|
Kennet, Clackmannanshire
Kennet is a small former coal-mining village in Clackmannanshire, Scotland. It is located south-east of Clackmannan, by the Kincardine railway line. The village is a conservation area Protected areas or conservation areas are locations which receive protection because of their recognized natural, ecological or cultural values. There are several kinds of protected areas, which vary by level of protection depending on the ena ..., designated by Clackmannanshire Council. Kennet House, the seat of the Bruces of Kennet, was located to the west of the village (). The house was built or rebuilt in the 1790s for the judge Robert Bruce, Lord Kennet. His descendant, the politician and banker Alexander Bruce, established a claim to the forfeited title of Lord Balfour of Burleigh in 1868. The house was demolished in 1967. Between 1905 and 1961 coal was mined at the Brucefield Colliery, located just to the north of Kennet (). In 1948, 75,000 tons of coal were extracted. A brick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochil And South Perthshire (UK Parliament Constituency)
Ochil and South Perthshire is a county constituency of the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It elects one Member of Parliament (MP) by the first-past-the-post voting, first-past-the-post system of election. The constituency was created for the 2005 United Kingdom general election, 2005 general election as a result of the Fifth Review of the Boundary Commission for Scotland. It has been represented since 2019 United Kingdom general election, 2019 by John Nicolson of the Scottish National Party (SNP). Boundaries The constituency is composed of the Clackmannanshire council area (all five wards), and the Perth and Kinross council wards of Strathtay (ward), Strathtay, Strathearn (ward), Strathearn, Strathallan (ward), Strathallan, Almond and Earn (ward), Almond and Earn, and Kinross-shire (ward), Kinross-shire. The constituency was created to cover Clackmannanshire and a southern portion of Perth and Kinross; the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clackmannanshire
Clackmannanshire (; sco, Clackmannanshire; gd, Siorrachd Chlach Mhannainn) is a historic county, council area, registration county and Lieutenancy area in Scotland, bordering the council areas of Stirling, Fife, and Perth & Kinross and the historic counties of Perthshire, Stirlingshire and Fife. The name consists of elements from three languages. The first element is from gd, Clach meaning "Stone". Mannan is a derivative of the Brythonic name of the Manaw, the Iron Age tribe who inhabited the area. The final element is the English word shire. As Britain's smallest historic county, it is often nicknamed "The Wee County". When written, Clackmannanshire is commonly abbreviated to Clacks. History Clackmannan, the old county town, is named after the ancient stone associated with the pre-Christian deity Manau or Mannan. The stone now rests on a larger stone beside the Tollbooth (built late 16th century) and Mercat Cross at the top of Main street, Clackmannan. Clackmannanshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clackmannanshire And Dunblane (Scottish Parliament Constituency)
Clackmannanshire and Dunblane (Gaelic: ''Siorrachd Chlach Mhanann agus Dùn Bhlàthain'') constituency of the Scottish Parliament ( Holyrood) covering part of the Stirling council area and the entirety of Clackmannanshire. It elects one Member of the Scottish Parliament (MSP) by the plurality (first past the post) method of election. It is also one of nine constituencies in the Mid Scotland and Fife electoral region, which elects seven additional members, in addition to the nine constituency MSPs, to produce a form of proportional representation for the region as a whole. Created in 2011, the constituency covers much of the area previously in the abolished Ochil. The seat has been held by Keith Brown of the Scottish National Party since its creation; Brown was previously the MSP for the preceding constituency of Ochil. Electoral region The other eight constituencies of the Mid Scotland and Fife region are Cowdenbeath, Dunfermline, Kirkcaldy, Mid Fife and Glenrothes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clackmannan, Clackmannanshire
Clackmannan ( ; gd, Clach Mhanainn, perhaps meaning "Stone of Manau"), is a small town and civil parish set in the Central Lowlands of Scotland. Situated within the Forth Valley, Clackmannan is south-east of Alloa and south of Tillicoultry. The town is within the county of Clackmannanshire, of which it was formerly the county town, until Alloa overtook it in size and importance. History and toponymy Name and toponymy The name ''Clackmannan'' may be of Brittonic origin. The first element is probably ''*clog'', meaning "rock, crag, cliff" (c.f. Welsh ''clog''), and the second is the personal name ''Manau'', from the root ''man-'' meaning "projecting''. The name of the town has been said to allude to the Stone of Manau or Stone of Mannan, a pagan monument that can be seen in the town square beside the Tolbooth or Tollbooth Tower, which dates from 1592. History The early growth of the town was due in large part to the port which lay on the banks of the tidal stretch of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
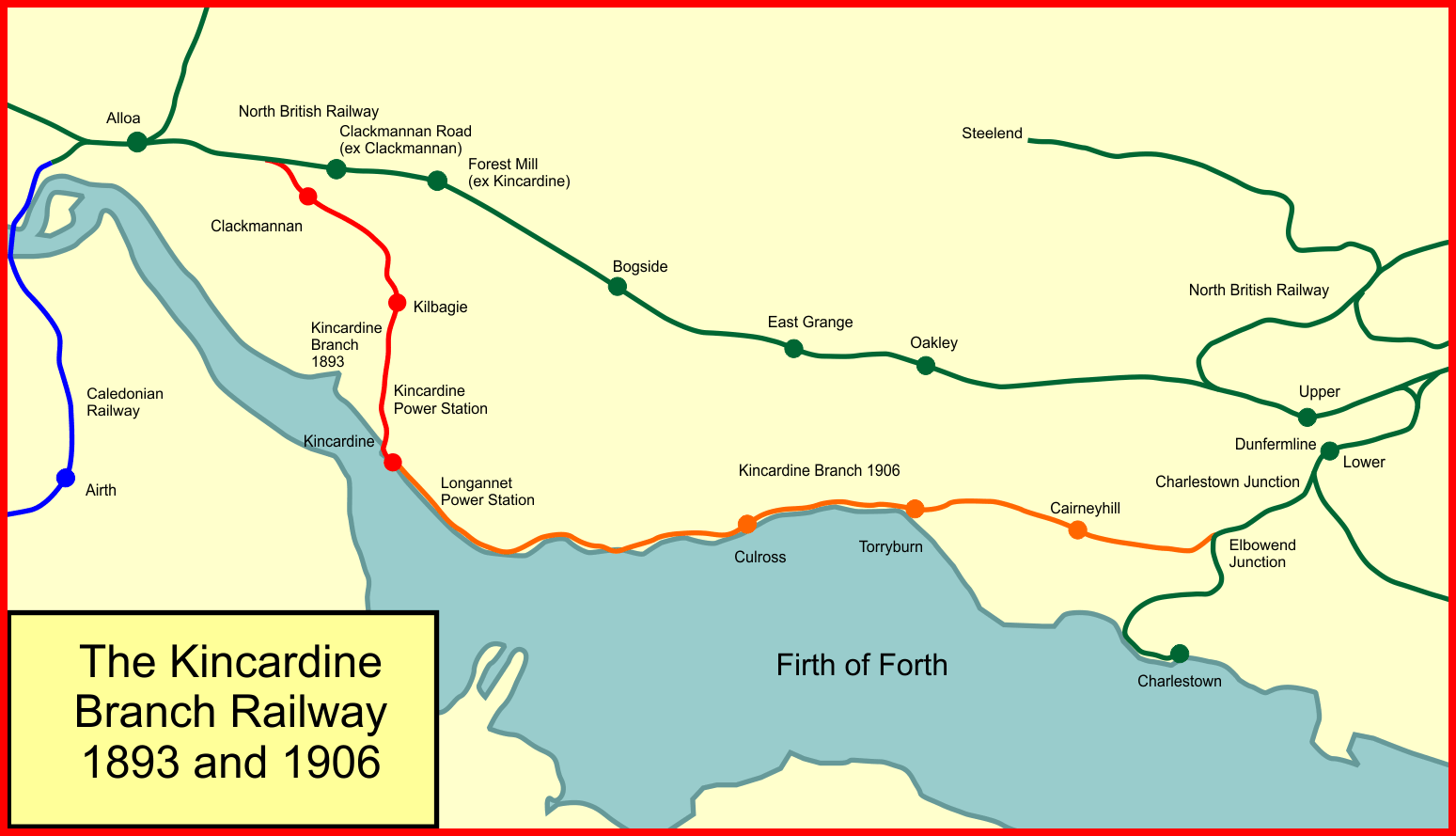
Kincardine Line
The Kincardine Line is a railway in Clackmannanshire and Fife, Scotland. It was originally built to serve settlements along the north shore of the Firth of Forth, between Alloa and Dunfermline. It was opened in two stages by the North British Railway: from Alloa to Kincardine in 1893, and the eastern section in 1903. Passenger traffic was disappointing, and closed in 1930. Goods traffic was poorly used as well, that is until in 1962, when a large coal-fired power station opened on the line. A second followed, and the entire line was re-opened in stages to bring in coal for the power station requirements. The power stations were decommissioned in 2016, bringing heavy mineral traffic to an end. There is a possibility of re-opening to passenger trains on the route. First railways During the promotion of railways in 1845 that resulted in the major expansion of the Scottish railway network, the Scottish Central Railway was authorised to build from Castlecary, on the Edinburgh and G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Bruce, Lord Kennet
Robert Bruce of Kennet, Lord Kennet FRSE (24 December 1718 – 8 April 1785) was a Scottish advocate, legal scholar and judge. Life Bruce was born at Kennet House in Clackmannanshire on 24 December 1718, the son of Mary Balfour, daughter of Robert Balfour, 4th Lord Burleigh and Alexander Bruce of Kennet (died 1747). He was admitted to the Faculty of Advocates in January 1743. He served as Professor of Law of Nature and Nations at the University of Edinburgh (1758–64) and was appointed Sheriff-Depute of Stirling & Clackmannan in 1760. He was elected a Senator of the College of Justice, as Lord Kennet, in 1764 and Lord of Justiciary in 1769. In 1783 he was a founder member of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. His Edinburgh address at this time was at George Square. He died at Kennet House on 8 April 1785. Family He married Helen Abercromby in 1745. Bruce was the uncle of James Abercromby, 1st Baron Dunfermline. His brothers-in-law included James Stuart-Mackenzie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Bruce, 6th Lord Balfour Of Burleigh
Alexander Hugh Bruce, 6th Lord Balfour of Burleigh, (13 January 1849 – 6 July 1921) was a Scottish Unionist politician, banker and statesman, who took a leading part in the affairs of the Church of Scotland. He was Secretary for Scotland between 1895 and 1903. Background The son of Robert Bruce, at one time Tory Member of Parliament for Clackmannan, he was born in Kennet in that county and educated at Loretto, Eton and Oriel College, Oxford. In 1868, four years after his death, Robert Bruce's claim to the peerage was recognised by the House of Lords, and so his son became sixth Lord Balfour of Burleigh on the reversal of the title's attainder by Act of Parliament in 1869. Political career In 1876 Balfour was elected a Scottish representative peer. Six years later, he was made an Education Commissioner for Scotland, and in 1887 he entered Lord Salisbury's administration as a Lord-in-waiting. The following year, Lord Balfour became Parliamentary Secretary to the Board of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Balfour Of Burleigh
Lord Balfour of Burleigh, in the County of Kinross, is a title in the Peerage of Scotland. It was created in 1607 for Sir Michael Balfour. He was succeeded by his daughter, Margaret, his only child. She married Robert Arnot, who assumed the surname of Balfour and sat as Lord Balfour of Burleigh in the Scottish Parliament in right of his wife. Their son, the third Lord, fought with the Covenanters at the Battle of Drumclog. His grandson, the fifth Lord, was tried and convicted of the murder of schoolmaster Henry Stenhouse at Inverkeithing in 1709. He was sentenced to death in 1710 but escaped to freedom by dressing in his sister's clothes. He was primarily known as Master of Burleigh, the title for the heir to the peerage, as he never took his seat in Parliament when his father died in 1713. He took part in the Jacobite rebellion in 1715 and was attainted for his role. He died childless in 1757. The lordship had been created by charter, a copy of which exists only in the family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canmore (database)
Canmore is an online database of information on over 320,000 archaeological sites, monuments, and buildings in Scotland. It was begun by the Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland The Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland (RCAHMS) was an executive non-departmental public body of the Scottish Government that was "sponsored" inanced and with oversightthrough Historic Scotland, an executive .... Historic Environment Scotland has maintained it since 2015. The Canmore database is part of the National Record of the Historic Environment (or NRHE), formerly the National Monuments Record of Scotland (or NMRS) and contains around 1.3 million catalogue entries. It includes marine monuments and designated official wreck sites (those that fall under the Protection of Wrecks Act), such as the wreck of . References External links * Archaeology of Scotland Architecture in Scotland Canmore Archives in Scotland Data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Commission On The Ancient And Historical Monuments Of Scotland
The Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland (RCAHMS) was an executive non-departmental public body of the Scottish Government that was "sponsored" inanced and with oversightthrough Historic Scotland, an executive agency of the Scottish Government. As one of the country's National Collections, it was responsible for recording, interpreting and collecting information about the built and historic environment. This information, which relates to buildings, sites, and ancient monuments of archaeological, architectural and historical interest (including maritime sites and underwater constructions), as well as historical aspects of the landscape, was then made available to the public, mainly at no cost. It was established (shortly ahead of parallel commissions for Wales and England) by a Royal Warrant of 1908, which was revised in 1992. The RCAHMS merged with government agency Historic Scotland to form Historic Environment Scotland, a new executive no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as stratum, rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. Coal is formed when dead plant matter decays into peat and is converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years. Vast deposits of coal originate in former wetlands called coal forests that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian (geology), Pennsylvanian) and Permian times. Many significant coal deposits are younger than this and originate from the Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Coal is used primarily as a fuel. While coal has been known and used for thousands of years, its usage was limited until the Industrial Revolution. With the invention of the steam engine, coal consumption increased. In 2020, coal supplied about a quarter of the world's primary energ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |