|
Joseph Lloyd Brereton
Prebendary Joseph Lloyd Brereton, (19 October 1822 – 15 August 1901), was a British clergyman, educational reformer and writer, who founded inexpensive schools for the education of the middle classes. Through his work and writings he influenced others to make similar foundations. Life Brereton was born on 19 October 1822 at Little Massingham Rectory, near King's Lynn. He was third son of eleven children of Charles David Brereton (1790–1868), for forty-seven years rector of Little Massingham, by his wife Frances (1796–1880), daughter of Joseph Wilson of Highbury Hill, Middlesex, and Stowlangtoft Hall, Suffolk. The father was an influential writer on poor law and agricultural questions between 1825 and 1828. Brereton's youngest brother, Robert Maitland Brereton, became a railway and civil engineer. Brereton was educated at Islington proprietary school under Dr. John Jackson (bishop), John Jackson, afterwards bishop of London, and at Rugby under Dr. Thomas Arnold (1838–4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
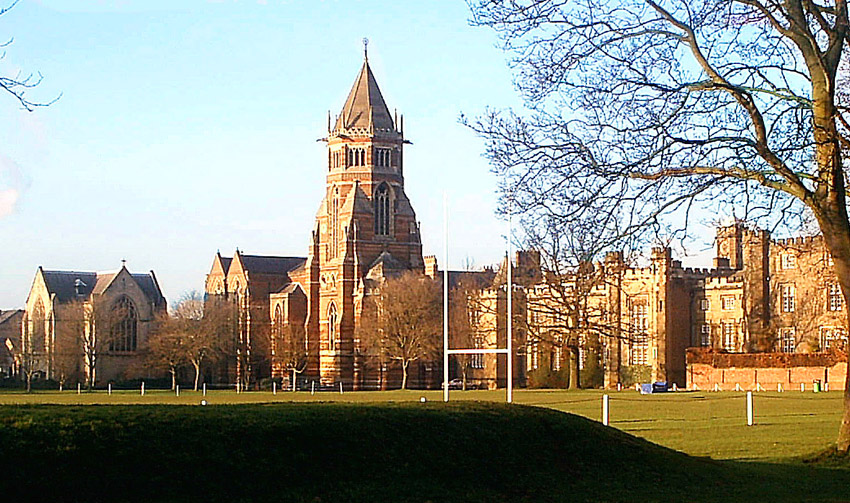
Rugby School
Rugby School is a public school (English independent boarding school for pupils aged 13–18) in Rugby, Warwickshire, England. Founded in 1567 as a free grammar school for local boys, it is one of the oldest independent schools in Britain. Up to 1667, the school remained in comparative obscurity. Its re-establishment by Thomas Arnold during his time as Headmaster, from 1828 to 1841, was seen as the forerunner of the Victorian public school. It was one of nine prestigious schools investigated by the Clarendon Commission of 1864 and later regulated as one of the seven schools included in the Public Schools Act 1868. The school's alumni – or "Old Rugbeians" – include a UK prime minister, several bishops, prominent poets, scientists, writers and soldiers. Rugby School is the birthplace of rugby football. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Church
The term ''high church'' refers to beliefs and practices of Christian ecclesiology, liturgy, and theology that emphasize formality and resistance to modernisation. Although used in connection with various Christian traditions, the term originated in and has been principally associated with the Anglican tradition, where it describes churches using a number of ritual practices associated in the popular mind with Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy. The opposite tradition is '' low church''. Contemporary media discussing Anglican churches erroneously prefer the terms evangelical to ''low church'' and Anglo-Catholic to ''high church'', even though their meanings do not exactly correspond. Other contemporary denominations that contain high church wings include some Lutheran, Presbyterian, and Methodist churches. Variations Because of its history, the term ''high church'' also refers to aspects of Anglicanism quite distinct from the Oxford Movement or Anglo-Catholicism. There rema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nathaniel Woodard
Nathaniel Woodard (; 21 March 1811 – 25 April 1891) was a priest in the Church of England. He founded 11 schools for the middle classes in England whose aim was to provide education based on "sound principle and sound knowledge, firmly grounded in the Christian faith". His educational principles are promoted today through the Woodard Corporation, a registered charity. Early life Woodard was born at Basildon Hall in Essex (now known as Barstable Hall) the son of John Woodard, a country gentleman of limited means. He was brought up and educated privately by his mother Mary née Silley, a pious and devout woman. In 1834 he entered Magdalen Hall, Oxford (now Hertford College, Oxford), where his academic studies were interrupted by his marriage in 1836 to Harriet Brill, although he took a pass degree in 1840. As a result of the influence of his mother, Woodard's religious sympathies were Evangelical when he first became a student at Oxford, but, whilst he was there, he soon found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exeter Cathedral
Exeter Cathedral, properly known as the Cathedral Church of Saint Peter in Exeter, is an Anglican cathedral, and the seat of the Bishop of Exeter, in the city of Exeter, Devon, in South West England. The present building was complete by about 1400, and has several notable features, including an early set of misericords, an astronomical clock and the longest uninterrupted medieval stone vaulted ceiling in the world. History The founding of the cathedral at Exeter, dedicated to Saint Peter, dates from 1050, when the seat of the bishop of Devon and Cornwall was transferred from Crediton because of a fear of sea-raids. A Saxon minster already existing within the town (and dedicated to Saint Mary and Saint Peter) was used by Leofric as his seat, but services were often held out of doors, close to the site of the present cathedral building. In 1107 William Warelwast was appointed to the see, and this was the catalyst for the building of a new cathedral in the Norman style. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prebendary
A prebendary is a member of the Roman Catholic or Anglican clergy, a form of canon with a role in the administration of a cathedral or collegiate church. When attending services, prebendaries sit in particular seats, usually at the back of the choir stalls, known as prebendal stalls. History At the time of the ''Domesday Book'' in 1086, the canons and dignitaries of the cathedrals of England were supported by the produce and other profits from the cathedral estates.. In the early 12th century, the endowed prebend was developed as an institution, in possession of which a cathedral official had a fixed and independent income. This made the cathedral canons independent of the bishop, and created posts that attracted the younger sons of the nobility. Part of the endowment was retained in a common fund, known in Latin as ''communia'', which was used to provide bread and money to a canon in residence in addition to the income from his prebend. Most prebends disappeared in 1547, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public School (UK)
In England and Wales (but not Scotland), a public school is a fee-charging endowed school originally for older boys. They are "public" in the sense of being open to pupils irrespective of locality, denomination or paternal trade or profession. In Scotland, a public school is synonymous with a state school in England and Wales, and fee-charging schools are referred to as private schools. Although the term "public school" has been in use since at least the 18th century, its usage was formalised by the Public Schools Act 1868, which put into law most recommendations of the 1864 Clarendon Report. Nine prestigious schools were investigated by Clarendon (including Merchant Taylors' School and St Paul's School, London) and seven subsequently reformed by the Act: Eton, Shrewsbury, Harrow, Winchester, Rugby, Westminster, and Charterhouse. Public schools are associated with the ruling class. Historically, public schools provided many of the military officers and administrators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Buckland School
West Buckland School is an independent school in West Buckland, Devon in the English public school tradition. It comprises a senior school, preparatory school, and a nursery. It is a relatively high performing school in Devon. It was one of eight schools shortlisted for 'Boarding School of the Year' in the TES Independent School Awards 2019, a category won by Cottesmore School. The school facilitates 640 pupils of whom around 140 board; 16% of students are international. The day pupils and weekly boarders are drawn from a wide area of North Devon and beyond, many using the large school bussing operation in collaboration with local coach operators. History West Buckland School was founded as the Devon County School in 1858 by Rev. J.L. Brereton to provide a public school education for sons of farmers and the middle class. The foundation stone of the Gothic(?)-style buildings was laid in October 1860 by Earl Fortescue, who had provided land and other support for the school. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
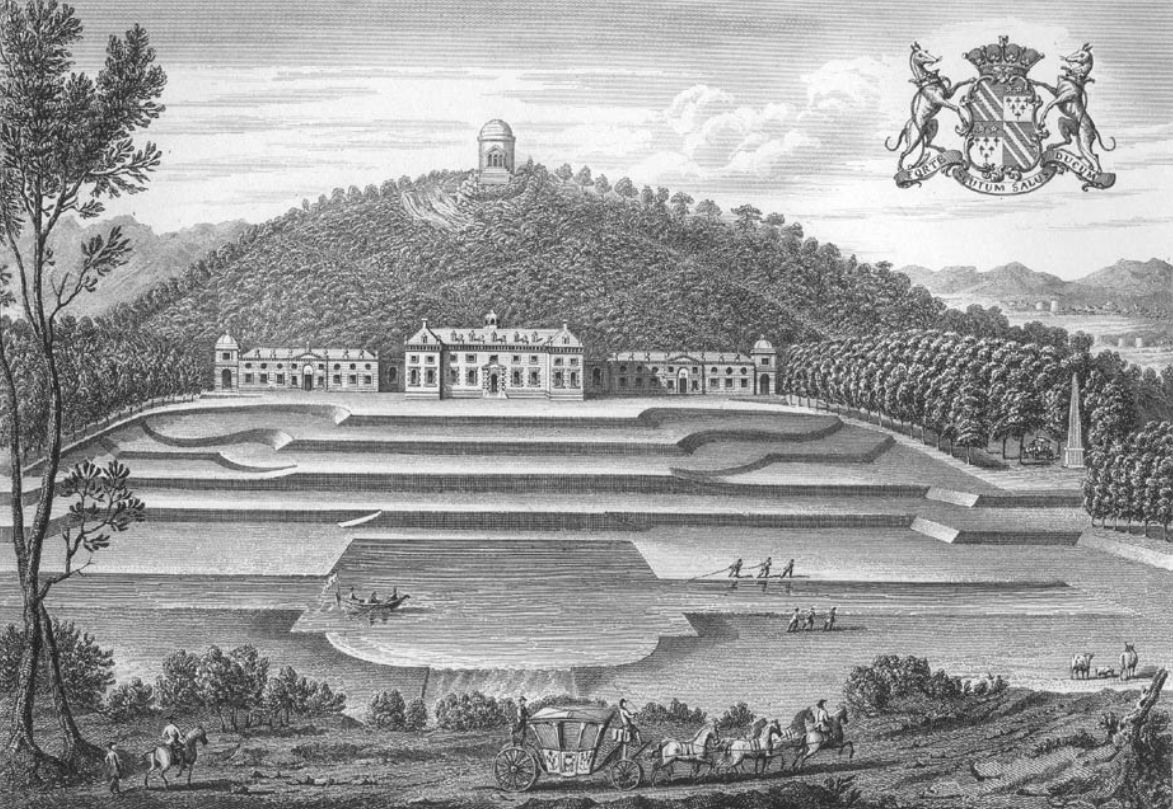
Castle Hill, Filleigh
Castle Hill in the parish of Filleigh in North Devon, is an early Neo-Palladian country house situated north-west of South Molton and south-east of Barnstaple. It was built in 1730 by Hugh Fortescue, 14th Baron Clinton (1696–1751), who was later created in 1751 1st Baron Fortescue and 1st Earl of Clinton, the son of Hugh Fortescue (died 1719), lord of the manor of Filleigh, Weare Giffard, etc., whose family is earliest recorded as residing in the 12th century at the manor of Whympston in the parish of Modbury in South Devon. The Fortescue family became major land owners, influential in British and West Country history. Castle Hill is a rare example in Devon of an 18th-century country mansion "on the grand scale". The house was substantially reconstructed following a disastrous fire in 1934. It was designated a Grade II* listed building in 1967. The park and gardens are Grade I listed in the National Register of Historic Parks and Gardens. Today the property is leased ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advowson
Advowson () or patronage is the right in English law of a patron (avowee) to present to the diocesan bishop (or in some cases the ordinary if not the same person) a nominee for appointment to a vacant ecclesiastical benefice or church living, a process known as ''presentation'' (''jus praesentandi'', Latin: "the right of presenting"). The word derives, via French, from the Latin ''advocare'', from ''vocare'' "to call" plus ''ad'', "to, towards", thus a "summoning". It is the right to nominate a person to be parish priest (subject to episcopal – that is, one bishop's – approval), and each such right in each parish was mainly first held by the lord of the principal manor. Many small parishes only had one manor of the same name. Origin The creation of an advowson was a secondary development arising from the process of creating parishes across England in the 11th and 12th centuries, with their associated parish churches. A major impetus to this development was the legal exac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh Fortescue, 3rd Earl Fortescue
Hugh Fortescue, 3rd Earl Fortescue DL (4 April 1818 – 10 October 1905), known as Viscount Ebrington from 1841 to 1861, was a British peer and occasional Liberal Party politician. Life He was born in London on 4 April 1818. He was the eldest son of Hugh Fortescue, 2nd Earl Fortescue (1783-1861), by his first wife, Lady Susan (died 1827), eldest daughter of Dudley Ryder, 1st Earl of Harrowby. He was a Cambridge Apostle. He was appointed Deputy Lieutenant of Devon on 4 March 1839. He entered the House of Commons in 1841 as a member for Plymouth. He lost this seat in 1852, but returned in 1854 for Marylebone, which seat he held until January 1859, when he resigned. In December of that year, however, he was called up to the House of Lords by a writ of acceleration. In 1861, he succeeded to his father's earldom. Family He married Georgiana Augusta Caroline Dawson-Damer (13 June 1826 – 8 Dec 1866), granddaughter of John Dawson, 1st Earl of Portarlington, on 1 March 1847. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |