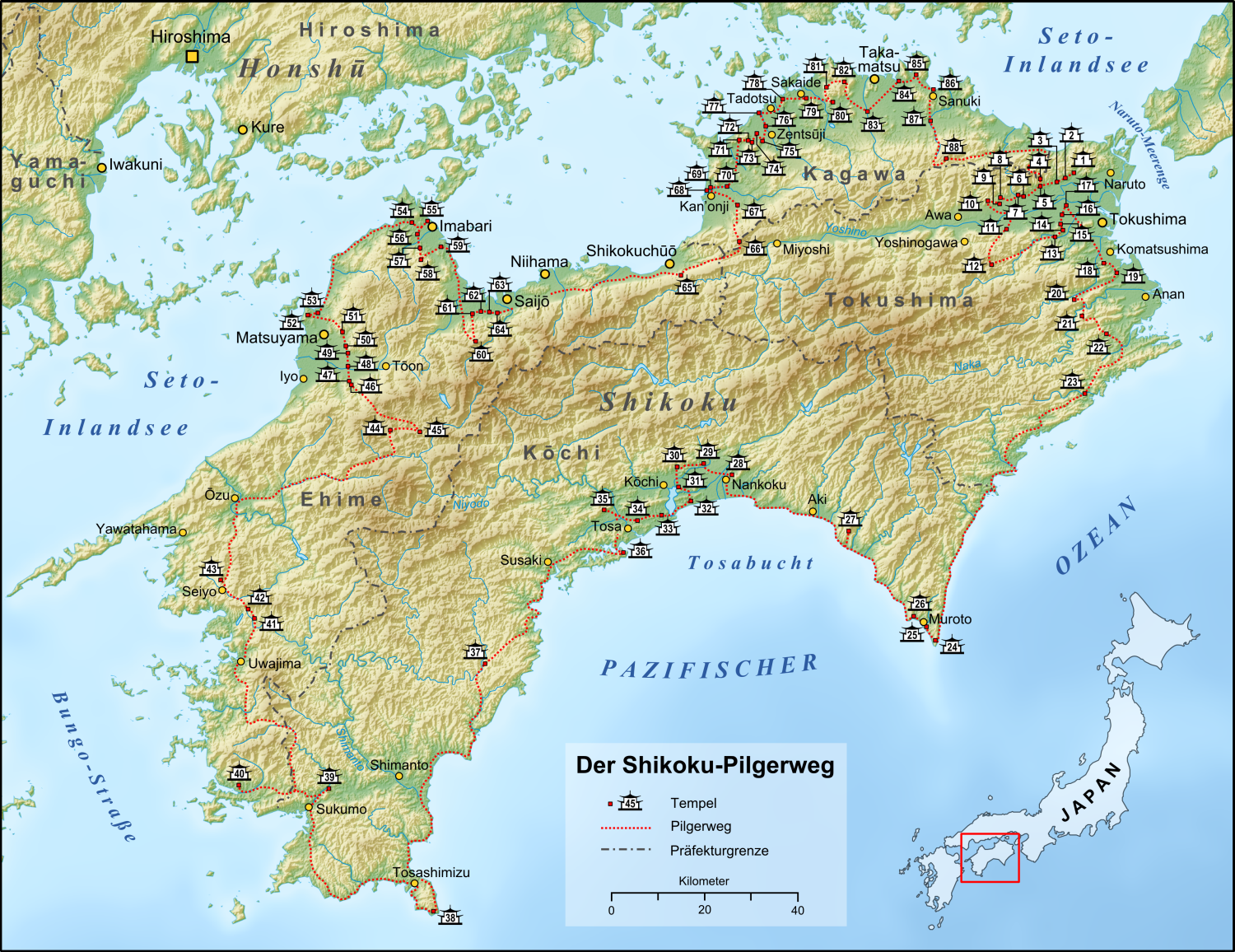
|
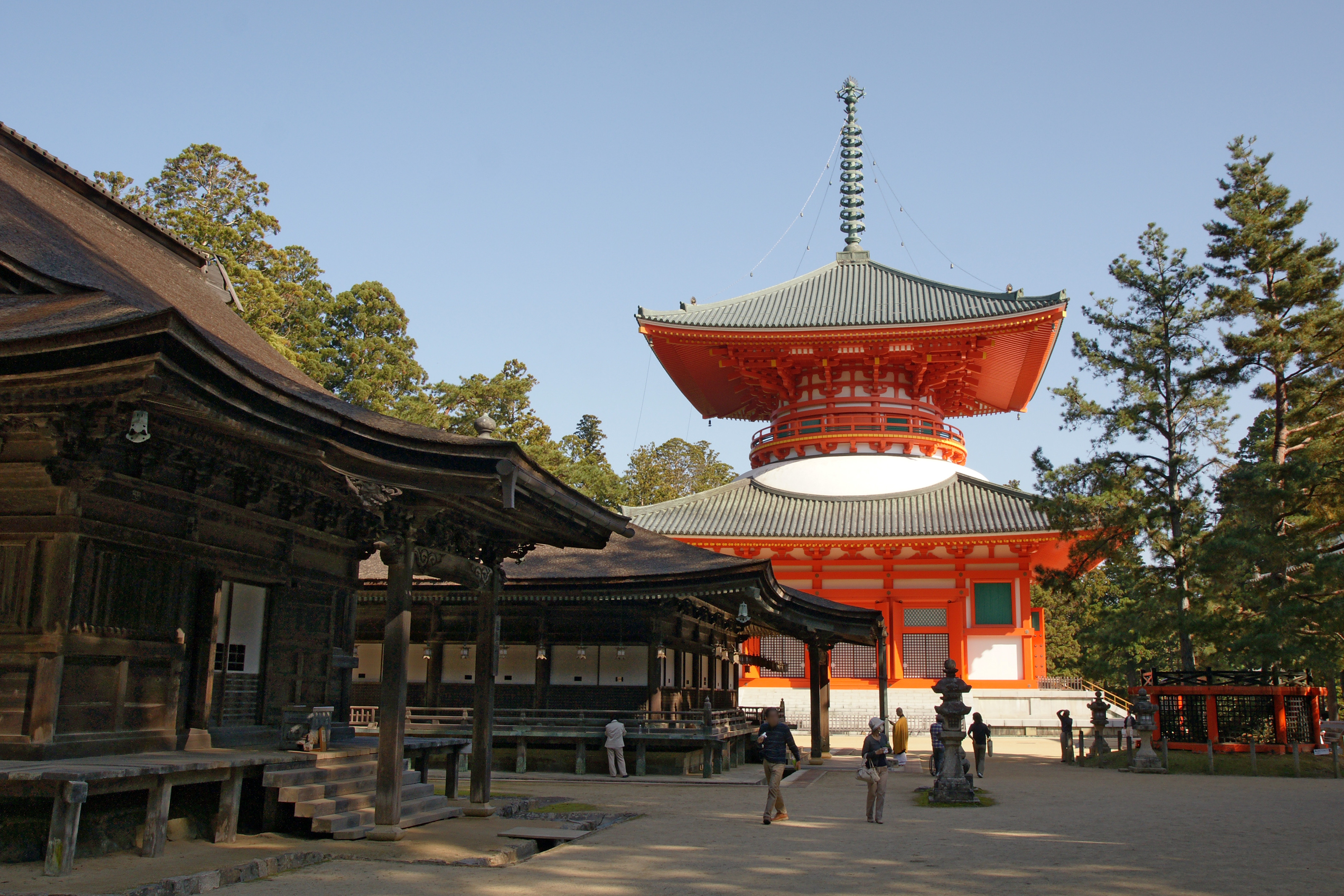
Jūraku-ji (Awa)
is a Kōya-san Shingon temple in Awa, Tokushima Prefecture, Japan. Temple 7 on the Shikoku 88 temple pilgrimage, the main image is of Amida Nyorai. The temple is said to have been founded by Kōbō Daishi, who carved the image. See also * Shikoku 88 temple pilgrimage The or is a multi-site pilgrimage of 88 temples associated with the Buddhist monk Kūkai (''Kōbō Daishi'') on the island of Shikoku, Japan. A popular and distinctive feature of the island's cultural landscape, and with a long history, ... References Buddhist pilgrimage sites in Japan Buddhist temples in Tokushima Prefecture Kōyasan Shingon temples Temples of Amitābha Shikoku Pilgrimage Sites {{Japan-Buddhist-temple-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P4022616ー7番十楽寺本堂
P4 may refer to: Computing * Intel Pentium 4, a processor series shipped from 2000 to 2008 ** The P4 power connector, introduced in the ATX12V 1.0 standard to power these and later CPUs * The i486DX (P4) model of the Intel 80486 microprocessor, introduced in 1989 * P4 (programming language), for controlling network data forwarding * P4, the Perforce software command line client Media * P4 Radio Hele Norge (PFI), a Norwegian radio company ** Kanal 24 (Kanal 4), which acquired the Norwegian P4 channel from PFI * Sveriges Radio P4, a Swedish radio channel * ''Persona 4'', a 2008 video game * '' Periphery IV: Hail Stan'', 2019 album by American progressive metal band Periphery Military * Skaraborg Regiment (armoured), a Swedish army unit, designated P 4 * Peugeot P4, a French military vehicle Science * P4 laboratory, a biosafety level 4 facility * Tetraphosphorus (P4), an allotrope of phosphorus * Group p4, the plane symmetry group wallpaper group ''p''4 * Progesterone (Pregn-4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shingon
is one of the major schools of Buddhism in Japan and one of the few surviving Vajrayana lineages in East Asian Buddhism. It is a form of Japanese Esoteric Buddhism and is sometimes called "Tōmitsu" (東密 lit. "Esoteric [Buddhism] of Tō-ji"). The word ''shingon'' is the Kan-on, Japanese reading of the Traditional Chinese characters, Chinese word ('), which is the translation of the Sanskrit word mantra. The Chinese Esoteric Buddhism, Zhēnyán lineage was founded in China (c. 7th–8th centuries) by Indian Vajracharya, vajrācāryas (esoteric masters) like Śubhakarasiṃha, Vajrabodhi and Amoghavajra. These esoteric teachings would later flourish in Japan under the auspices of a Buddhist monk named Kūkai (, 774–835), who traveled to Tang dynasty, Tang China and received these esoteric transmissions from a Chinese master named Huiguo (746–805). Kūkai established his tradition at Mount Kōya (in Wakayama Prefecture), which remains the central pilgrimage center of Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Temples In Japan
Buddhist temples or monasteries are (along with Shinto shrines) the most numerous, famous, and important religious buildings in Japan.The term "Shinto shrine" is used in contrast to "Buddhist temple" to mirror the distinction made in Japanese between Shinto and Buddhist religious structures. In Japanese the first are called , the second . The shogunates or leaders of Japan have made it a priority to update and rebuild Buddhist temples since the Azuchi–Momoyama period, Momoyama period (late 16th century). The Japanese language, Japanese word for a Buddhist monastery is (kanji, ''kun'' reading), and the same kanji also has the pronunciation ''ji'' (''on'' reading), so temple names frequently end in ''-dera'' (rendaku, voiced) or ''-ji''. Another ending, , is normally used to refer to minor temples. Examples of temple names that have these suffixes are Kiyomizu-dera, Enryaku-ji and Kōtoku-in. Etymology The Japanese word for a Buddhist temple, , was anciently also written phonetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awa, Tokushima
270px, Awa-no-dochu earthen pillars Natural Monument 270px, Kumadani-ji Sanmon 270px, Yoshino River is a city located in Tokushima Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 35,631 in 15432 households and a population density of 190 persons per km2. The total area of the city is . Geography Awa is located in the northeastern part of Tokushima Prefecture, between the northern bank of the Yoshino River and Kagawa Prefecture. Parts of the city are within the borders of the Okumiyagawa-Uchidani Prefectural Natural Park. Neighbouring municipalities Kagawa Prefecture * Higashikagawa * Sanuki Tokushima Prefecture * Kamiita * Mima * Yoshinogawa Climate Awa has a Humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by warm summers and cool winters with light to no snowfall. The average annual temperature in Awa is 14.9 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1,335 mm with September as the wettest month. Demographics Per Japanese census data, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokushima Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located on the island of Shikoku. Tokushima Prefecture has a population of 682,439 (1 February 2025) and has a geographic area of 4,146 Square kilometre, km2 (1,601 sq mi). Tokushima Prefecture borders Kagawa Prefecture to the north, Ehime Prefecture to the west, and Kōchi Prefecture to the southwest. Tokushima, Tokushima, Tokushima is the capital and largest city of Tokushima Prefecture, with other major cities including Anan, Tokushima, Anan, Naruto, Tokushima, Naruto, and Yoshinogawa, Tokushima, Yoshinogawa. Tokushima Prefecture is located on the Kii Channel, connecting the Pacific Ocean and Seto Inland Sea, across from Wakayama Prefecture on the Kii Peninsula of the island of Honshu. Tokushima Prefecture is connected to Awaji Island across the Naruto Strait by the Ōnaruto Bridge as part of the Kobe-Awaji-Naruto Expressway, connecting the prefecture to the city of Kobe and the San'yō Expressway on Honshu. History Until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shikoku Pilgrimage
The or is a multi-site pilgrimage of 88 temples associated with the Buddhist monk Kūkai (''Kōbō Daishi'') on the island of Shikoku, Japan. A popular and distinctive feature of the island's cultural landscape, and with a long history, large numbers of pilgrims, known as , still undertake the journey for a variety of ascetic, pious, and tourism-related purposes. The pilgrimage is traditionally completed on foot, but modern pilgrims use cars, taxis, buses, bicycles, or motorcycles, and often augment their travels with public transportation. The standard walking course is approximately long and can take anywhere from 30 to 60 days to complete. In addition to the 88 "official" temples of the pilgrimage, there are 20 ''bekkaku'' (別格) temples, which are officially associated with the Shikoku Pilgrimage (and hundreds more ''bangai'' (番外) temples, simply meaning "outside the numbers," which are not considered part of the official 88). To complete the pilgrimage, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amida Nyorai
Amida can mean : Places and jurisdictions * Amida (Mesopotamia), now Diyarbakır, an ancient city in Asian Turkey; it is (nominal) seat of: ** The Chaldean Catholic Archeparchy of Amida ** The Latin titular Metropolitan see of Amida of the Romans ** The Armenian Catholic titular see Amida of the Armenians ** The Syrian Catholic (Antiochian Rite) titular Metropolitan see Amida of the Syriacs * Mount Amida, mountain in Saeki-ku, Hiroshima, Japan Other * Amitābha Buddha, in Japanese * ''Amida'' (beetle), a beetle genus * ''Amida'', a ladder climbing puzzle video game * Amida, is Swiss watchmaker founded in 1925 in Grenchen. See also * Amitabha (other) * Amidah, the central prayer of Jewish worship * Amidakuji, a way of drawing lots * Aëtius of Amida Aëtius of Amida (; ; Latin: ''Aëtius Amidenus''; fl. mid-5th century to mid-6th century) was a Byzantine Greek physician and medical writer, particularly distinguished by the extent of his erudition. His birt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Pilgrimage Sites In Japan
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century BCE. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of development which leads to awakening and full liberation from '' dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes such as asceticism or sensual indulgence. Teaching that ''dukkha'' arises alongside attachment or clinging, the Buddha advised meditation practices and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Temples In Tokushima Prefecture
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century BCE. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of development which leads to awakening and full liberation from '' dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes such as asceticism or sensual indulgence. Teaching that ''dukkha'' arises alongside attachment or clinging, the Buddha advised meditation practices and eth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |