|
Jugular Vein
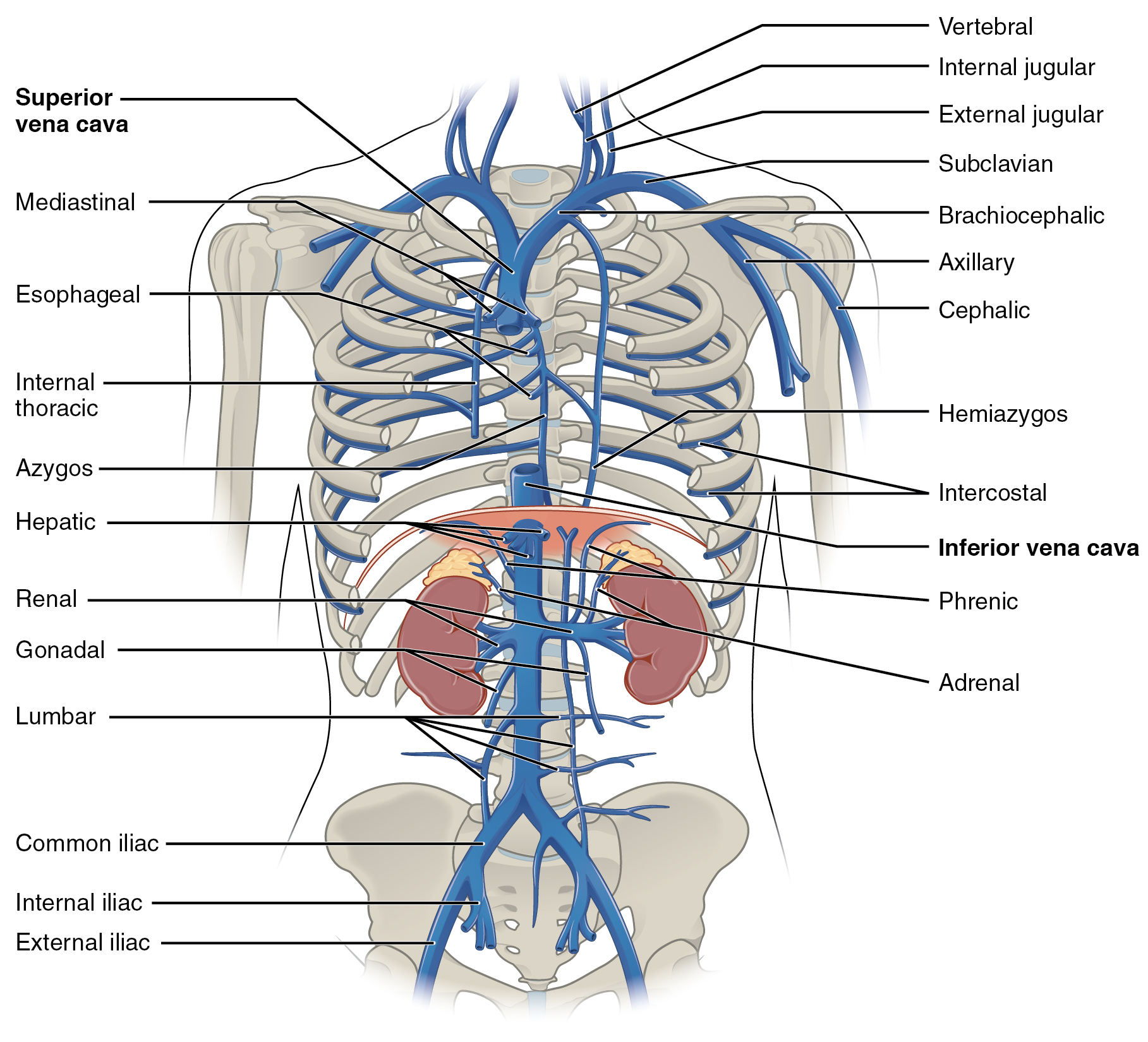
The jugular veins () are veins that take blood from the head back to the heart via the superior vena cava. The internal jugular vein descends next to the internal carotid artery and continues posteriorly to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Structure and function There are two sets of jugular veins: external and internal. The left and right external jugular veins drain into the subclavian veins. The internal jugular veins join with the subclavian veins more medially to form the brachiocephalic veins. Finally, the left and right brachiocephalic veins join to form the superior vena cava, which delivers deoxygenated blood to the right atrium of the heart. The jugular vein has tributaries consisting of petrosal sinus, facial, lingual, pharylingual, the thyroid, and sometimes the occipital vein. Internal The internal jugular vein is formed by the anastomosis of blood from the sigmoid sinus of the dura mater and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachiocephalic Vein
The left and right brachiocephalic veins (previously called innominate veins) are major veins in the Thorax, upper chest, formed by the union of the ipsilateral internal jugular vein and subclavian vein (the so-called venous angle) behind the sternoclavicular joint. The left brachiocephalic vein is more than twice the length of the right brachiocephalic vein. These veins merge to form the superior vena cava, a great vessel, posterior to the junction of the first costal cartilage with the Manubrium, manubrium of the sternum. The brachiocephalic veins are the major veins returning blood to the superior vena cava. Left and right veins Left brachiocephalic vein The left brachiocephalic vein is about 6cm, more than twice the length of the right brachiocephalic vein. and is formed by the confluence of the left subclavian vein, subclavian and left internal jugular veins. In addition the left vein receives drainage from the following tributaries: * The left vertebral vein, internal thor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the isthmus (: isthmi). Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis and growth and development in children. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by thy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Jugular Vein
The anterior jugular vein is a vein in the neck. Structure The anterior jugular vein lies lateral to the cricothyroid membrane. It begins near the hyoid bone by the confluence of several superficial veins from the submandibular region. Its tributaries are some laryngeal veins, and occasionally a small thyroid vein. It descends between the median line and the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, and, at the lower part of the neck, passes beneath that muscle to open into the termination of the external jugular vein, or, in some instances, into the subclavian vein. Just above the sternum the two anterior jugular veins communicate by a transverse trunk, the venous jugular arch, which receive tributaries from the inferior thyroid veins; each also communicates with the internal jugular. There are no valves in this vein. The pretracheal lymph nodes follow the anterior jugular vein on each side of the midline. Variation The anterior jugular vein varies consider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternocleidomastoid
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and flexion of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the accessory nerve. Etymology and location It is given the name ''sternocleidomastoid'' because it originates at the manubrium of the sternum (''sterno-'') and the clavicle (''cleido-'') and has an insertion at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull. Structure The sternocleidomastoid muscle originates from two locations: the manubrium of the sternum and the clavicle, hence it is said to have two heads: sternal head and clavicular head. It travels obliquely across the side of the neck and inserts at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull by a thin aponeurosis. The sternocleidomastoid is thick and narrow at its center, and broader and thinner at either end. The sternal head is a round fasciculus, tendinous in front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superficial Vein
Superficial veins are veins that are close to the surface of the body, as opposed to deep veins, which are far from the surface. Superficial veins are not paired with an artery, unlike the deep veins, which are typically associated with an artery of the same name. Superficial veins are important physiology, physiologically for cooling of the body. When the body is too hot, the body shunts blood from the deep veins to the superficial veins to facilitate heat transfer to the body's surroundings. Superficial veins are often visible underneath the skin. Those below the level of the heart tend to bulge out, which can be readily witnessed in the hand, where the veins bulge significantly less after the arm has been raised above the head for a short time. Veins become more visually prominent when lifting heavy weight, especially after a period of proper strength training. Physiologically, the superficial veins are not as important as the deep veins (as they carry less blood) and ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Jugular Vein
The external jugular vein is a paired jugular vein which receives the greater part of the blood from the exterior of the cranium and the deep parts of the face, being formed by the junction of the posterior division of the retromandibular vein with the posterior auricular vein. Structure The external jugular vein commences in the substance of the parotid gland, on a level with the angle of the mandible, and runs perpendicularly down the neck, in the direction of a line drawn from the angle of the mandible to the middle of the clavicle superficial to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. In its course, it crosses the sternocleidomastoid muscle obliquely, and in the subclavian triangle perforates the deep fascia, and ends in the subclavian vein lateral to or in front of the scalenus anterior, piercing the roof of the posterior triangle. It is separated from the sternocleidomastoid muscle by the investing layer of the deep cervical fascia, and is covered by the platysma, the superfici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate. In the human, the skull comprises two prominent parts: the neurocranium and the facial skeleton, which evolved from the first pharyngeal arch. The skull forms the frontmost portion of the axial skeleton and is a product of cephalization and vesicular enlargement of the brain, with several special senses structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, tongue and, in fish, specialized tactile organs such as barbels near the mouth. The skull is composed of three types of bone: cranial bones, facial bones and ossicles, which is made up of a number of fused flat and irregular bones. The cranial bones are joined at firm fibrous junctions called sutures and contains many foramina, fossae, processes, and sinuses. In zoology, the openings in the skull are called fenestrae, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Sheath
The carotid sheath is a condensation of the deep cervical fascia enveloping multiple vital neurovascular structures of the neck, including the common and internal carotid arteries, the internal jugular vein, the vagus nerve (CN X), and ansa cervicalis. The carotid sheath helps protects the structures contained therein. Anatomy One carotid sheath is situated on each side of the neck, extending between the base of the skull superiorly and the thorax inferiorly. Superiorly, the carotid sheath encircles the margins of the carotid canal and jugular foramen. Inferiorly, it terminates at the arch of the aorta; it is continuous inferiorly with the axillary sheath at the venous angle. Its inferior end occurs at the level of the first rib and sternum inferiorly (varying between the levels of C7 and T4). Structure The carotid sheath is a fibrous connective tissue formation surrounding several important structures of the neck. It is thicker around the arteries than around the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve (CN X), plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating involuntary functions within the human body. This nerve carries both sensory and motor fibers and serves as a major pathway that connects the brain to various organs, including the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. As a key part of the parasympathetic nervous system, the vagus nerve helps regulate essential involuntary functions like heart rate, breathing, and digestion. By controlling these processes, the vagus nerve contributes to the body's "rest and digest" response, helping to calm the body after stress, lower heart rate, improve digestion, and maintain homeostasis. The vagus nerve consists of two branches: the right and left vagus nerves. In the neck, the right vagus nerve contains approximately 105,000 fibers, while the left vagus nerve has about 87,000 fibers, according to one source. However, other sources report sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Carotid Artery
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) () are artery, arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external carotid artery, external and internal carotid artery, internal carotid arteries. Structure The common carotid arteries are present on the left and right sides of the body. These arteries originate from different arteries but follow symmetrical courses. The right common carotid originates in the neck from the brachiocephalic trunk; the left from the aortic arch in the thorax. These split into the external and internal carotid arteries at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage, at around the level of the fourth cervical vertebra. The left common carotid artery can be thought of as having two parts: a thoracic (chest) part and a cervical (neck) part. The right common carotid originates in or close to the neck and contains only a small thoracic portion. There are studies in the bioengineering l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Petrosal Sinus
The inferior petrosal sinuses are two small sinuses situated on the inferior border of the petrous part of the temporal bone, one on each side. Each inferior petrosal sinus drains the cavernous sinus into the internal jugular vein. Structure The inferior petrosal sinus is situated in the inferior petrosal sulcus, formed by the junction of the petrous part of the temporal bone with the basilar part of the occipital bone. It begins below and behind the cavernous sinus and, passing through the anterior part of the jugular foramen, ends in the superior bulb of the internal jugular vein. Function The inferior petrosal sinus receives the internal auditory veins and also veins from the medulla oblongata, pons, and under surface of the cerebellum. Additional images File:Gray568.png, Sagittal section of the skull, showing the sinuses of the dura. See also * Dural venous sinuses The dural venous sinuses (also called dural sinuses, cerebral sinuses, or cranial sinuses) are veno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |