|
Kalyptos
In Sethian Gnosticism, Kalyptos ("the Hidden One") is one of the three emanations of Barbelo (along with Protophanes and Autogenes according to '' Zostrianos''). Kalyptos is mentioned in Nag Hammadi texts such as '' Zostrianos'', ''The Three Steles of Seth'', '' Allogenes the Stranger'', and '' Marsanes''. See also *Aeon (Gnosticism) *Hypostasis (philosophy and religion) Hypostasis (plural: hypostases), from the Greek (''hypóstasis''), is the underlying, fundamental state or substance that supports all of reality. It is not the same as the concept of a substance. In Neoplatonism, the hypostasis of the soul, the ... References Gnostic deities {{Gnosticism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zostrianos
''Zostrianos'' is a Sethian Gnostic text. It is the first tractate of two in Codex VIII of the Nag Hammadi library. It takes up 132 of the 140 pages in the codex, making ''Zostrianos'' the longest tractate of the entire library. However the text is extensively damaged, especially in the center, making the document difficult to fully understand. The Coptic manuscript is a translation of a Greek original, likely written in Alexandria in c. 200 AD. In the text, Zostrianos goes on a heavenly journey and receives divine knowledge from the aeons. The work is likely the same ''Zostrianos'' that Porphyry criticized in ''Life of Plotinus.'' Like other Sethian Gnostic texts Marsanes, Allogenes, and Three Steles of Seth, its ideas appear more Middle Platonic or Neoplatonic than Christian. However, Porphyry said that these works belonged to Christian heretics. Bentley Layton explains this apparent contradiction with the belief that ''Zostrianos'' was written by a Gnostic Christian auth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbelo
Barbēlō (Greek: Βαρβηλώ) refers to the first emanation of God in several forms of Gnostic cosmogony. Barbēlō is often depicted as a supreme female principle, the single passive antecedent of creation in its manifold. This figure is also variously referred to as 'Mother-Father' (hinting at her apparent androgyny), 'The Triple Androgynous Name', or 'Eternal Aeon'. So prominent was her place amongst some Gnostics that some schools were designated as ''Barbeliotae'', Barbēlō worshippers or Barbēlō gnostics. The nature of Barbēlō Nag Hammadi Library In the ''Apocryphon of John'', a tractate in the Nag Hammadi Library containing the most extensive recounting of the Sethian Gnostic creation myth, the Barbēlō is described as "the first power, the glory, Barbēlō, the perfect glory in the aeons, the glory of the revelation". All subsequent acts of creation within the divine sphere (save, crucially, that of the lowest aeon Sophia) occurs through her coaction with Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protophanes
In Sethian Gnosticism, Protophanes ("the First-Appearing One") is one of the three emanations of Barbelo (along with Kalyptos and Autogenes according to '' Zostrianos''). Protophanes is mentioned in Nag Hammadi texts such as '' Zostrianos'', ''The Three Steles of Seth'', '' Allogenes the Stranger'', and Marsanes''. See also *Aeon (Gnosticism) *Phanes In Orphic cosmogony Phanes (, genitive ) or Protogonos () is a primeval deity who was born from the cosmic egg at the beginning of creation. He is referred by various names, including Erikepaios "Power" () and Metis "Thought". Mythology ... References Gnostic deities {{Gnosticism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autogenes
In Sethian Gnosticism, Autogenes (Meaning "Self-Born One" in Greek) is an emanation or son of Barbelo (along with Kalyptos and Protophanes according to '' Zostrianos''). Autogenes is mentioned in Nag Hammadi texts such as '' Zostrianos'', ''The Three Steles of Seth'', '' Allogenes the Stranger'', and '' Marsanes''. Autogenes in Gnosticism is roughly parallel to the Platonic soul. See also *Aeon (Gnosticism) *Plato's theory of soul Plato's theory of the soul, which was inspired variously by the teachings of Socrates, considered the psyche () to be the essence of a person, being that which decides how people behave. Plato considered this essence to be an incorporeal, etern ... References Gnostic deities {{Gnosticism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allogenes The Stranger
Allogenes is a series of Gnostic texts. The main character in these texts is Allogenes (Greek: ἀλλογενής), which translates as 'stranger,' 'foreigner,' or 'of another race.' The first text discovered was ''Allogenes'' as the third tractate in Codex XI of the Nag Hammadi library. The Coptic manuscript is a translation of a Greek original, likely written in Alexandria before 300 AD. In this text, containing Middle Platonic or Neoplatonic elements, Allogenes receives divine revelations. A different text, '' The Temptation of Allogenes'', was discovered as the fourth tractate in the Codex Tchacos. In this text, Allogenes resists temptation and ascends. Codex Tchacos, also written in Coptic, is likely older than NHC XI based on radiocarbon dating, but it is unknown exactly when the original texts were composed. Both texts have some damage and are incomplete. Other ''Allogenes'' texts may have been written. In section 39.5.1 of the ''Panarion'', Epiphanius of Salamis writes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsanes
Marsanes is a Sethian Gnostic text from the New Testament apocrypha. The only surviving copy comes from the Nag Hammadi library, albeit with 14 pages completely missing and a large number of lines throughout the text damaged beyond recovery. Scholars speculate that the text was originally written by a Syrian in Greek during the third century. The content of the text focuses on the 13 seals, the Triple-Powered One, the shape and structure of the soul, acquiring power and knowledge, and an apocalyptic vision. Summary The opening lines of the document are mostly unrecoverable. The thirteenth seal is established "with the summit of knowledge and the certainty of rest." The text discusses the other 12 seals, first mentioning the power that will provide rest and protect those who receive it from passions and division. Other seals concern the conversion of those within, the self-begotten ones, salvation and wisdom, the mind, Barbelo, the Invisible One, and the Spirit. The thirteenth se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypostasis (philosophy And Religion)
Hypostasis (plural: hypostases), from the Greek (''hypóstasis''), is the underlying, fundamental state or substance that supports all of reality. It is not the same as the concept of a substance. In Neoplatonism, the hypostasis of the soul, the intellect (''nous'') and " the one" was addressed by Plotinus. In Christian theology, the Holy Trinity consists of three hypostases: that of the Father, that of the Son, and that of the Holy Spirit. Ancient Greek philosophy Pseudo-Aristotle used "hypostasis" in the sense of material substance. Neoplatonists argue that beneath the surface phenomena that present themselves to our senses are three higher spiritual principles (or ''hypostases''): each one more sublime than the preceding. For Plotinus, these are the Soul, the Intellect, and the One.''Neoplatonism (Ancient Philosophies)'' by Pauliina Remes (2008), University of California Press , pp. 48–52. Christian theology The term ''hypostasis'' has particular significance in Chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sethian Gnosticism
The Sethians (Greek: Σηθιανοί) were one of the main currents of Gnosticism during the 2nd and 3rd century AD, along with Valentinianism and Basilideanism. According to John D. Turner, it originated in the 2nd century AD as a fusion of two distinct Hellenistic Judaic philosophies and was influenced by Christianity and Middle Platonism. However, the exact origin of Sethianism is not properly understood. History Mentions The Sethians (Latin ''Sethoitae'') are first mentioned, alongside the Ophites, in the 2nd century, by Irenaeus (who was antagonistic towards Gnosticism) and in Pseudo-Tertullian (Ch. 30). According to Frederik Wisse, all subsequent accounts appear to be largely dependent on Irenaeus. Hippolytus repeats information from Irenaeus. According to Epiphanius of Salamis (c. 375), Sethians were in his time found only in Egypt and Palestine, but fifty years earlier, they had been found as far away as Greater Armenia. Philaster's (4th century AD) ''Catalogue of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emanationism
Emanationism is a speculative theory in the cosmology or cosmogony of certain religious and philosophical systems, that posits the concept of ''emanation''. According to this theory, emanation, from the Latin ''emanare'' meaning "to flow from" or "to pour forth or out of", is the mode by which all existing things are derived from a 'first reality', or first principle. In the emanationist concept all things are derived from this first reality or perfect God, by consecutive steps of degradation, to a lower degree of this first reality or God: at every consecutive step the emanating beings are less pure, less perfect, less divine. Emanationism posits a transcendent principle from which everything is derived, as opposed to creationism, that considers the universe to be created by a sentient God who is separate from creation, and to materialism, which posits no underlying subjective and/or ontological nature behind phenomena, all phenomena being considered immanent. Origins Ema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nag Hammadi Library
The Nag Hammadi library (also known as the Chenoboskion Manuscripts and the Gnostic Gospels) is a collection of early Christian and Gnostic texts discovered near the Upper Egyptian town of Nag Hammadi in 1945. Thirteen leather-bound papyrus codices buried in a sealed jar were found by a local farmer named Muhammed al-Samman. The writings in these codices comprise 52 mostly Gnostic treatises, but they also include three works belonging to the '' Corpus Hermeticum'' and a partial translation/alteration of Plato's ''Republic''. In his introduction to ''The Nag Hammadi Library in English'', James Robinson suggests that these codices may have belonged to a nearby Pachomian monastery and were buried after Saint Athanasius condemned the use of non-canonical books in his Festal Letter of 367 A.D. The Pachomian hypothesis has been further expanded by Lundhaug & Jenott (2015, 2018) and further strengthened by Linjamaa (2024). In his 2024 book, Linjamaa argues that the Nag Hammadi l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Steles Of Seth
The ''Three Steles of Seth'' is a Sethian Gnostic text. It is the fifth tractate in Codex VII of the Nag Hammadi library. The writing is in Coptic and takes up the last nine pages of the codex. Background A common theme in Sethian works is a descent or ascent theme. The ''Three Steles of Seth''—along with ''Zostrianos'', '' Allogenes'', and ''Marsanes''—uses the ascent pattern. Furthermore, these four Sethian texts are grouped together because of their extensive use of terminology from Platonic philosophy. Thus, the original work was likely written before Plotinus's ''Against the Gnostics'' in c. 265. The text lacks specifically Christian elements; the triadic nature of God is instead a Neoplatonic belief. Thus, the traditional two steles made of brick and stone are increased to three to represent the threefold divine: the Father, the mother Barbelo, and the son Autogenes. Summary In the text, Seth uses the three steles to record three doxologies or hymns of praise. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
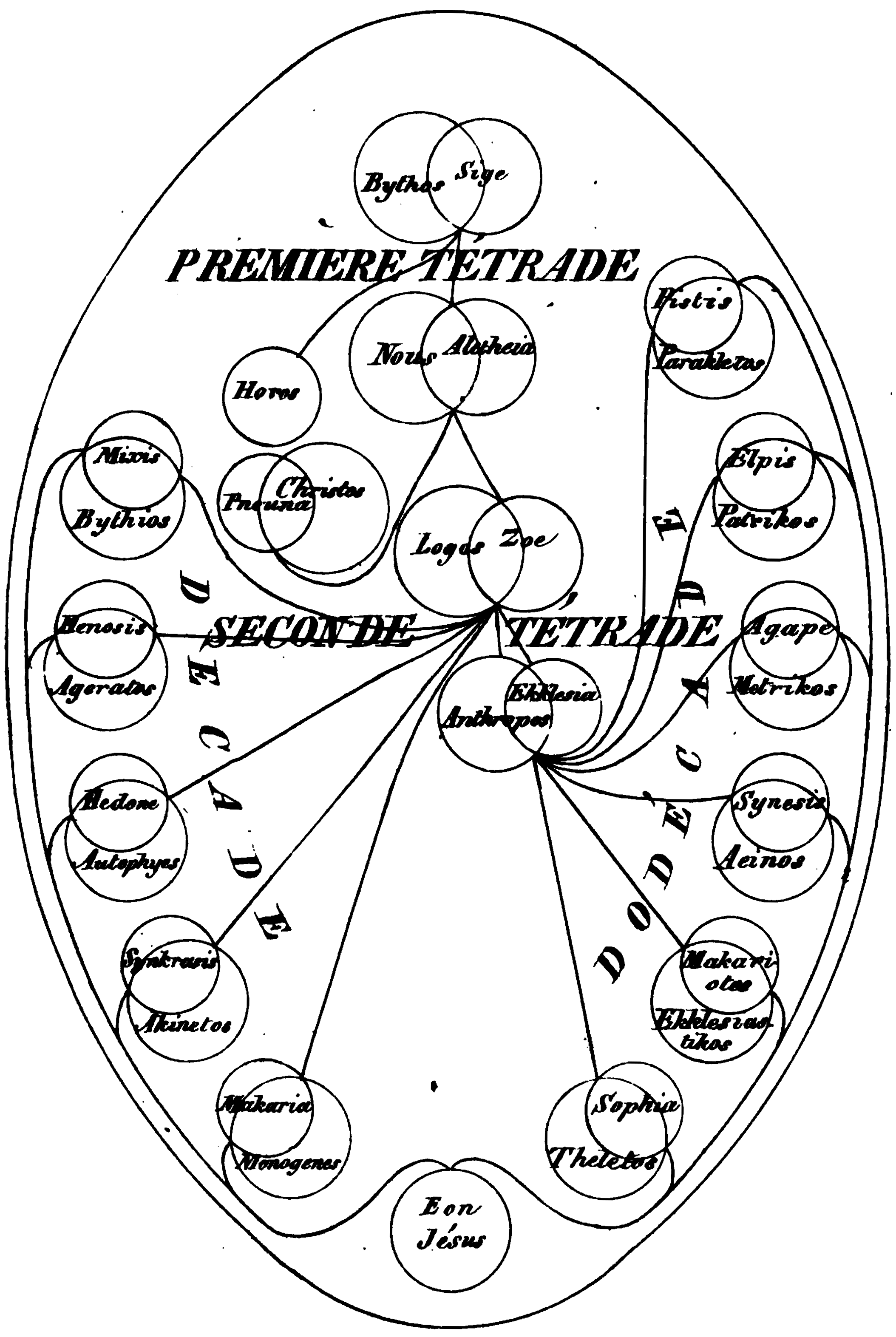
Aeon (Gnosticism)
In many Gnosticism, Gnostic systems, there are various emanationism, emanations of God, who is known by such names as One, Monad (Gnosticism), Monad, ''Aion teleos'' (αἰών τέλεος "The Broadest Aeon"), Bythos (, "depth" or "profundity"), ''Arkhe'' (, "the beginning"). In Gnosticism these emanations of God are named as ''ARKHIRES'' (, "''before'' the beginning") and as Aeons (which are also often named and may be paired or grouped). In different systems these emanations are differently named, classified, and described (but emanation is common to all forms of 'Gnosticism'). In Basilidian Gnosis they are called sonships (υἱότητες ''huiotetes''; sing.: υἱότης ''huiotes''); according to Marcosians, Marcus, they are numbers and sounds; in Valentinianism they form male/female pairs called syzygies (, from σύζυγοι ''syzygoi'': lit. "yokings together"). This source of all being is an Aeon, in which an inner being dwells, known as ''Ennoea'' (, "thought, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |