|
Jaculus (rodent)
The genus ''Jaculus'' is a member of the Dipodinae subfamily of dipodoid rodents (jerboas). ''Jaculus'' species are distributed in desert and semi-arid regions across northern Africa, the Sahara, the Horn of Africa, Arabia, the Middle East, and Central Asia. Collectively, the species within the genus may be commonly referred to as "desert jerboas", although this more particularly applied to the lesser Egyptian jerboa (''Jaculus jaculus'').Myers ''et al.'' (2006). Species The following species are recognised for the genus ''Jaculus'': * Blanford's jerboa, ''Jaculus blanfordi'' * Lesser Egyptian jerboa, ''Jaculus jaculus'' * Greater Egyptian jerboa The greater Egyptian jerboa (''Jaculus orientalis'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is found in Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Saudi Arabia, Tunisia, and is possibly extinct in the Negev Desert of Israel. Its natural habitat ..., ''Jaculus orientalis'' * Thaler's jerboa ''Jaculus thaleri'' * African hamma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. At , the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world. Geographically, the Arabian Peninsula includes Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Yemen, as well as the southern portions of Iraq and Jordan. The largest of these is Saudi Arabia. In the classical era, the southern portions of modern-day Syria, Jordan, and the Sinai Peninsula were also considered parts of Arabia (see Arabia Petraea). The Arabian Peninsula formed as a result of the rifting of the Red Sea between 56 and 23 million years ago, and is bordered by the Red Sea to the west and southwest, the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the northeast, the Levant and Mesopotamia to the north and the Arabian Sea and the Indian Oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Of Western Asia
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipodidae
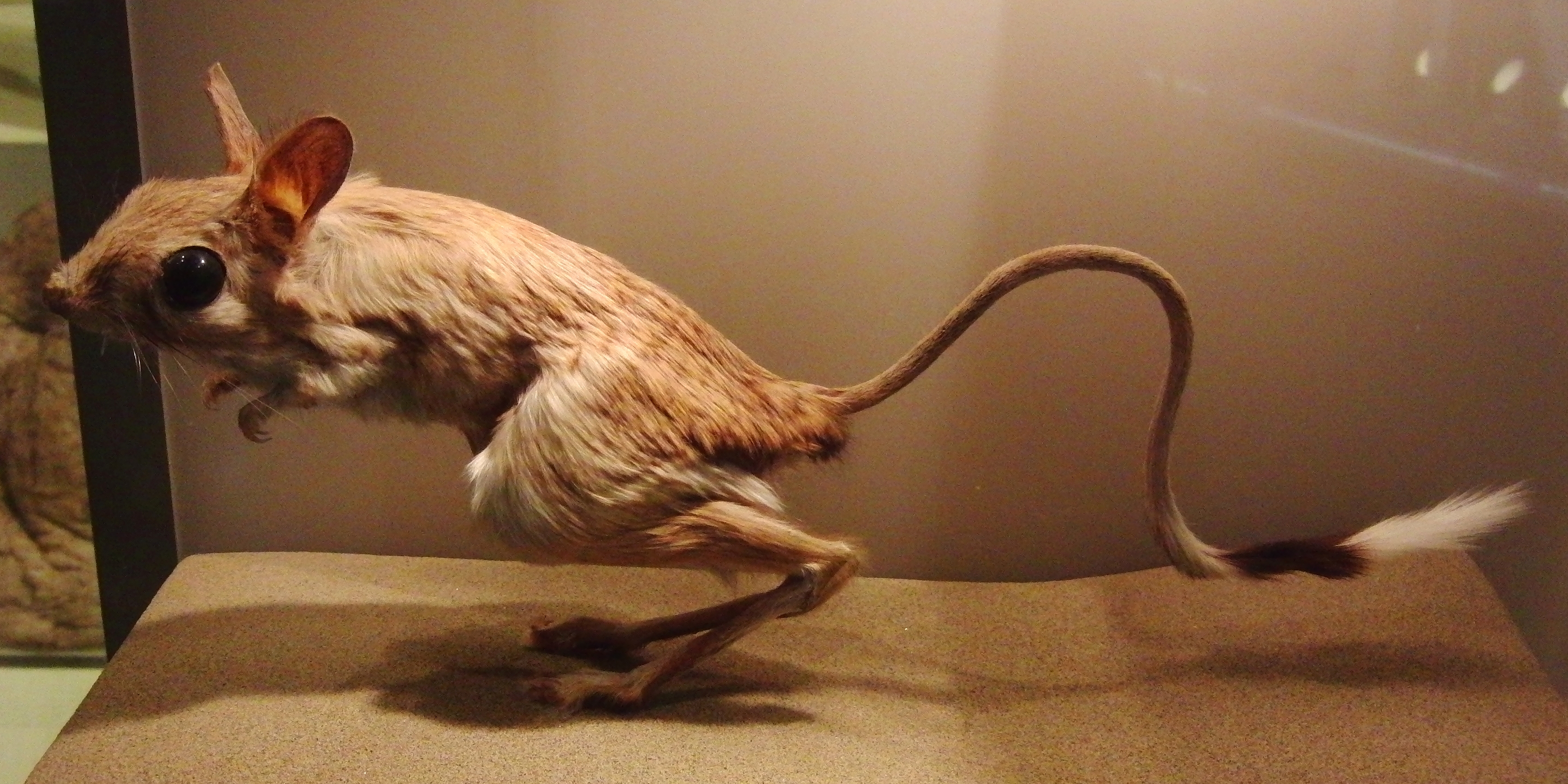
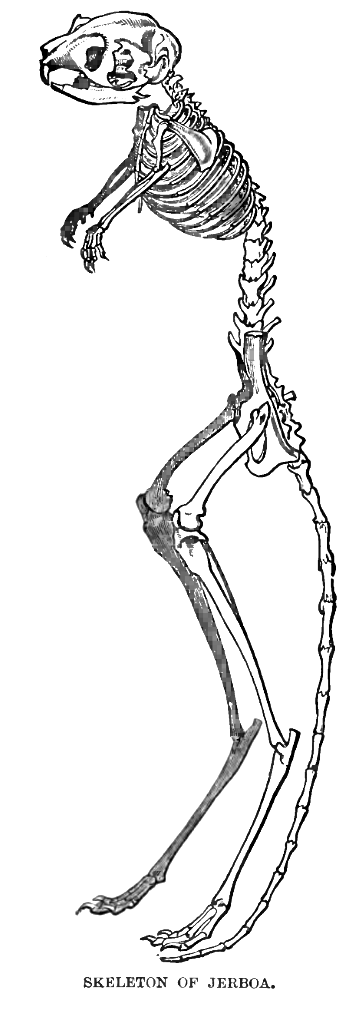
Jerboas (from ar, جربوع ') are hopping desert Rodent, rodents found throughout North Africa and Asia, and are members of the family Dipodidae. They tend to live in hot deserts. When chased, jerboas can run at up to . Some species are preyed on by little owls (''Athene noctua'') in central Asia. Most species of jerboas have excellent hearing that they use to avoid becoming the prey of nocturnal predators. The typical lifespan of a jerboa is around 6 years. Taxonomy Jerboas, as previously defined, were thought to be Paraphyly, paraphyletic, with the jumping mice (Zapodidae) and Birch mouse, birch mice (Sminthidae) also classified in the family Dipodidae. However, phylogenetic analysis split all three as distinct families, leaving just the jerboas in Dipodidae and revealing them to be a monophyletic group. Anatomy and body features Jerboas look somewhat like miniature kangaroos, and have some external similarities. Both have long hind legs, short forelegs, and long tails. J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaculus (rodent)
The genus ''Jaculus'' is a member of the Dipodinae subfamily of dipodoid rodents (jerboas). ''Jaculus'' species are distributed in desert and semi-arid regions across northern Africa, the Sahara, the Horn of Africa, Arabia, the Middle East, and Central Asia. Collectively, the species within the genus may be commonly referred to as "desert jerboas", although this more particularly applied to the lesser Egyptian jerboa (''Jaculus jaculus'').Myers ''et al.'' (2006). Species The following species are recognised for the genus ''Jaculus'': * Blanford's jerboa, ''Jaculus blanfordi'' * Lesser Egyptian jerboa, ''Jaculus jaculus'' * Greater Egyptian jerboa The greater Egyptian jerboa (''Jaculus orientalis'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is found in Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Saudi Arabia, Tunisia, and is possibly extinct in the Negev Desert of Israel. Its natural habitat ..., ''Jaculus orientalis'' * Thaler's jerboa ''Jaculus thaleri'' * African hamma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Michigan
, mottoeng = "Arts, Knowledge, Truth" , former_names = Catholepistemiad, or University of Michigania (1817–1821) , budget = $10.3 billion (2021) , endowment = $17 billion (2021)As of October 25, 2021. , president = Santa Ono , provost = Laurie McCauley , established = , type = Public research university , academic_affiliations = , students = 48,090 (2021) , undergrad = 31,329 (2021) , postgrad = 16,578 (2021) , administrative_staff = 18,986 (2014) , faculty = 6,771 (2014) , city = Ann Arbor , state = Michigan , country = United States , coor = , campus = Midsize City, Total: , including arboretum , colors = Maize & Blue , nickname = Wolverines , sporti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Hammada Jerboa
African or Africans may refer to: * Anything from or pertaining to the continent of Africa: ** People who are native to Africa, descendants of natives of Africa, or individuals who trace their ancestry to indigenous inhabitants of Africa *** Ethnic groups of Africa *** Demographics of Africa *** African diaspora ** African, an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to the African Union ** Citizenship of the African Union ** Demographics of the African Union **Africanfuturism ** African art ** *** African jazz (other) ** African cuisine ** African culture ** African languages ** African music ** African Union ** African lion, a lion population in Africa Books and radio * ''The African'' (essay), a story by French author J. M. G. Le Clézio * ''The African'' (Conton novel), a novel by William Farquhar Conton * ''The African'' (Courlander novel), a novel by Harold Courlander * ''The Africans'' (radio program) Music * "African", a song by Peter Tosh f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Egyptian Jerboa
The greater Egyptian jerboa (''Jaculus orientalis'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is found in Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Saudi Arabia, Tunisia, and is possibly extinct in the Negev Desert of Israel. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry shrubland, sandy shores, and arable land. Description An adult greater Egyptian jerboa has a head-and-body length of about and a tail of . The upper parts are yellowish-brown or sandy-brown and the underparts are white. The hind legs are very large and are about four times longer than the forelimbs. The feet have hairy pads which improves locomotion on sand. The tail is nearly naked but ends in a large tuft of hair which is black at the base and white at the tip. The tail is used as a prop to stabilise the animal when it stands and moves on its hind legs. Distribution and habitat On the African continent, the greater Egyptian jerboa is found in Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya and Egypt. It is also prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blanford's Jerboa
Blanford's jerboa (''Jaculus blanfordi'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is native to Central Asia and is found in Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Iran and Pakistan. Taxonomy Blanford's jerboa was first described in 1884 by the British zoologist James Albert Murray, curator of the Karachi Museum and author of a number of books on the birds and mammals of the Indian subcontinent. He named it "''Jaculus blanfordi''" in honour of the British geologist and zoologist William Thomas Blanford who was a member of the Indian Geological Survey and later published works on the fauna of India. Distribution and habitat Blanford's jerboa is native to Central Asia. Its range extends from Turkmenistan and Iran, through the Kyzyl Kum Desert and Karakum Desert to central Uzbekistan, Afghanistan and southwestern Pakistan. Its typical habitat is bare clayey or gravelly areas in deserts and other arid localities, but not sandy areas with dunes. Behaviour Blanford's jerb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)