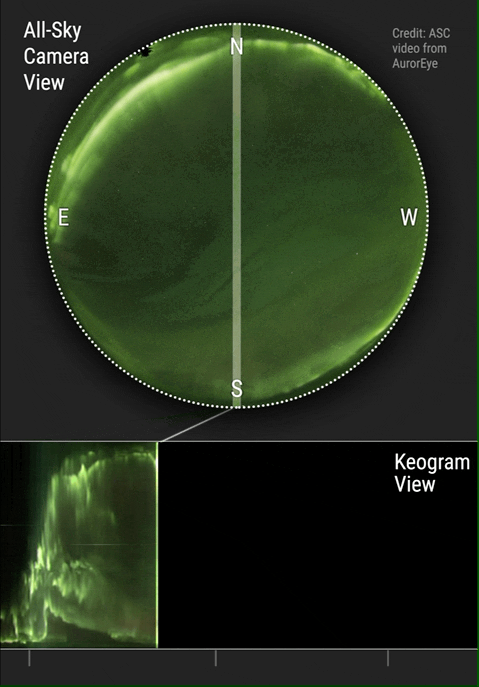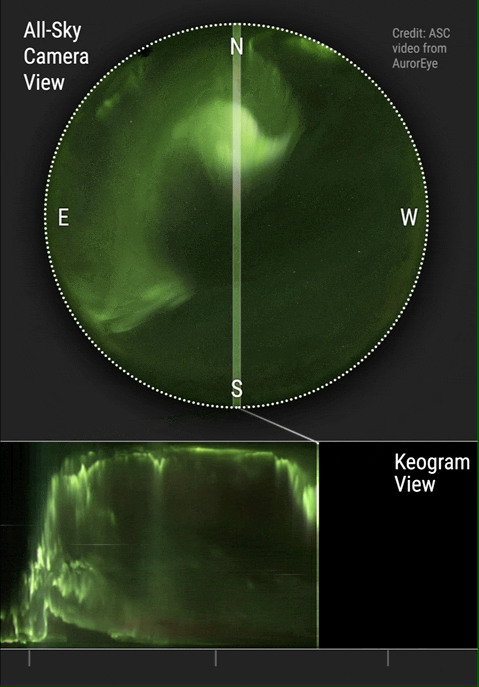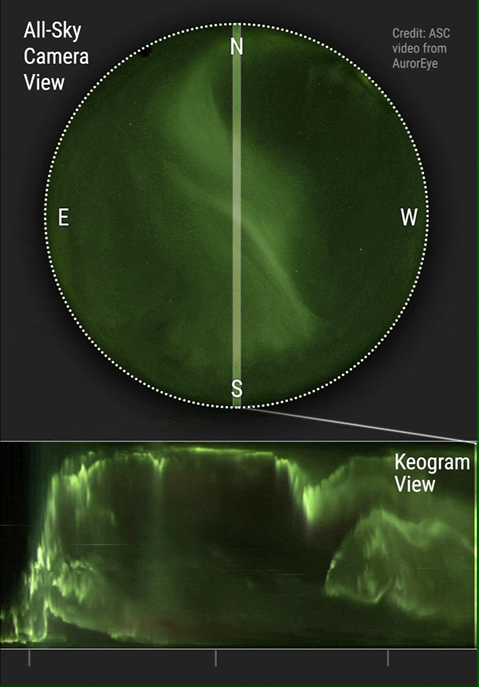
A keogram ("keo" from "Keoeeit" – Inuit word for " Aurora Borealis") is a way of displaying the intensity of an auroral display, taken from a narrow part of a round screen recorded by a camera, more specifically and ideally in practice a " whole sky camera". These images from the narrow band, which usually face up in the north-south orientation in the Northern Hemisphere and the south-north orientation in the Southern Hemisphere, are collected and form a time-dependent graph of the aurora from that part of the sky. This allows one to easily realize the general activity of the display that night, whether it had been interrupted by weather conditions or not, and allows the determination of the regions in which the aurora was seen in terms of latitude and longitude of the area. The use of keograms started in the 1970s by Eather et al. to allow a more practical and efficient way of determining the activity of the aurora throughout the recorded night and provide a view of the detailed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inuit Languages
The Inuit languages are a closely related group of Indigenous languages of the Americas, indigenous American languages traditionally spoken across the North American Arctic and the adjacent subarctic regions as far south as Labrador. The Inuit languages are one of the two branches of the Eskimoan languages, Eskimoan language family, the other being the Yupik languages, which are spoken in Alaska and the Russian Far East. Most Inuit people live in one of three countries: Greenland, a self-governing territory within the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark; Canada, specifically in Nunavut, the Inuvialuit Settlement Region of the Northwest Territories, the Nunavik region of Quebec, and the Nunatsiavut and NunatuKavut regions of Labrador; and the United States, specifically in northern and western Alaska. The total population of Inuit speaking their traditional languages is difficult to assess with precision, since most counts rely on self-reported census data that may not accurately re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurora
An aurora ( aurorae or auroras), also commonly known as the northern lights (aurora borealis) or southern lights (aurora australis), is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly observed in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). Auroras display dynamic patterns of radiant lights that appear as curtains, rays, spirals or dynamic flickers covering the entire sky. Auroras are the result of disturbances in the Earth's magnetosphere caused by enhanced speeds of solar wind from coronal holes and coronal mass ejections. These disturbances alter the trajectories of charged particles in the magnetospheric plasma. These particles, mainly electrons and protons, precipitate into the upper atmosphere ( thermosphere/exosphere). The resulting ionization and excitation of atmospheric constituents emit light of varying color and complexity. The form of the aurora, occurring within bands around both polar regions, is also dependent on the amount of acceler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whole Sky Camera
A whole sky camera is a specialized camera used in meteorology and astronomy for capturing a photograph of the entire sky. Another application is that of hemispherical photography to study plant canopy geometry and to calculate near-ground solar radiation. Development Whole sky cameras typically use a fisheye lens that takes in an extremely wide, hemispherical image. Such lenses were originally developed for use in meteorology. However, alternative techniques are based on the photography of a mirror-like hemisphere which are more common. One of the first reported whole sky cameras was based on a series of pictures with lenses inclined to the horizon at an altitude of 45 degrees. With a lens that covers an angular field of 90 degrees, such camera revolves about a vertical axis. Meteorological applications In meteorological applications, whole sky cameras are used to study cloud cover, the current level of UV radiation, fractional cloud coverage, sky polarization, the computation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visible Spectrum
The visible spectrum is the spectral band, band of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visual perception, visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called ''visible light'' (or simply light). The optical spectrum is sometimes considered to be the same as the visible spectrum, but some authors define the term more broadly, to include the ultraviolet and infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum as well, known collectively as ''optical radiation''. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 380 to about 750 nanometers. In terms of frequency, this corresponds to a band in the vicinity of 400–790 Terahertz (unit), terahertz. These boundaries are not sharply defined and may vary per individual. Under optimal conditions, these limits of human perception can extend to 310 nm (ultraviolet) and 1100 nm (near infrared). The spectrum does not contain all the colors that the human visual system can distinguish. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equatorial Plasma Bubble
Equatorial plasma bubbles are an ionospheric phenomenon near the Earth's geomagnetic equator at night time. They affect radio waves by causing varying delays. They degrade the performance of GPS. Different times of the year and locations have different frequencies of occurrence. In Northern Australia The unofficial geographic term Northern Australia includes those parts of Queensland and Western Australia north of latitude 26th parallel south, 26° and all of the Northern Territory. Those local government areas of Western Australia and Q ..., the most common times are February to April and August to October, when a plasma bubble is expected every night. Plasma bubbles have dimensions around 100 km. Plasma bubbles form after dark when the sun stops ionising the ionosphere. The ions recombine, forming a lower-density layer. This layer can rise through the more ionized layers above via convection, which makes a plasma bubble. The bubbles are turbulent with irregular edges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Night Sky
The night sky is the nighttime appearance of celestial objects like stars, planets, and the Moon, which are visible in a clear sky between sunset and sunrise, when the Sun is below the horizon. Natural light sources in a night sky include moonlight, starlight, and airglow, depending on location and timing. Aurorae light up the skies above the polar circles. Occasionally, a large coronal mass ejection from the Sun or simply high levels of solar wind may extend the phenomenon toward the Equator. The night sky and studies of it have a historical place in both ancient and modern cultures. In the past, for instance, farmers have used the status of the night sky as a calendar to determine when to plant crops. Many cultures have drawn constellations between stars in the sky, using them in association with legends and mythology about their deities. The history of astrology has generally been based on the belief that relationships between heavenly bodies influence or explain events on Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteorological Instrumentation And Equipment
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agriculture, construction, weather warnings and disaster management. Along with climatology, atmospheric physics and atmospheric chemistry, meteorology forms the broader field of the atmospheric sciences. The interactions between Earth's atmosphere and its oceans (notably El Niño and La Niña) are studied in the interdisciplinary field of hydrometeorology. Other interdisciplinary areas include biometeorology, space weather and planetary meteorology. Marine weather forecasting relates meteorology to maritime and coastal safety, based on atmospheric interactions with large bodies of water. Meteorologists study meteorological phenomena driven by solar radiation, Earth's rotation, ocean currents and other factors. These include everyday weather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |