|
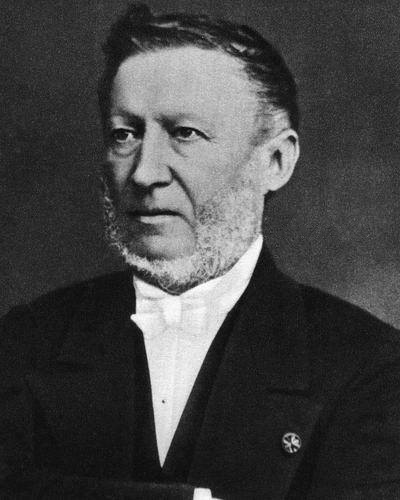
Jules Malou
Jules Edouard Xavier Malou (19 October 1810 – July 1886) was a Belgian statesman, a leader of the clerical party. Career Malou was born at Ypres. He was a civil servant in the department of justice when he was elected to the Chamber of Deputies by his native constituency in 1841, and was for some time governor of the province of Antwerp. He served as Minister of Finance in the coalition ministry of Jean Baptiste, Baron Nothomb in 1844 and formed with B. T. de Theux de Meylandt a Catholic cabinet in 1846 which lost power after the Liberal victory of 1847. Malou then became a member of the senate, and his party only regained ascendancy in 1870. The distinctly clerical ministry of Baron Jules d'Anethan retired in December 1871 after serious rioting in Brussels, and Malou was the real, though not the nominal, head of the more moderate clerical administrations of de Theux and Aspremont-Lynden (1870–1878). He disavowed the sympathy of Belgian Ultramontane politicians with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1884 Belgian General Election
Legislative elections were held in Belgium in June and July 1884, for partial Chamber and full Senate elections respectively.Sternberger, D, Vogel, B & Nohlen, D (1969) ''Die Wahl der Parlamente: Band I: Europa - Erster Halbband'', p105 Voter turnout was 79.1% in the Chamber of Representatives elections, although only 69,276 people were eligible to vote. Background The election occurred during the First School War. The incumbent Liberal government under Walthère Frère-Orban aimed to secularize education, which sparked heavy protests from Catholics. Regular partial elections for the Chamber of Representatives were held on Tuesday 10 June 1884, with a run-off on Tuesday 17 June. Under the alternating system, elections for the Chamber of Representatives were only held in five out of the nine provinces: Antwerp, Brabant, Luxembourg, Namur and West Flanders. Special elections were held in the arrondissements of Aalst and Sint-Niklaas, for one representative in each. The result wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Minister Of Belgium
german: Premierminister von Belgien , insignia = State Coat of Arms of Belgium.svg , insigniasize = 100px , insigniacaption = Coat of arms , insigniaalt = , flag = Government Ensign of Belgium.svg , flagsize = 125px , flagalt = , flagborder = yes , flagcaption = State Ensign , image = Informal meeting of ministers responsible for development (FAC). Arrivals Alexander De Croo (36766610160) (cropped2).jpg , imagesize = 200px , alt = , imagecaption = , incumbent = Alexander De Croo , acting = , incumbentsince = 1 October 2020 , department = Executive branch of the Belgian Federal Government , style = Mr Prime Minister His Excellency , type = , status = , abbreviation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules D'Anethan
Jules Joseph, Baron d'Anethan (23 April 1803 – 8 October 1888) was a Belgian Catholic Party politician. After serving as minister for Justice and Religion, D'Anethan was named the prime minister of Belgium and minister of Foreign Affairs by King Leopold II on 2 July 1870. During his term in office, d'Anethan was responsible for directing the Belgian reaction to the Franco-Prussian War. D'Anethan and the king agreed a programme whereby the King's favoured military reforms—in particular the abolition of ''Remplacement'' conscription—would be implemented, along with an agreement not to institute electoral reforms. He served as Foreign and War minister in his own government. D'Anethan was obliged to include in his cabinet ministers who were opposed to the abolition of ''Remplacement'' which led to conflicts with the King. A political crisis following his nomination of Pierre de Decker as governor of Limburg led to the resignation of d'Anethan's government. He later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legion Of Honour
The National Order of the Legion of Honour (french: Ordre national de la Légion d'honneur), formerly the Royal Order of the Legion of Honour ('), is the highest French order of merit, both military and civil. Established in 1802 by Napoleon, Napoleon Bonaparte, it has been retained (with occasional slight alterations) by all later French governments and regimes. The order's motto is ' ("Honour and Fatherland"); its Seat (legal entity), seat is the Palais de la Légion d'Honneur next to the Musée d'Orsay, on the left bank of the Seine in Paris. The order is divided into five degrees of increasing distinction: ' (Knight), ' (Officer), ' (Commander (order), Commander), ' (Grand Officer) and ' (Grand Cross). History Consulate During the French Revolution, all of the French Order of chivalry, orders of chivalry were abolished and replaced with Weapons of Honour. It was the wish of Napoleon, Napoleon Bonaparte, the French Consulate, First Consul, to create a reward to commend c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Leopold (Belgium)
The Order of Leopold ( nl, Leopoldsorde, french: Ordre de Léopold, ) is one of the three current Belgian national honorary orders of knighthood. It is the oldest and highest order of Belgium and is named in honour of its founder, King Leopold I. It consists of a military, a maritime and a civil division. The maritime division is only awarded to personnel of the merchant navy, and the military division to military personnel. The decoration was established on 11 July 1832 and is awarded by Royal order. History When Belgium became independent of the Netherlands, there was an urgent need to create a national honour system that could serve as a diplomatic gift. The national congress provided this exclusive right to the sovereign, this military honour system was written in Article 76. The first King of the Belgians, Leopold I of Belgium, used his constitutional right in a larger way than foreseen: not only military merit, but every service in honour of the Kingdom. Two years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minister Of State
Minister of State is a title borne by politicians in certain countries governed under a parliamentary system. In some countries a Minister of State is a Junior Minister of government, who is assigned to assist a specific Cabinet Minister. In other countries a Minister of State is a holder of a more senior position, such as a Cabinet Minister or even a Head of Government. High government ranks In several national traditions, the title "Minister of State" is reserved for government members of cabinet rank, often a formal distinction within it, or even its chief. *Brazil: Minister of State ( pt, Ministro de Estado) is the title borne by all members of the Federal Cabinet. *Kenya: A Minister of State generically refers to a more senior minister by virtue of the revenue power, or security implications of their ministry. For instance, ministries housed under the Office of the President, Office of the Deputy President and Office of the Prime Minister are titled as "Ministries of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Bruges
The Diocese of Bruges (in Dutch Bisdom Brugge) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in Belgium. It is a suffragan in the ecclesiastical province of the metropolis (religious jurisdiction), metropolitan Archdiocese of Mechelen-Brussels, which covers all of Belgium. A diocese from 1558 to its suppression in 1801, in 1832 it became a pre-diocesan apostolic vicariate as the Apostolic Administration of West Flanders. Its territory coincides with West Flanders. The episcopal see of the diocese is Sint-Salvator Cathedral, dedicated to Our Savior, in Bruges, West Flanders, which is also a minor basilica. The patron saint of the diocese is Saint Donatian, so the cathedral is also known as ''Sint-Salvators- en Donaaskathedraal''. Statistics , it pastorally served 965,000 Catholics (82.1% of 1,174,752 total) on 3,145 km² in 362 parishes and 65 missions with 708 priests (499 diocesan, 209 religious), 91 deacons, 1,986 lay religious (290 broth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
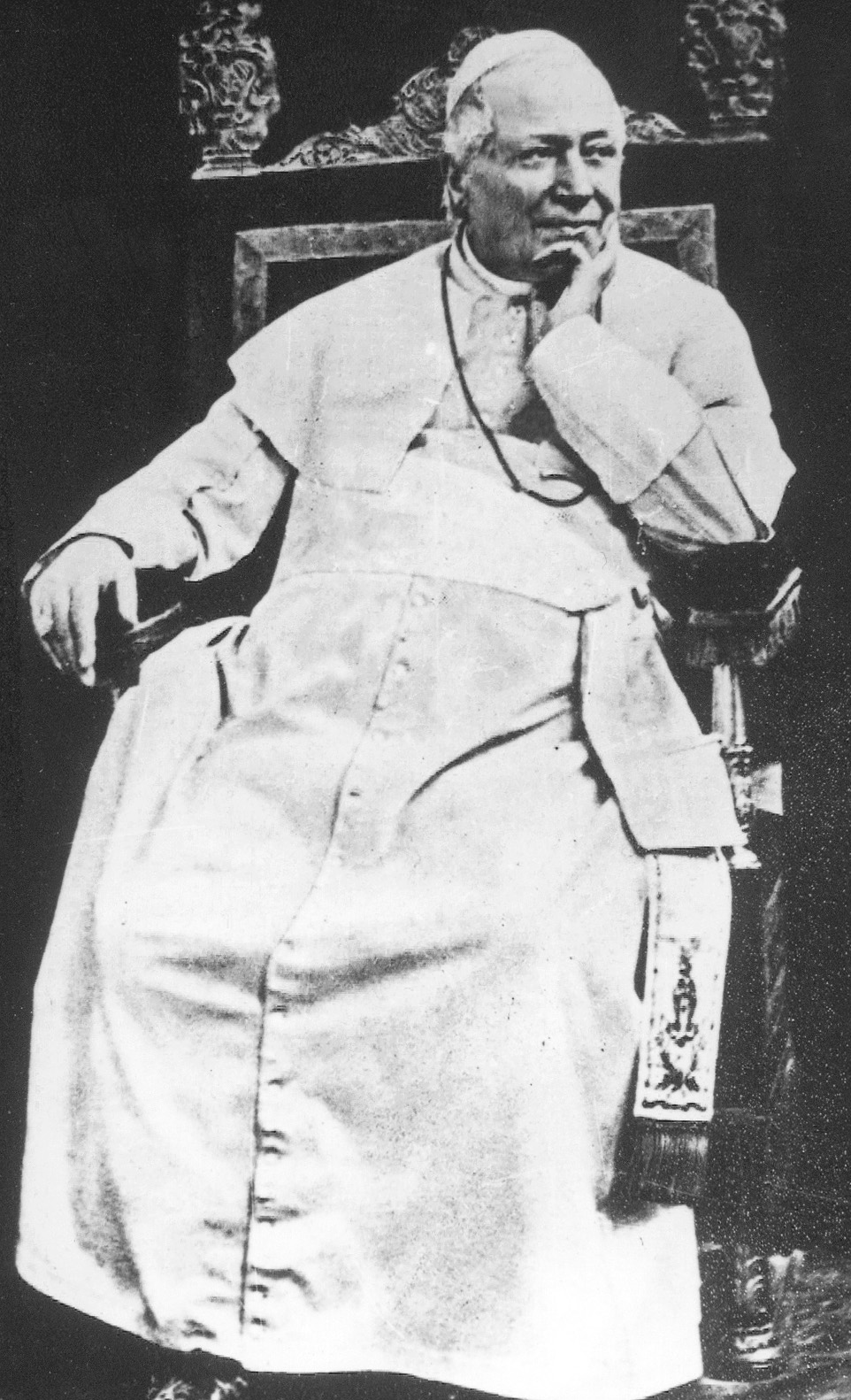
Jean-Baptiste Malou
Joannes Baptista or Jean-Baptiste Malou (1809–1864) was a Belgian theologian who became bishop of Bruges. Life Malou was born in Ypres on 30 June 1809, the son of Senator Jean-Baptiste Malou and Marie-Thérèse Vanden Peereboom. His older brother, Jules Malou, would be a prime minister of Belgium. He was educated at the Jesuit-run Collège de Saint-Acheul in France until 1828. During the Belgian Revolution he made a pilgrimage to Rome, where he determined to pursue a vocation to the priesthood and enrolled in theological studies at the Pontifical Ecclesiastical Academy and the Collegium Germanicum et Hungaricum. Thomas Joseph Lamy, "Malou (Jean-Baptiste)", ''Biographie Nationale de Belgique''vol. 13(Brussels, 1895), 253-258. Malou was ordained to the priesthood on 2 November 1834 and graduated Doctor of Sacred Theology in 1835, after which he returned to Belgium. He initially taught at the Major Seminary, Bruges, and from 1836 to 1848 was professor of dogmatic theology at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brabant (province)
The Province of Brabant (, , ) was a province in Belgium from 1830 to 1995. It was created in 1815 as South Brabant, part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. In 1995, it was split into the Dutch-speaking Flemish Brabant, the French-speaking Walloon Brabant and the bilingual Brussels-Capital Region. History United Kingdom of the Netherlands After the defeat of Napoleon in 1815, the United Kingdom of the Netherlands was created at the Congress of Vienna, consisting of territories which had been added to France by Napoleon: the former Dutch Republic and the Southern Netherlands. In the newly created kingdom, the former French département of Dyle became the new province of South Brabant, distinguishing it from Central Brabant (later Antwerp province); and from North Brabant (now part of the Netherlands), all named after the former Duchy of Brabant. The provincial governors during this time were: * 1815–1818: François Joseph Charles Marie de Mercy-Argenteau * 1818– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Woeste
Charles, Count Woeste (26 February 1837 – 5 April 1922), was a Belgian Roman Catholic politician of German descent. He was born in Brussels, the son of Edouard Woeste, who was of Prussian descent who became a naturalized Belgian on 15 January 1841. Edouard Woeste was consul for Prussia from 1843 to 1853 and married Constance Vauthier on 24 September 1834. In August 1855 Charles converted from Lutheranism, Prussian aristocracy's religion, to Catholicism, under the influence of his mother and father Delcourt. On 4 January 1866, he married Marie Greindl, daughter of lieutenant-general Léonard Greindl, who had been minister of war in the government of Pierre de Decker (1855). Education In October 1847, Charles joined the ''Royal Athenaeum'' of Brussels. Among his classmates were Edmond Picard, Charles Graux, Emile de Mot, Xavier Olin, and Pierre Van Humbeeck. He obtained the title of Doctor in Law at the Universite Libre de Bruxelles in 1858. Career He began his career as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Schools' War
The First School War (french: Première guerre scolaire, nl, Eerste schoolstrijd) was a political crisis in Belgium over the issue of religion in education. The School War marks the high water mark of the conflict between the conservative Catholic Party, and the secular Liberal Party. The war lasted from 1879 to 1884 and resulted in a period of nearly fifty years of Catholic political dominance. It was followed by a Second School War between 1950 and 1959. Background In the preceding centuries, education in Belgium had been dominated by the Catholic Church. In 1842, a new education law formalized religious education in primary schools, while also conceding the freedom of education guaranteed in Article 17 of the Constitution of 1831: Under the terms of Article 6 of the Education Act of 1842: In practice, the interpretation of the law varied and, since the vast majority of the Belgian population was Catholic, the Church was allowed considerable influence in schools. The quali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kulturkampf
(, 'culture struggle') was the conflict that took place from 1872 to 1878 between the Catholic Church led by Pope Pius IX and the government of Prussia led by Otto von Bismarck. The main issues were clerical control of education and ecclesiastical appointments. A unique feature of , compared to other struggles between the state and the Catholic Church in other countries, was Prussia's anti-Polish component. By extension the term is sometimes used to describe any conflict between secular and religious authorities or deeply opposing values, beliefs between sizable factions within a nation, community, or other group. Background Europe and the Catholic Church Under the influence of new emerging philosophies and ideologies, such as the enlightenment, realism, positivism, materialism, nationalism, secularism, and liberalism, the role of religion in society and the relationship between society and established churches underwent profound changes in the 18th and 19th centuries. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |