|
Kara, Togo
Kara is a city in northern Togo, situated in Kara Region, 413 km north of the capital Lomé. Kara is the capital of the Kara Region and, according to the 2010 census, had a population of 94,878. The Kara River flows through the city and is its main resource of water. The city developed from the 1970s onwards from the village originally known as '' Lama-Kara''. Its growth was largely due to the influence of the previous Togolese head of state Gnassingbé Eyadéma; he was born in the nearby village of Pya and understood Kara's strategic position at a crossroads of two trade routes. History In 1902, a bridge over the Kara River was built by the Germans, which marks the beginning of the city. Under the presidency of Gnassingbé Eyadéma, in the 1970s, the city developed particularly because of its role in holding political events. Geography The city lies at the southern tip of the southern Kabiye mountain range. Kara is at an altitude of about 400 meters. The Kara River r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Togo
The national flag of Togo consists of five horizontal stripes, alternating between green and yellow, with a red square bearing a five-pointed white star in the Canton (flag), canton. It is one of many Flags of Africa, African flags that use the pan-African colours of green, yellow, and red. Togolese artist Paul Ahyi designed the flag in 1960, just before its adoption on 27 April of that year, coinciding with Togo's proclamation of independence. When Togo was an autonomous republic within the French Union (the successor to the French colonial empire), it flew a green flag with the Flag of France, French tricolour in the canton and two five-pointed yellow stars, one in the lower hoist and one in the upper fly. Design Togolese artist Paul Ahyi (1930–2010) was the designer of the flag. Ahyi studied art in France and graduated from the Beaux-Arts de Paris, École nationale supérieure des beaux-arts in Paris in 1959 before returning to Togo. The following year, he designed the fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
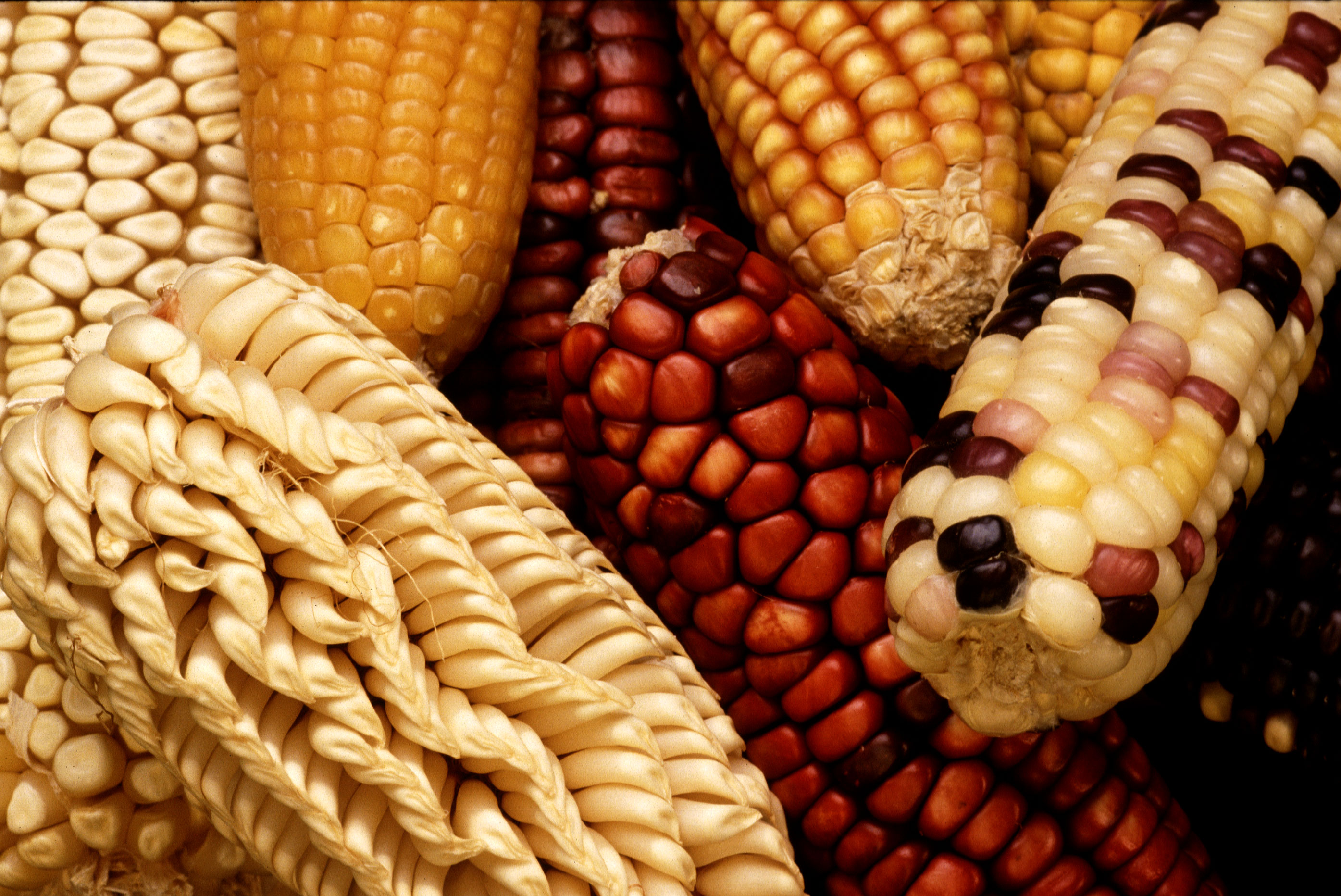
Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears. The ears yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors. Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is used for animal feed, whether as grain or as the whole plant, which can either be baled or made into the more palatable silage. Sugar-rich varieties called sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
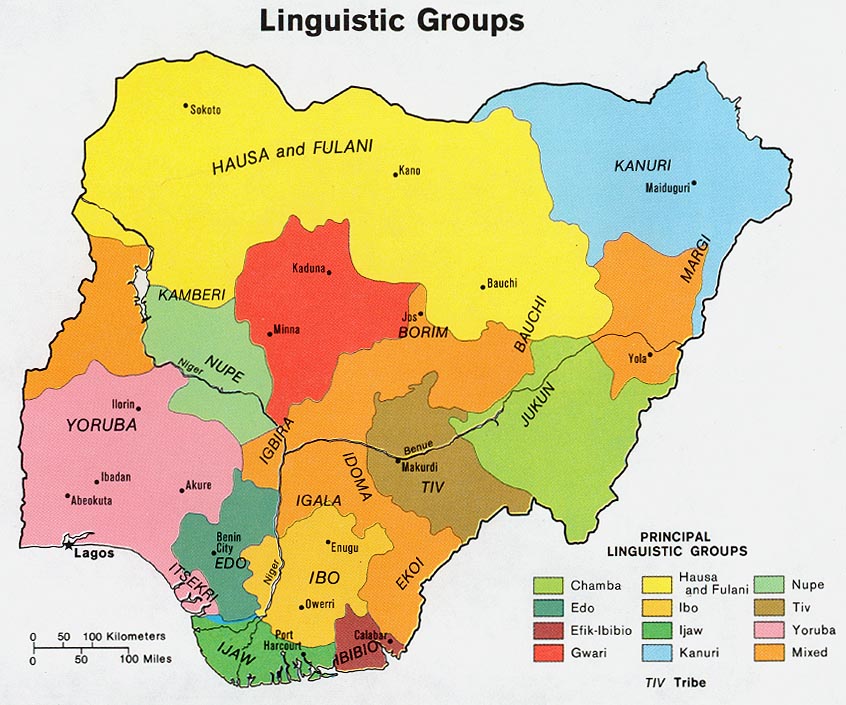
Yoruba Language
Yoruba (, ; Yor. ) is a Niger–Congo languages, Niger-Congo language that is spoken in West Africa, primarily in South West (Nigeria), Southwestern and Middle Belt, Central Nigeria, Benin, and parts of Togo. It is spoken by the Yoruba people. Yoruba speakers number roughly 50 million, including around 2 million second-language or L2 speakers. As a pluricentric language, it is primarily spoken in a dialectal area spanning Nigeria, Benin, and Togo with smaller migrated communities in Côte d'Ivoire, Sierra Leone and The Gambia. Yoruba vocabulary is also used in African diaspora religions such as the Afro-Brazilian religion of Candomblé, the Caribbean religion of Santería in the form of the liturgical Lucumí language, and various Afro-American religions of North America. Most modern practitioners of these religions in the Americas are not fluent in the Yoruba language, yet they still use Yoruba words and phrases for songs or chants—rooted in cultural traditions. For such pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hausa Language
Hausa (; / ; Hausa Ajami, Ajami: ) is a Chadic language spoken primarily by the Hausa people in the northern parts of Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon, Benin and Togo, and the southern parts of Niger, and Chad, with significant minorities in Ivory Coast. A small number of speakers also exist in Sudan. Hausa is a member of the Afroasiatic language family and is the most widely spoken language within the Chadic branch of that family. Despite originating from a non-tonal language family, Hausa utilizes differences in pitch to distinguish words and grammar. ''Ethnologue'' estimated that it was spoken as a first language by some 58 million people and as a second language by another 36 million, bringing the total number of Hausa speakers to an estimated 94 million. In Nigeria, the Hausa film industry is known as Kannywood. Classification Hausa belongs to the West Chadic languages subgroup of the Chadic languages group, which in turn is part of the Afroasiatic languages, Afro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zarma Language
Zarma (''Zarma Ciine/Sanni''; Ajami: ) is one of the Songhay languages. It is the leading indigenous language of the southwestern lobe of the West African nation of Niger, where the Niger River flows and the capital city, Niamey, is located. Zarma is the second-most common language in the country, after Hausa, which is spoken in south-central Niger. With over 6 million speakers, Zarma is the most widely spoken Songhay language. In earlier decades, Zarma was rendered ''Djerma'', using French orthography, but it is usually now 'Zarma', the form that the Zarma people use in their language. Alternative names for Zarma are Djerma, Jerma, Dyabarma, Dyarma, Dyerma, Adzerma, Zabarma, Zarbarma, Zarmaci or Zerma. Geographic distribution The majority of people who speak Zarma live in Southwestern Niger. It is also spoken in other parts of Niger, Mali, Burkina Faso, and Nigeria. Cities where Zarma is spoken include Tillaberi, Dosso, Niamey, Tahoua and Agadez. In Nigeria, where the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tem Language
Tem, or Kotokoli (Cotocoli), is a Gur language spoken in Togo, Ghana, Benin and Burkina Faso. It is used by neighboring peoples. In Ghana the Kotokoli people come from the northern part of the Volta Region, primarily Koue along the border with Togo. Besides their traditional home in Koue, the Tem/Kotokoli people are scattered all over Ghanaian communities. They mainly live in Zongo settlements in Nima-Mamobi, Madina, Dodowa, Asaman, Jamasi, Aboaso, Mamponteng, Ahwiaa, Offinso Asamankama, Kokoti, Fanteakwa, Kinyako, Fianko, Ahmasu, Kejebi, Hohoe, Nkwanta, Kpassa, Karachi, Dambai and a host of others. The Chieftain is called the Wuro and is the overlord of the Koue lands, the Kotokoli people, at home and in diaspora. He name is Wuro Dauda Cheddere Brenae I. Some notable Kotokoli tribesmen include the National Youth Chief of Kotokoli, Wuro Alhaj Ismael Bameiyin, Wuro Alhaj Salifu Haruna of Madina, Sheikh Salis Shaban, Sheikh Muhammad Qassim Kpakpaturu of Jamasi, Mallam Abdul Muhaim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabiye Language
Kabiye (; also rendered ''Kabiyé'', ''Kabiyè'', ''Kabye'', ''Kabyé'', ''Kabyè'', ''Cabrai'' or ''Cabrais'') is an Eastern Gurunsi Gur language spoken primarily in northern Togo. Throughout the 20th century, there was extensive migration to the centre and south of Togo and also to Ghana and Benin. Kabiye speakers made up over 23% of the Togolese population in 1999. Status Kabiye is one of two national languages of Togo (along with Ewe). In the Togolese context, ''national language'' currently means that the language is promoted in national media and, in the formal education sector, as an optional exam subject in grades 9 and 10. Linguistic research The missionary-linguist Jacques Delord published the first descriptive grammar of Kabiye in 1976. This was followed by Kezié Lébikaza's descriptive grammar in 1999, which remains the key reference work in Kabiye linguistics. There is also a Kabiye-French dictionary. Other topics that have been the focus of research include: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European family. Like all other Romance languages, it descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. French evolved from Northern Old Gallo-Romance, a descendant of the Latin spoken in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien language, Francien) largely supplanted. It was also substratum (linguistics), influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul and by the Germanic languages, Germanic Frankish language of the post-Roman Franks, Frankish invaders. As a result of French and Belgian colonialism from the 16th century onward, it was introduced to new territories in the Americas, Africa, and Asia, and numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole, were established. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Kara
The University of Kara (abbreviated UK) is the second university in Togo Togo, officially the Togolese Republic, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to Ghana–Togo border, the west, Benin to Benin–Togo border, the east and Burkina Faso to Burkina Faso–Togo border, the north. It is one of the le ... after the University of Lomé. Located in the city of Kara, it was established by a presidential (Gnassingbé Eyadema) decree on 21 January 1999, and opened on 23 January 2004. History The university opened on 23 January 2004 with ca. 1600 students. The Kara American Space was opened in the university's campus on 4 December 2012. The second largest centre of computing resources of the subregion, after that of the University of Ouagadougou in Burkina Faso, was created in 2013. References External links University of Kara {{DEFAULTSORT:University Of Kara Universities and colleges established in 2004 Universities and colleges in Togo Kara Region 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niamtougou International Airport
Niamtougou International Airport is an airport serving the north of Togo near Niamtougou. It is an international airport and Togo's second largest after Lomé-Tokoin Airport. The airport is located in Baga, north of Niamtougou. History Opened in 1981, it has a 2500m runway, accessible to DC 10-30 planes and parking for 4 planes. It is primarily used by the Togolese Air Force and by civilian government airplanes, and only occasionally by chartered and private flights. Attempts have been made to schedule regular commercial flights to serve northern Togo, such as Air Burkina Ouagadougou– Niamtougou–Lomé round-trip flights, but to date these have not proved to be commercially viable. Redevelopment Redevelopment of the airport began in April 2016 to bring it up to ICAO standards. The project involves lengthening the runway by 500 meters and resurfacing it, incorporating a turning area, renovating the departure lounge, and building a perimeter wall. The project, which h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor percentages of waxes, fats, pectins, and water. Under natural conditions, the cotton bolls will increase the dispersal of the seeds. The plant is a shrub native to tropical and subtropical regions around the world, including the Americas, Africa, Egypt and India. The greatest diversity of wild cotton species is found in Mexico, followed by Australia and Africa. Cotton was independently domesticated in the Old and New Worlds. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable, and durable textile. The use of cotton for fabric is known to date to prehistoric times; fragments of cotton fabric dated to the fifth millennium BC have been found in the Indus Valley civilizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearl Millet
Pearl millet (''Cenchrus americanus'', commonly known as the synonym ''Pennisetum glaucum'') is the most widely grown type of millet. It has been grown in Africa and the Indian subcontinent since prehistoric times. The center of diversity, and suggested area of domestication, for the crop is in the Sahel zone of West Africa. Recent archaeobotanical research has confirmed the presence of domesticated pearl millet on the Sahel zone of northern Mali between 2500 and 2000 BC. 2023 was the , declared by the United Nations General Assembly in 2021. Description Pearl millet has ovoid grains of length, the largest kernels of all varieties of millet (not including sorghum). These can be nearly white, pale yellow, brown, grey, slate blue or purple. The 1000-seed weight can be anything from 2.5 to 14 g with a mean of 8 g. The height of the plant ranges from . Cultivation Pearl millet is well adapted to growing areas characterized by drought, low soil fertility, low moisture, and high t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |