|
KBKhA
Chemical Automatics Design Bureau (CADB), also KB Khimavtomatika (, KBKhA), is a Russian OKB, design bureau founded by the NKAP (People's Commissariat of the Aircraft Industry) in 1941 and led by Semyon Kosberg until his death in 1965. Its origin dates back to a 1940 Moscow carburetor factory, evacuated to Berdsk in 1941, and then relocated to Voronezh city in 1945, where it now operates. Originally designated OKB-296 and tasked to develop fuel equipment for aviation engines, it was redesignated OKB-154 in 1946. In 1965 took over leadership. He was succeeded by in 1993, then by (RD-0124 Chief designer) in 2015. During this time the company designed a wide range of high technology products, including liquid propellant rocket engines, a nuclear reactor for space use, the first Soviet laser with an output of 1 MW and the USSR's only operational nuclear rocket engine. The company has designed more than 60 liquid propellant engines with some 30 having entered production. In Novem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RD-0124
The RD-0124 (, GRAU index: 14D23) is a rocket engine burning liquid oxygen and kerosene in an oxygen-rich staged combustion cycle, developed by the Chemical Automatics Design Bureau in Voronezh. RD-0124 engines are used on the Block I stage used on Soyuz-2.1b and Soyuz-2.1v. A variant of the engine, the RD-0124A, is used on the Angara rocket family's URM-2 upper stage. Design RD-0124 engines use a multi-stage turbopump powered by pre-combustion of the engine propellants in the preburner. The kerosene fuel is used for regenerative cooling of the engine. Vehicle attitude control during ascent is provided by gimbaling the engine in two planes. The propellant tanks are helium-pressurized. Four combustion chambers are fed by a single turbopump system. The engine operates at a high chamber pressure and, for the type of propellants used, achieves a very high specific impulse of nearly 360 seconds in vacuum. History The inaugural flight of a launch vehicle using an RD-0124 engin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voronezh Mechanical Plant
Voronezh Mechanical Plant (Russian: , ''ВМЗ'') is a Russian engine and heavy machinery manufacturing plant. It is located in the city of Voronezh, in the Voronezh Oblast. History Voronezh Mechanical Plant started as a diesel engine manufacturing plant, and has been the plant that serially manufactures the engines designed by Chemical Automatics Design Bureau (KBKhA). In later years, it has branched into producing oil and gas products like valves, manifolds and fittings. In January 2017, Roscosmos announced that firing tests revealed problems with the Voronezh-produced Proton rocket upper stage engines. According to the investigation, expensive alloys had been replaced by cheaper less heat-resistant alloys. Voronezh director-general Ivan Tikhonovich Koptev resigned. On November 1, 2019, enterprises ''ВМЗ'' and the Chemical Automatics Design Bureau were merged. Products Current engines Engines in production at the plant as of 2015: * RD-0110 - Upper stage engine of the So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS-19
The UR-100N, also known as RS-18A, is an intercontinental ballistic missile in service with Soviet and Russian Strategic Missile Troops. The missile was given the NATO reporting name SS-19 Stiletto and carries the industry designation 15A30. Development Development of the UR-100N began at OKB-52 in 1970 and flight tests were carried out from 1973 through 1975. In 1976, the improved UR-100NUTTKh (NATO designation SS-19 Mod 3) version entered development with flight tests in the later half of the decade. The rocket's control system was developed at NPO "Electropribor" (Kharkiv, Ukraine). Description The UR-100N is a fourth-generation silo-launched liquid-propellant ICBM similar to the UR-100 but with much increased dimensions, mass, performance, and payload. The missile was not designed to use existing UR-100 silos, and therefore had new silos constructed for it. The missile has a preparation time to start of 25 minutes, a storage period of 22 years, and 6 MIRVs. Operational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voronezh
Voronezh ( ; , ) is a city and the administrative centre of Voronezh Oblast in southwestern Russia straddling the Voronezh River, located from where it flows into the Don River. The city sits on the Southeastern Railway, which connects western Russia with the Urals and Siberia, the Caucasus and Ukraine, and the M4 highway (Moscow–Voronezh– Rostov-on-Don– Novorossiysk). In recent years the city has experienced rapid population growth, rising in 2021 to 1,057,681, up from 889,680 recorded in the 2010 Census, making it the 14th-most populous city in the country. History Foundation and name The first chronicle references to the word "Voronezh" are dated 1177, when the Ryazan prince Yaropolk, having lost the battle, fled "to Voronozh" and there was moving "from town to town". Modern data of archeology and history interpret Voronezh as a geographical region, which included the Voronezh river (tributary of the Don) and a number of settlements. In the lower rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roscosmos
The State Corporation for Space Activities "Roscosmos", commonly known simply as Roscosmos (), is a State corporation (Russia), state corporation of the Russian Federation responsible for space science, space flights, List of space agencies, cosmonautics programs, and aerospace research. Originating from the Soviet space program founded in the 1950s, Roscosmos emerged following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It initially began as the Russian Space Agency,, ''Rossiyskoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', or RKA (). which was established on 25 February 1992 and restructured in 1999 and 2004 as the Russian Aviation and Space Agency, ''Rossiyskoye aviatsionno-kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', commonly known as (), established on 25 May 1999. and the Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), (Роскосмос), ''Federalnoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo (Roskosmos)''. respectively. In 2015, the Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) was merged with the United Rocket and Space Corporation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
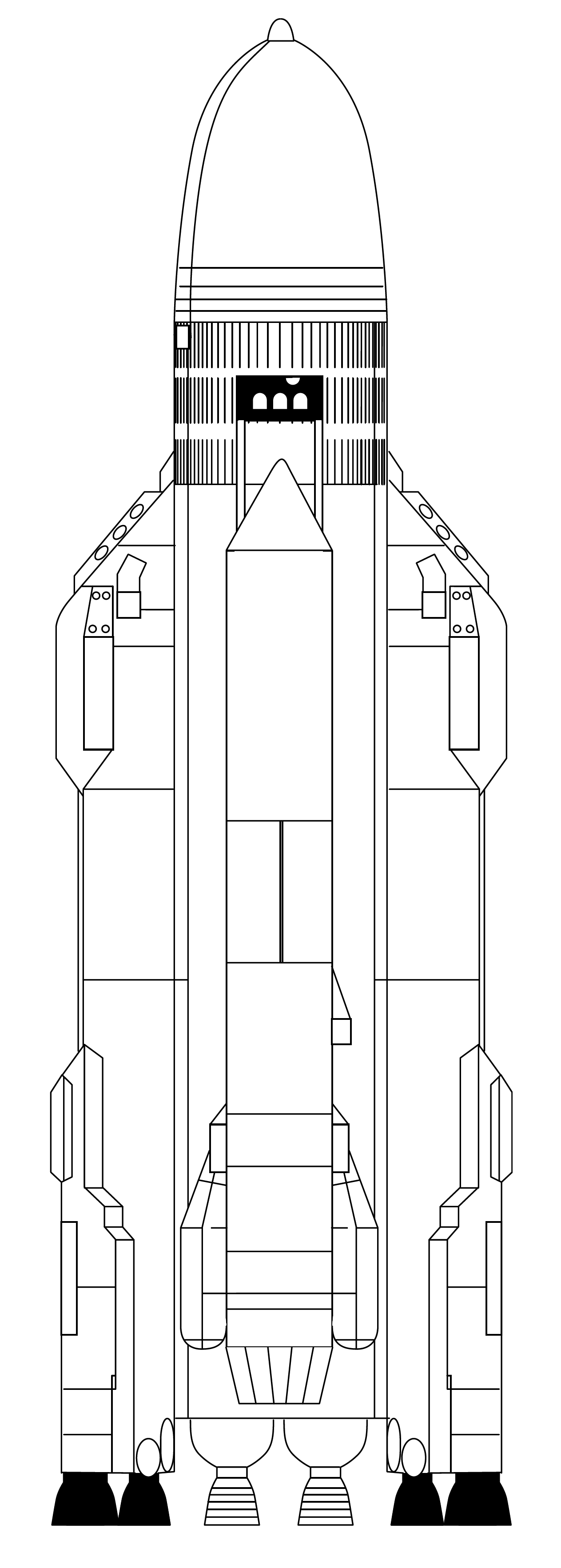
Soyuz (rocket Family)
Soyuz (, GRAU index: 11A511) is a family of Soviet and later Russian expendable Medium-lift launch vehicle, medium-lift launch vehicles initially developed by the OKB-1 design bureau and manufactured by the Progress Rocket Space Centre factory in Samara, Russia. It holds the record for the most launches in the history of spaceflight. Soyuz rockets are part of the R-7 (rocket family), R-7 rocket family, which evolved from the R-7 Semyorka, the world's first intercontinental ballistic missile. As with many Soviet rockets, the names of recurring payloads became associated with the launch vehicle itself. Consequently, the Soyuz rockets are best known as the launch vehicles for crewed Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz spacecraft under the Soyuz programme, as well as for uncrewed Progress (spacecraft), Progress cargo spacecraft to the International Space Station (ISS). Despite this recognition, the majority of Soyuz launches have been dedicated to deploying satellites for both governmental a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-29RM Shtil
The R-29RM (, NATO reporting name SS-N-23 Skiff) was a liquid propellant, submarine-launched ballistic missile in use by the Russian Navy. It had the alternate Russian designations RSM-54 and GRAU index 3M27. It was designed to be launched from the Delta IV submarine, each of which is capable of carrying 16 missiles. The R-29RM could carry four 100 kiloton warheads and had a range of about . They were replaced with the newer R-29RMU2 Sineva and later with the enhanced variant R-29RMU2.1 Layner. History Development Development of the R-29RM started in 1979 at the Makeyev Rocket Design Bureau. The navy accepted the armament in 1986 and subsequently installed the D-9RM launch system consisting of a cluster of 16 R-29RM on board the nuclear-propelled Project 667BDRM submarines. Operation Behemoth On 6 August 1991 at 21:09, K-407 , under the command of Captain Second Rank Sergey Yegorov, became the world's only submarine to successfully launch an all-missile salvo, laun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UDMH
Unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (abbreviated as UDMH; also known as 1,1-dimethylhydrazine, heptyl or Geptil) is a chemical compound with the formula H2NN(CH3)2 that is primarily used as a rocket propellant. At room temperature, UDMH is a colorless liquid, with a sharp, fishy, ammonia-like smell typical of organic amines. Samples turn yellowish on exposure to air and absorb oxygen and carbon dioxide. It is miscible with water, ethanol, and kerosene. At concentrations between 2.5% and 95% in air, its vapors are flammable. It is not sensitive to shock. Symmetrical dimethylhydrazine (1,2-dimethylhydrazine) also exists, but it is not as useful. UDMH can be oxidized in air to form many different substances, including toxic ones. Synthesis In 1875, UDMH was first prepared by Emil Fischer, who discovered and named the class of hydrazines, by reducing N-Nitrosodimethylamine with zinc in boiling acetic acid. Fischer's student Edward Renouf later studied UDMH more extensively as part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Chelomey
Vladimir Nikolayevich Chelomey or Chelomei (, ; 30 June 1914 – 8 December 1984) was a Soviet people, Soviet engineer and designer in the missile program of the former Soviet Union. He invented the first Soviet Pulsejet, pulse jet engine and was responsible for developing the world's first anti-ship cruise missiles and the ICBM program of the Soviet Union such as the UR-100, UR-200, UR-500 and UR-700. Early life Chelomey was born to a Ukrainian family in Siedlce, Lublin Governorate, Russian Empire (now Poland). At the age of three months, his family fled to Poltava, Ukraine, when the Eastern Front (World War I), Eastern Front of World War I came close to Siedlce. When Chelomey was 12 years old, the family moved again to Kyiv. In 1932, Chelomey was admitted to the Kyiv Polytechnic Institute (later the basis of Kyiv Aviation Institute), where he showed himself as a student with outstanding talent. In 1936, his first book ''Vector Analysis'' was published. Studying at the insti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton (rocket)
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an electron (the proton-to-electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with a mass of approximately one dalton, are jointly referred to as ''nucleons'' (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each element is identified by the number of protons in its nucleus, each element has its own atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristics of the element. The word ''proton'' is Greek for "first", and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
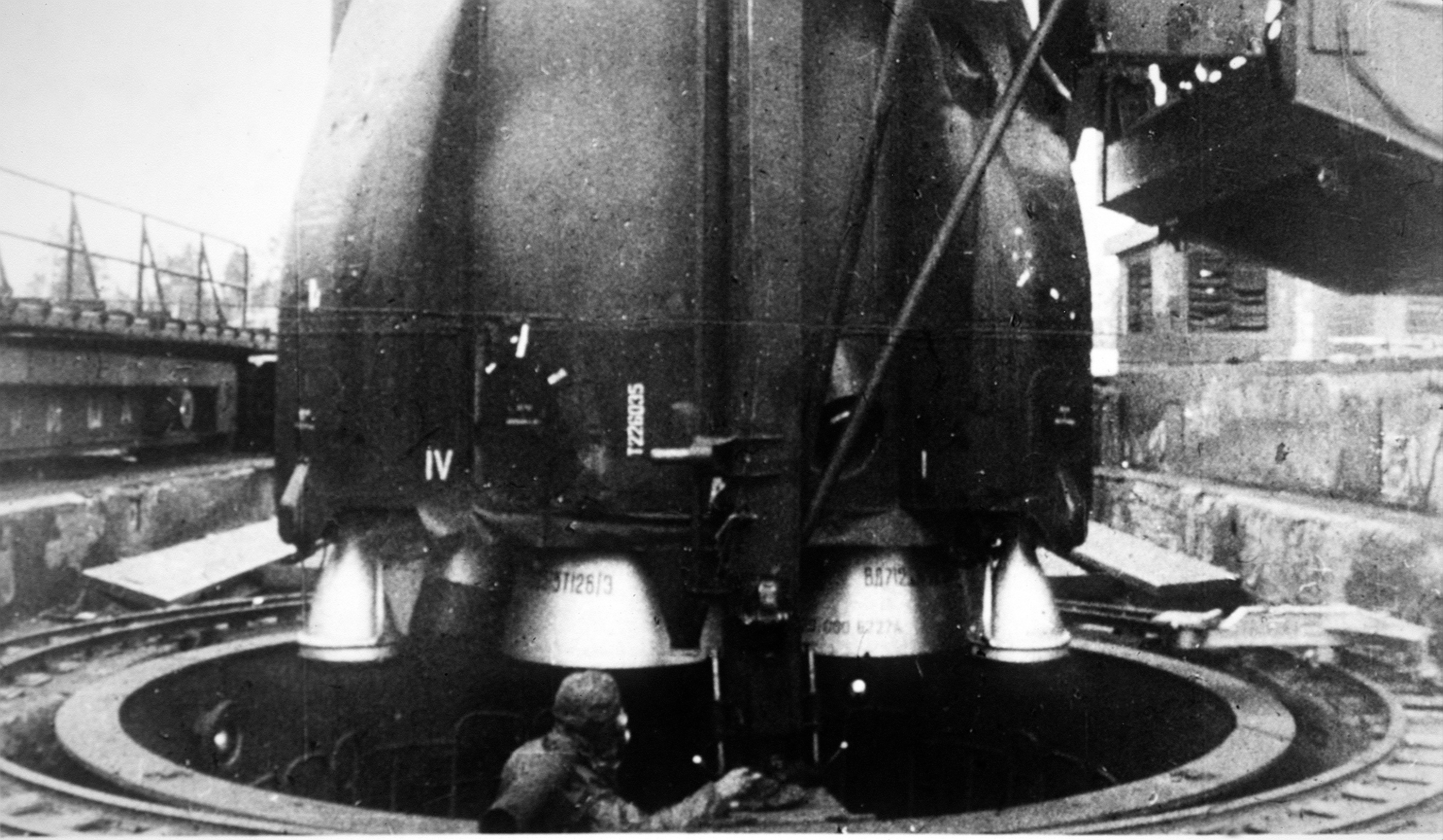
Energia (rocket)
Energia (; GRAU 11K25) was a 1980s super-heavy lift launch vehicle. It was designed by NPO Energia of the Soviet Union as part of the Buran programme, Buran program for a variety of payloads including the Buran (spacecraft), Buran spacecraft. Control system main developer enterprise was the Khartron NPO "Electropribor". The Energia used four strap-on boosters each powered by a four-chamber RD-170 engine burning kerosene/Liquid oxygen, LOX, and a central core stage with four single-chamber RD-0120 (11D122) engines fueled by liquid hydrogen/LOX. The launch vehicle had two functionally different operational variants: Energia-Polyus, the initial test configuration, in which the Polyus (spacecraft), Polyus system was used as a final stage intended to put the payload into orbit, and Energia-Buran, in which the Buran programme, ''Buran'' orbiter was the payload and the source of the orbit insertion impulse. The launch vehicle had the capacity to place about 100 tonnes in Low Earth orbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS-18
The R-36 () is a family of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and space launch vehicles (Tsyklon) designed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. The original R-36 was deployed under the GRAU index 8K67 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-9 Scarp. It was able to carry three warheads and was the first Soviet MIRV (multiple re-entry vehicle, multiple independently targetable re-entry vehicle) missile. The later version, the R-36M, also known as RS20, was produced under the GRAU designations 15A14 and 15A18 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-18 Satan. This missile was viewed by certain United States analysts as giving the Soviet Union Pre-emptive nuclear strike, first strike advantage over the U.S., particularly because of its rapid silo-reload ability, very heavy throw weight and extremely large number of atmospheric re-entry, re-entry vehicles. Some versions of the R-36M were deployed with 10 warheads and up to 40 penetration aids and the missile's high thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |