|
Katō Sadakichi
Baron was an admiral in the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War I. His brother, Katō Yasuhisa, was a general in the Imperial Japanese Army, and his adoptive son was the biological son of Admiral Dewa Shigetō. Biography Katō was born in Tokyo, as the third son of Katō Yasukichi, a ''hatamoto'' retainer of the Tokugawa shogunate. He attended the Numazu Military Academy, and in October 1883 graduated at the top of his class from the 10th class of the Imperial Japanese Naval Academy. One of his classmates was Yamashita Gentarō. He served as a torpedo officer on the ''Jingei'', and . With the opening of the Sasebo Naval District, he was appointed secretary to Admiral Akamatsu Noriyoshi. From July 1891 to March 1893, Katō served as chief weapons officer on the cruiser . He was then sent to Germany as part of the entourage of Prince Fushimi Hiroyasu. He remained with the prince in Germany through the duration of the First Sino-Japanese War. After his return to Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo
Tokyo, officially the Tokyo Metropolis, is the capital of Japan, capital and List of cities in Japan, most populous city in Japan. With a population of over 14 million in the city proper in 2023, it is List of largest cities, one of the most populous urban areas in the world. The Greater Tokyo Area, which includes Tokyo and parts of six neighboring Prefectures of Japan, prefectures, is the most populous metropolitan area in the world, with 41 million residents . Lying at the head of Tokyo Bay, Tokyo is part of the Kantō region, on the central coast of Honshu, Japan's largest island. It is Japan's economic center and the seat of the Government of Japan, Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan. The Tokyo Metropolitan Government administers Tokyo's central Special wards of Tokyo, 23 special wards, which formerly made up Tokyo City; various commuter towns and suburbs in Western Tokyo, its western area; and two outlying island chains, the Tokyo Islands. Although most of the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokugawa Shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars of the Sengoku period following the collapse of the Ashikaga shogunate. Ieyasu became the ''shōgun,'' and the Tokugawa clan governed Japan from Edo Castle in the eastern city of Edo (Tokyo), Edo (Tokyo) along with the ''daimyō'' lords of the ''samurai'' class. The Tokugawa shogunate organized Japanese society under the strict Edo society, Tokugawa class system and banned most foreigners under the isolationist policies of ''Sakoku'' to promote political stability. The Tokugawa shoguns governed Japan in a feudal system, with each ''daimyō'' administering a ''Han system, han'' (feudal domain), although the country was still nominally organized as provinces of Japan, imperial provinces. Under the Tokugawa shogunate, Japan experienced rapid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tsushima
The Battle of Tsushima (, ''Tsusimskoye srazheniye''), also known in Japan as the , was the final naval battle of the Russo-Japanese War, fought on 27–28 May 1905 in the Tsushima Strait. A devastating defeat for the Imperial Russian Navy, the battle was the only Decisive victory, decisive engagement ever fought between modern steel battleship fleets and the first in which wireless telegraphy (radio) played a critically important role. The battle was described by contemporary Sir George Sydenham Clarke, Sir George Clarke as "by far the greatest and the most important naval event since Battle of Trafalgar, Trafalgar". The battle involved the Japanese Combined Fleet under Admiral Tōgō Heihachirō and the Russian Second Pacific Squadron under Admiral Zinovy Rozhestvensky, which had sailed over seven months and from the Baltic Sea. The Russians hoped to reach Vladivostok and establish naval control of the Far East in order to relieve the Imperial Russian Army in Manchuria. The R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itō Sukeyuki
Marshal-Admiral Count (20 May 1843 – 16 January 1914) was a Japanese career officer and admiral in the Imperial Japanese Navy in Meiji-period Japan. Biography Born in what is now part of Kagoshima City as the son of a ''samurai'' of the Satsuma Domain, Itō studied naval engineering and gunnery at the Kobe Naval Training Center together with Sakamoto Ryōma and Mutsu Munemitsu. He participated in the Anglo-Satsuma War as a member of the Satsuma domain's navy. Before the Boshin War, Itoh had already relocated to Edo and had placed his naval skills at the service of the forces striving to overthrow the Tokugawa Shogunate. He escaped from the burning of the Satsuma Domain residence in Edo and subsequently fought in many of the naval engagements of the Boshin War. After the Meiji Restoration, Itō was commissioned as a lieutenant and served on the corvette '' Nisshin '' in the fledgling Imperial Japanese Navy, commanding the ''Nisshin'' from 1877. Promoted to captain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Japanese Navy General Staff
The was the highest organ within the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). In charge of planning and operations, it was headed by an Admiral headquartered in Tokyo. History Created in 1893, the Navy General Staff took over operational (as opposed to administrative) authority over the Imperial Japanese Navy from the Navy Ministry. It was responsible for the planning and execution of national defense strategy. Through the Imperial General Headquarters it reported directly to the Emperor, not to the Prime Minister, National Diet or even the Navy Ministry. It was always headed by an admiral on active duty, and was based in Tokyo. "The ministry was responsible for the naval budget, ship construction, weapons procurement, personnel, relations with the Diet and the cabinet and broad matters of naval policy. The General Staff directed the operations of the fleet and the preparation of war plans".Spector After the Washington Naval Conference of 1921–22, where Japan agreed to keep the siz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executive Officer
An executive officer is a person who is principally responsible for leading all or part of an organization, although the exact nature of the role varies depending on the organization. In many militaries and police forces, an executive officer (XO) is the second-in-command, reporting to the commanding officer (CO). The XO is typically responsible for the management of day-to-day activities, freeing the commander to concentrate on strategy and planning the unit's next move. Administrative law While there is no clear line between principal executive officers and inferior executive officers, principal officers are high-level officials in the executive branch of U.S. government such as department heads of independent agencies. In ''Humphrey's Executor v. United States'', 295 U.S. 602 (1935), the Court distinguished between executive officers and quasi-legislative or quasi-judicial officers by stating that the former serve at the pleasure of the President of the United States, presid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gensui (Imperial Japanese Navy)
, formal rank designations: was the highest rank in the Imperial Japanese Navy. The term was used for both the navy and the Imperial Japanese Army, and was a largely honorific title awarded for extremely meritorious service to the Emperor. In the Meiji period, the title was awarded to five generals and three admirals. In the Taishō period it was awarded to six generals and six admirals, and in the Shōwa period it was awarded to six generals and four admirals. It was similar to Admiral of the Fleet in the Royal Navy and Fleet admiral in the United States Navy. List of ''Kaigun-gensui'' Note that several were promoted the same year they died; these were posthumous promotions. See also * ''Gensui'' (Imperial Japanese Army) *Imperial Japanese Navy *Grand admiral Grand admiral is a historic naval rank, the highest rank in the several European navies that used it. It is best known for its use in Germany as . A comparable rank in modern navies is that of admiral of the fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saigō Tsugumichi
Saigō may refer to: Places * Saigō, Shimane * Saigō, Miyazaki People * Saigō-no-Tsubone (Lady Saigō) (1552–1589), consort of Tokugawa Ieyasu, the samurai lord and shōgun * Saigō Takamori * Saigō Tanomo was a Japanese samurai of the late Edo period. Chief senior councilor (''hittōgarō'' 筆頭家老) of the Aizu clan, he achieved fame due to his distinguished action in the Boshin War. He adopted the name Hoshina Chikanori (保科 近野里) ... * Teruhiko Saigō * Saigō Tsugumichi {{DEFAULTSORT:Saigo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
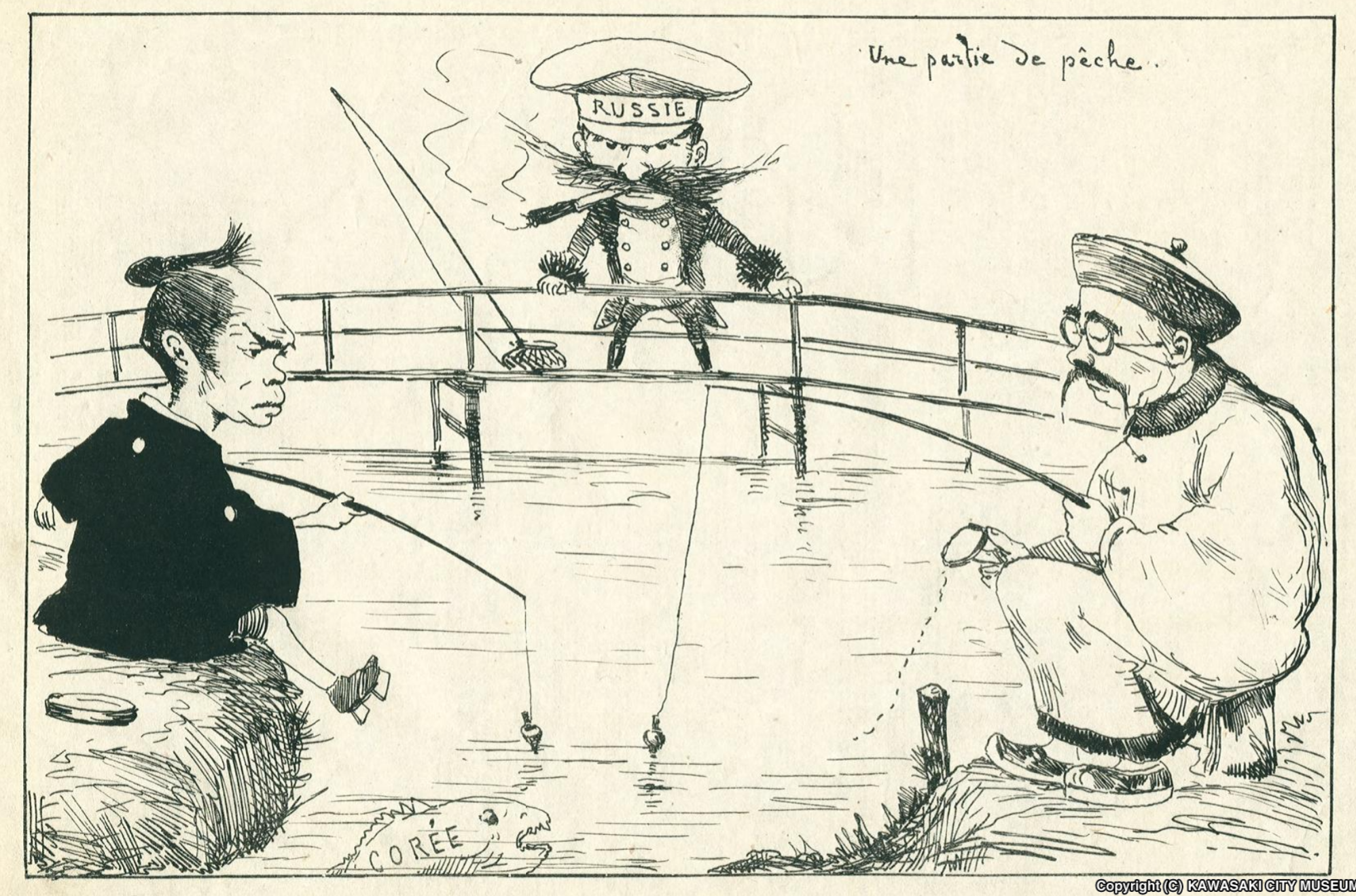
First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 189417 April 1895), or the First China–Japan War, was a conflict between the Qing dynasty of China and the Empire of Japan primarily over influence in Joseon, Korea. In Chinese it is commonly known as the Jiawu War. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the ports of Lüshunkou (Port Arthur) and Weihaiwei, the Qing government sued for peace in February 1895 and signed the Unequal treaties, unequal Treaty of Shimonoseki two months later, ending the war. In the late 19th century, Korea remained one of China's tributary states, while Japan viewed it as a target of imperial expansion. In June 1894, the Qing government, at the request of the Korean emperor Gojong of Korea, Gojong, sent 2,800 troops to aid in suppressing the Donghak Peasant Revolution. The Japanese considered this a violation of the 1885 Convention of Tientsin, and sent an expeditionary force of 8,000 troops, which la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Fushimi Hiroyasu
was a scion of the Japanese imperial family and a career naval officer who served as chief of staff of the Imperial Japanese Navy from 1932 to 1941. Early life Prince Hiroyasu was born in Tokyo as Prince Narukata, the eldest son of Prince Fushimi Sadanaru (1858–1923) by one of his concubines. He was the twenty-third head of the Fushimi-no-miya, one of the four ''shinnōke'' cadet branches of the imperial family entitled to succeed to the throne in default of a direct heir. Prince Fushimi was a second cousin to both Emperor Shōwa (Hirohito) and Empress Kōjun, and nephew of Prince Kan'in Kotohito He succeeded to title Kachō-no-miya on April 23, 1883, upon which he changed his name from "Narukata" to "Hiroyasu," but returned to the house of Fushimi-no-miya on January 16, 1904. Marriage & family On January 9, 1896, Prince Hiroyasu married Tokugawa Tsuneko (1882–1939), the ninth daughter of Prince Tokugawa Yoshinobu, Japan's last ''shōgun'', with whom he had six childr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasebo Naval District
was the third of five main administrative districts of the pre-war Imperial Japanese Navy. Its territory included the western and southern coastline of Kyūshū, the Ryukyu Islands, Taiwan and Korea, as well as patrols in the East China Sea and the Pacific Sasebo also contained the Sasebo Naval Arsenal, specializing mostly in destroyers and smaller warships; and its anchorage was one of the largest in Japan. The District encompassed anchorages at Imari and Hirado ports as well as the designated third echelon naval ports of Takeshiki ( Tsushima), Kagoshima, Kuji ( Amami-Ōshima), and Wakamatsu ( Gotō Islands) History The location of Sasebo facing China and Korea, and near the foreign treaty port of Nagasaki was recognized of strategic importance by the leaders of the early Meiji government and early Imperial Japanese Navy. In 1883, the then Lieutenant Commander Tōgō Heihachirō nominated what was a tiny fishing village as the ideal location for a naval base. With the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |