|
Józef Czapski
Józef Czapski (3 April 1896 – 12 January 1993) was a Polish artist, author, and critic, as well as an officer of the Polish Army. As a painter, he is notable for his membership in the Kapist movement, which was heavily influenced by Cézanne. Following the Polish Defensive War, he was made a prisoner of war by the Soviets and was among the very few officers to survive the Katyn massacre of 1940. Following the Sikorski-Mayski Agreement, he was an official envoy of the Polish government searching for the missing Polish officers in Russia. After World War II, he remained in exile in the Paris suburb of Maisons-Laffitte, where he was among the founders of ''Kultura'' monthly, one of the most influential Polish cultural journals of the 20th century. Life Early life Józef Marian Franciszek hrabia Hutten-Czapski of Leliwa, as was his full name, was born on 3 April 1896 in Prague, to an aristocratic family. Among his relatives were hr. Emeryk Hutten-Czapski, hr. Karol Hutt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate oceanic climate, with relatively warm summers and chilly winters. Prague is a political, cultural, and economic hub of central Europe, with a rich history and Romanesque, Gothic, Renaissance and Baroque architectures. It was the capital of the Kingdom of Bohemia and residence of several Holy Roman Emperors, most notably Charles IV (r. 1346–1378). It was an important city to the Habsburg monarchy and Austro-Hungarian Empire. The city played major roles in the Bohemian and the Protestant Reformations, the Thirty Years' War and in 20th-century history as the capital of Czechoslovakia between the World Wars and the post-war Communist era. Prague is home to a number of well-known cultural attractions, many of which survived the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgy Chicherin
Georgy Vasilyevich Chicherin (24 November 1872 – 7 July 1936), also spelled Tchitcherin, was a Russian Marxist revolutionary and a Soviet politician who served as the first People's Commissar for Foreign Affairs in the Soviet government from March 1918 to July 1930. Childhood and early career A distant relative of Aleksandr Pushkin, Georgy Chicherin was born into an old noble family. He was born on the estate of his uncle, Boris Chicherin, in Karaul, Tambov. His father, Vasily N. Chicherin, was a diplomat employed by the Foreign Office of the Russian Empire. His uncle was an influential legal philosopher and historian. As a young man, Chicherin became fascinated with history; classical music, especially Richard Wagner; and Friedrich Nietzsche, passions that he would pursue throughout his life. He wrote a book about Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and spoke all major European languages and a number of Asian ones. After graduating from St. Petersburg University with a degree in history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Civil War
, date = October Revolution, 7 November 1917 – Yakut revolt, 16 June 1923{{Efn, The main phase ended on 25 October 1922. Revolt against the Bolsheviks continued Basmachi movement, in Central Asia and Tungus Republic, the Far East through the 1920s and 1930s.{{cite book, last=Mawdsley, first=Evan, title=The Russian Civil War, location=New York, publisher=Pegasus Books, year=2007, isbn=9781681770093, url=https://archive.org/details/russiancivilwar00evan, url-access=registration{{rp, 3,230(5 years, 7 months and 9 days) {{Collapsible list , bullets = yes , title = Peace treaties , Treaty of Brest-LitovskSigned 3 March 1918({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=11, day1=7, year1=1917, month2=3, day2=3, year2=1918) , Treaty of Tartu (Russian–Estonian)Signed 2 February 1920({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=11, day1=7, year1=1917, month2=2, day2=2, year2=1920) , Soviet–Lithuanian Peace TreatySigned 12 July 1920({{Age in years, months, weeks and da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English as the Bolshevists,. It signifies both Bolsheviks and adherents of Bolshevik policies. were a far-left, revolutionary Marxist faction founded by Vladimir Lenin that split with the Mensheviks from the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP), a revolutionary socialist political party formed in 1898, at its Second Party Congress in 1903. After forming their own party in 1912, the Bolsheviks took power during the October Revolution in the Russian Republic in November 1917, overthrowing the Provisional Government of Alexander Kerensky, and became the only ruling party in the subsequent Soviet Russia and later the Soviet Union. They considered themselves the leaders of the revolutionary proletariat of Russia. Their beliefs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacifism
Pacifism is the opposition or resistance to war, militarism (including conscription and mandatory military service) or violence. Pacifists generally reject theories of Just War. The word ''pacifism'' was coined by the French peace campaigner Émile Arnaud and adopted by other peace activists at the tenth Universal Peace Congress in Glasgow in 1901. A related term is '' ahimsa'' (to do no harm), which is a core philosophy in Indian Religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. While modern connotations are recent, having been explicated since the 19th century, ancient references abound. In modern times, interest was revived by Leo Tolstoy in his late works, particularly in '' The Kingdom of God Is Within You''. Mahatma Gandhi propounded the practice of steadfast nonviolent opposition which he called " satyagraha", instrumental in its role in the Indian Independence Movement. Its effectiveness served as inspiration to Martin Luther King Jr., James Lawson, Mary and Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanisław Lentz
Stanisław Lentz (April 23, 1861 – October 19, 1920) was a Polish painter, portraitist, illustrator, and a professor at the Academy of Fine Arts in Warsaw from 1909. Biography Stanisław Lentz was born in Warsaw, Poland, and studied at the Krakow School of Fine Arts with Feliks Szynalewski and Izydor Jabłoński 1877–1879, then continued his studies in Wojciech Gerson's drawing class in Warsaw. In 1880–1884 he studied abroad at the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich with Alexander von Wagner and Gyula Benczúr, and in 1884–1887 at the Académie Julian in Paris. After returning to Warsaw he teamed up with magazines. His illustrations were published by: *''Kłosy'' (1887–1890), *''Tygodnik Ilustrowany'' (1887–1898, 1905–1906, 1909–1910), *''Kurier Codzienny'' (1890–1891) In 1888, he became a member of the Society for the Encouragement of Fine Arts. In 1910 he joined the Society of Polish Artists ''Sztuka''. He traveled frequently abroad: in 1896 he visited Berlin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academy Of Fine Arts In Warsaw
Academy of Fine Arts in Warsaw ( pl, Akademia Sztuk Pięknych w Warszawie) is a public university of visual arts and applied arts located in the Polish capital. The Academy traces its history back to the Department of Arts founded at the Warsaw University in the Duchy of Warsaw in 1812. As a separate institution it was founded in 1844 in Congress Poland. In an upgrade in 1904 it was named the Warsaw School of Fine Arts; and in 1932 it received recognition as an Academy. At first the institute did not have its own building and classes were held in several locations around the city. Following an architectural competition a design by Alfons Gravier was chosen and construction began in 1911. The building was completed by the outbreak of the First World War. Faculties *Faculty of Painting *Faculty of Sculpture *Faculty of Graphic Arts *Faculty of Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art *Faculty of Interior Design *Faculty of Industrial Design *Faculty of Media Art Notable s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of the First World War. The Second Republic ceased to exist in 1939, when Invasion of Poland, Poland was invaded by Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union and the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic, marking the beginning of the European theatre of World War II, European theatre of the Second World War. In 1938, the Second Republic was the sixth largest country in Europe. According to the Polish census of 1921, 1921 census, the number of inhabitants was 27.2 million. By 1939, just before the outbreak of World War II, this had grown to an estimated 35.1 million. Almost a third of the population came from minority groups: 13.9% Ruthenians; 10% Ashkenazi Jews; 3.1% Belarusians; 2.3% Germans and 3.4% Czechs and Lithuanians. At the same time, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Revolution Of 1917
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government following two successive revolutions and a bloody civil war. The Russian Revolution can also be seen as the precursor for the other European revolutions that occurred during or in the aftermath of WWI, such as the German Revolution of 1918. The Russian Revolution was inaugurated with the February Revolution in 1917. This first revolt focused in and around the then-capital Petrograd (now Saint Petersburg). After major military losses during the war, the Russian Army had begun to mutiny. Army leaders and high ranking officials were convinced that if Tsar Nicholas II abdicated, the domestic unrest would subside. Nicholas agreed and stepped down, ushering in a new government led by the Russian Duma (parliament) which became the Russian Prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish I Corps In Russia
Polish I Corps in Russia ( pl, I Korpus Polski w Rosji; russian: 1-й Польский корпус) was a military formation formed on 24 July 1917 in Minsk from Polish and Lithuanian personnel serving in the Western and Northern Fronts of the Russian Army. In the chaotic period at the end of World War I on the Eastern Front, the Polish I Corps fought against the Bolshevik Red Army, cooperated with the German Ober Ost forces in taking Minsk, and after acknowledging the Regency Council in May 1918, it surrendered to the German forces in Babruysk. The soldiers were given safe passage to Warsaw, where they became part of the newly created Polish Army. History Formation The corps was formed at the initiative of the Chief Polish Military Committee (''Naczelny Polski Komitet Wojskowy''), a Polish faction in the revolutionary and split Russian Empire military. Its goal was to defend Poles inhabiting parts of Poland under Russian partitions and support the formation of independ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
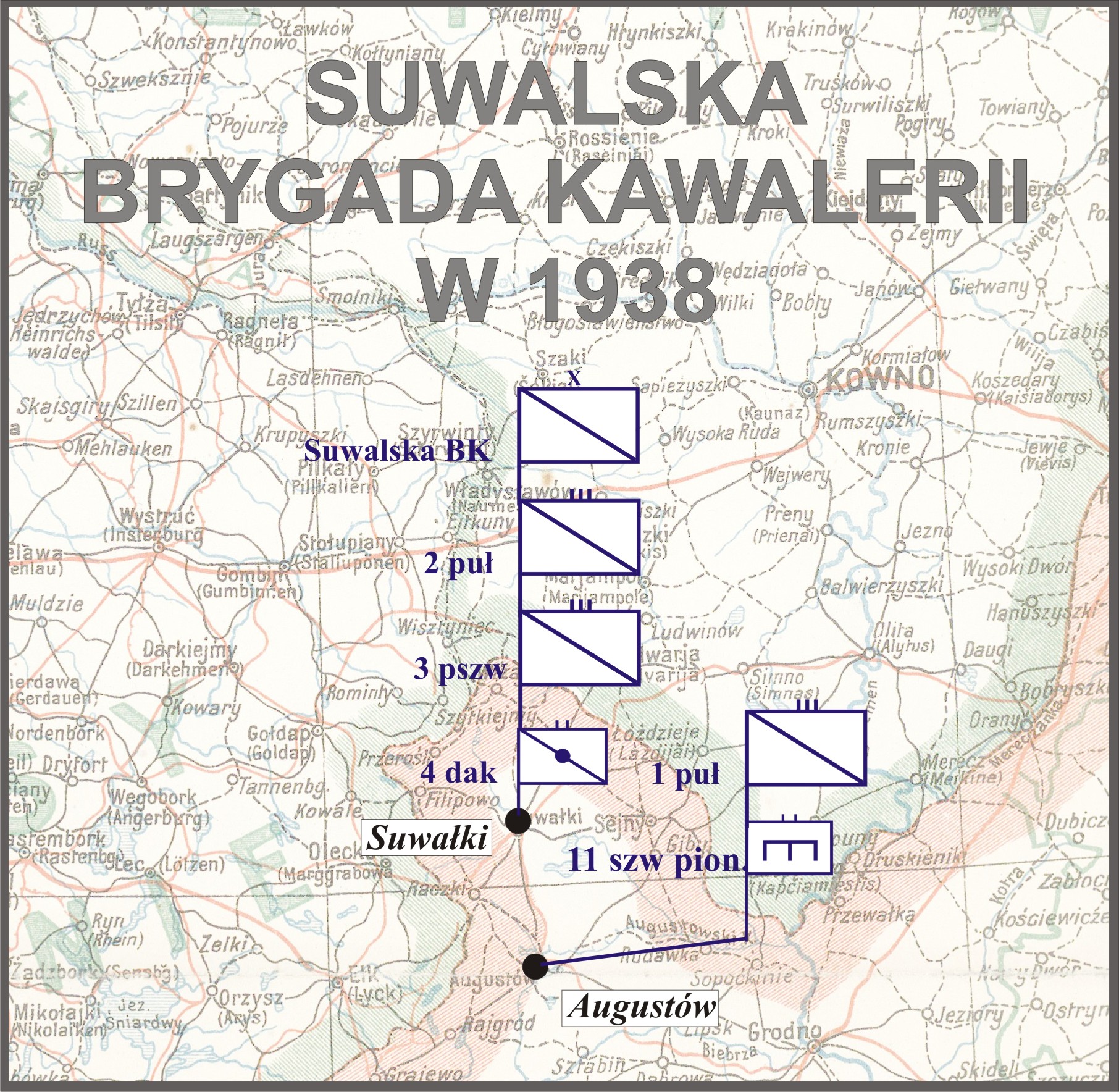
1st Krechowce Uhlan Regiment
The First Krechowce Uhlan Regiment was a mounted unit of the Polish Army, active in the Second Polish Republic. Its traditions were continued during World War II, by a regiment of the same name, which was part of Polish Armed Forces in the West. 1st Krechowce Uhlan Regiment was formed in 1915, as a unit of the Imperial Russian Army. It fought in World War I, Polish–Soviet War and the Invasion of Poland, as part of Suwalska Cavalry Brigade. Until 1939, the regiment was stationed in Augustów. It ceased to exist in 1947. First commandant of the regiment was a Tsarist officer of Polish ethnicity, Colonel Bolesław Mościcki, who was killed in 1918 near Luninets. Last commandant was Colonel Leon Strzelecki. First Uhlan Regiment was formed in 1915, as part of Imperial Russian Army's Puławy Legion. To commemorate its first victorious battle against German forces, the Battle of Krechowce, which took place on July 24, 1917, the Regiment was named after the village of Krechowce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Saint Petersburg
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |