|
Juan Miguel De Agüero
Juan Miguel de Agüero was a 16th-century Spanish architect from Santander who participated in the design and construction of the Mexico City Metropolitan Cathedral, the Mérida Cathedral, and the fortifications of Havana, Cuba. Biography Juan Miguel de Agüero was born in Trasmiera, Cantabria. Juan Miguel de Agüero spent time in Santander, Havana Cuba, Mexico City, and Yucatan. He died in Mexico City, Mexico in 1610. His style was consistent with 17th century Spanish architectural design.Velasco Ballesteros, Maricarmen. "The Cathedral of Mexico City." ''Voices of Mexico: News, Commentary, Documents on Current Events in Mexico and Latin America'' (2018). Education Juan Miguel de Agüero received his education in Spain and became a Master Builder. Juan Miguel de Agüero was also a distinguished Spanish military architect. Artworks Mexico City Metropolitan Cathedral Juan Miguel de Agüero’s worked on the Mexico City Metropolitan Cathedral, located in Mexico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance-speaking ethnic group native to the Iberian Peninsula, primarily associated with the modern nation-state of Spain. Genetically and ethnolinguistically, Spaniards belong to the broader Southern and Western European populations, exhibiting a high degree of continuity with other Indo-European-derived ethnic groups in the region. Spain is also home to a diverse array of national and regional identities, shaped by its complex history. These include various languages and dialects, many of which are direct descendants of Latin, the language imposed during Roman rule. Among them, Spanish (also known as Castilian) is the most widely spoken and the only official language across the entire country. Commonly spoken regional languages include, most notably, the sole surviving indigenous language of Iberia, Basque, as well as other Latin-descended Romance languages like Spanish itself, Catalan and Galician. Many populations outside Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master Builder
A master builder or master mason is a central figure leading construction projects in pre-modern times (a combination of a modern expert carpenter, construction site supervisor, and architect / engineer). Historically, the term has generally referred to "the head of a construction project in the Middle Ages or Renaissance period",Olga Popovic Larsen, Andy Tyas, Conceptual Structural Design: Bridging the Gap Between Architects and Engineers' (2003), p. 29-30. with an 1887 source describing the status as follows: The term has also been applied to more broadly include "designers and builders of large-scale construction work who learned their trade in a more formal way than the builders of primitive forms in pre-technological societies... from the times of the Egyptians and Sumerians until (and in some cases beyond) the Industrial Revolution". The phrase has been in use since at least 1610, when William Camden William Camden (2 May 1551 – 9 November 1623) was an English anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathedral Of Mérida, Yucatán
The Mérida Cathedral in Mérida, Yucatán, Mexico, is one of the oldest cathedrals in the Americas. History Construction of the cathedral of Mérida began in 1561, and it was completed in 1598. It was the second cathedral to be completed in the Americas (the Cathedral of Santo Domingo, completed in 1550, was the first). It is a unique monument with clear antecedents in Andalusia. The seat of the bishopric of Yucatán, the cathedral was built on the site of Mayan ruins T'ho. The bishopric of Yucatán had an uncertain start. The Yucatán peninsula was explored by Francisco Hernandez de Córdoba and Juan de Grijalva on behalf of Diego Velazquez de Cuellar, the adelantado of Cuba, in 1517 and 1518. The creation of a diocese in the recently discovered country was urged by Velazquez, who presumed to have jurisdiction over the region and hoped to colonize it. An episcopal see known as "Carolense" was indeed created by Pope Leo X Pope Leo X (; born Giovanni di Lorenzo de' Medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tezontle
Tezontle () is a porous, highly oxidized, volcanic rock used extensively in construction in Mexico. It is usually reddish in color due to iron oxide. Tezontle is a well-cemented, agglomeritic and scoriaceous rock. Uses Construction Tezontle can be mixed with concrete to form lightweight concrete blocks, or mixed with cement to create stucco finishes. Many colonial buildings in Mexico use the reddish cut tezontle on their facades. Tezontle is a common construction material in the Historic Center of Mexico City as the relatively light-weight stone helps impede a building from sinking into the unstable lake bed on which Mexico City was built. Other uses Non-building uses include its inclusion in flower arrangements and botanical gardens, as substrate for aquariums, and for temazcales and ovens. Tezontle is often used as the top layer of gravel on unpaved roads in Mexico. Facades Many buildings use tezontle to create an aesthetic facade. Here are some examples. * Church of San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance Revival Architecture
Renaissance Revival architecture (sometimes referred to as "Neo-Renaissance") is a group of 19th-century Revivalism (architecture), architectural revival styles which were neither Greek Revival architecture, Greek Revival nor Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic Revival but which instead drew inspiration from a wide range of classicizing Italian modes. Under the broad designation Renaissance architecture 19th-century architects and critics went beyond the architectural style which began in Florence and Central Italy in the early 15th century as an expression of Renaissance humanism; they also included styles that can be identified as Mannerism, Mannerist or Baroque. Self-applied style designations were rife in the mid- and later 19th century: "Neo-Renaissance" might be applied by contemporaries to structures that others called "Italianate", or when many French Baroque features are present (Second Empire (architecture), Second Empire). The divergent forms of Renaissance architect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture, sometimes referred to as Classical Revival architecture, is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassicism, Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy, France and Germany. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of Roman architecture, ancient Rome and ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer, more complete, and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churrigueresque
Churrigueresque (; Spanish: ''Churrigueresco''), also but less commonly "Ultra Baroque", refers to a Spanish Baroque style of elaborate sculptural architectural ornament which emerged as a manner of stucco decoration in Spain in the late 17th century and was used until about 1750, marked by extreme, expressive and florid decorative detailing, normally found above the entrance on the main façade of a building. Origins Named after the architect and sculptor, José Benito de Churriguera (1665–1725), who was born in Madrid and who worked primarily in Madrid and Salamanca, the origins of the style are said to go back to an architect and sculptor named Alonso Cano, who designed the façade of the cathedral at Granada, in 1667. A distant, early 15th century precursor of the highly elaborate Churrigueresque style can be found in the Lombard Charterhouse of Pavia. Development The development of the style passed through three phases. Between 1680 and 1720, the Churriguera popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque Architecture
Baroque architecture is a highly decorative and theatrical style which appeared in Italy in the late 16th century and gradually spread across Europe. It was originally introduced by the Catholic Church, particularly by the Jesuits, as a means to combat the Reformation and the Protestantism, Protestant church with a new architecture that inspired surprise and awe. It reached its peak in the High Baroque (1625–1675), when it was used in churches and palaces in Italy, Spain, Portugal, France, Bavaria and Austria. In the Late Baroque period (1675–1750), it reached as far as Russia, the Ottoman Baroque architecture, Ottoman Empire and the Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish and Portuguese colonization of the Americas, Portuguese colonies in Latin America. In about 1730, an even more elaborately decorative variant called Rococo appeared and flourished in Central Europe. Baroque architects took the basic elements of Renaissance architecture, including domes and colonnades, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Architecture
Gothic architecture is an architectural style that was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High Middle Ages, High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture. It originated in the Île-de-France and Picardy regions of northern France. The style at the time was sometimes known as ''opus Francigenum'' (); the term ''Gothic'' was first applied contemptuously during the later Renaissance, by those ambitious to revive the Classical architecture, architecture of classical antiquity. The defining design element of Gothic architecture is the Pointed arch (architecture), pointed arch. The use of the pointed arch in turn led to the development of the pointed rib vault and flying buttresses, combined with elaborate tracery and stained glass windows. At the Abbey of Basilica of Saint-Denis, Saint-Denis, near Paris, the choir was rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type building, the strict definition of the term "nave" is restricted to the central aisle. In a broader, more colloquial sense, the nave includes all areas available for the lay worshippers, including the side-aisles and transepts.Cram, Ralph Adams Nave The Catholic Encyclopedia. Vol. 10. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1911. Accessed 13 July 2018 Either way, the nave is distinct from the area reserved for the choir and clergy. Description The nave extends from the entry—which may have a separate vestibule (the narthex)—to the chancel and may be flanked by lower side-aisles separated from the nave by an arcade. If the aisles are high and of a width comparable to the central nave, the structure is sometimes said to have three nave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
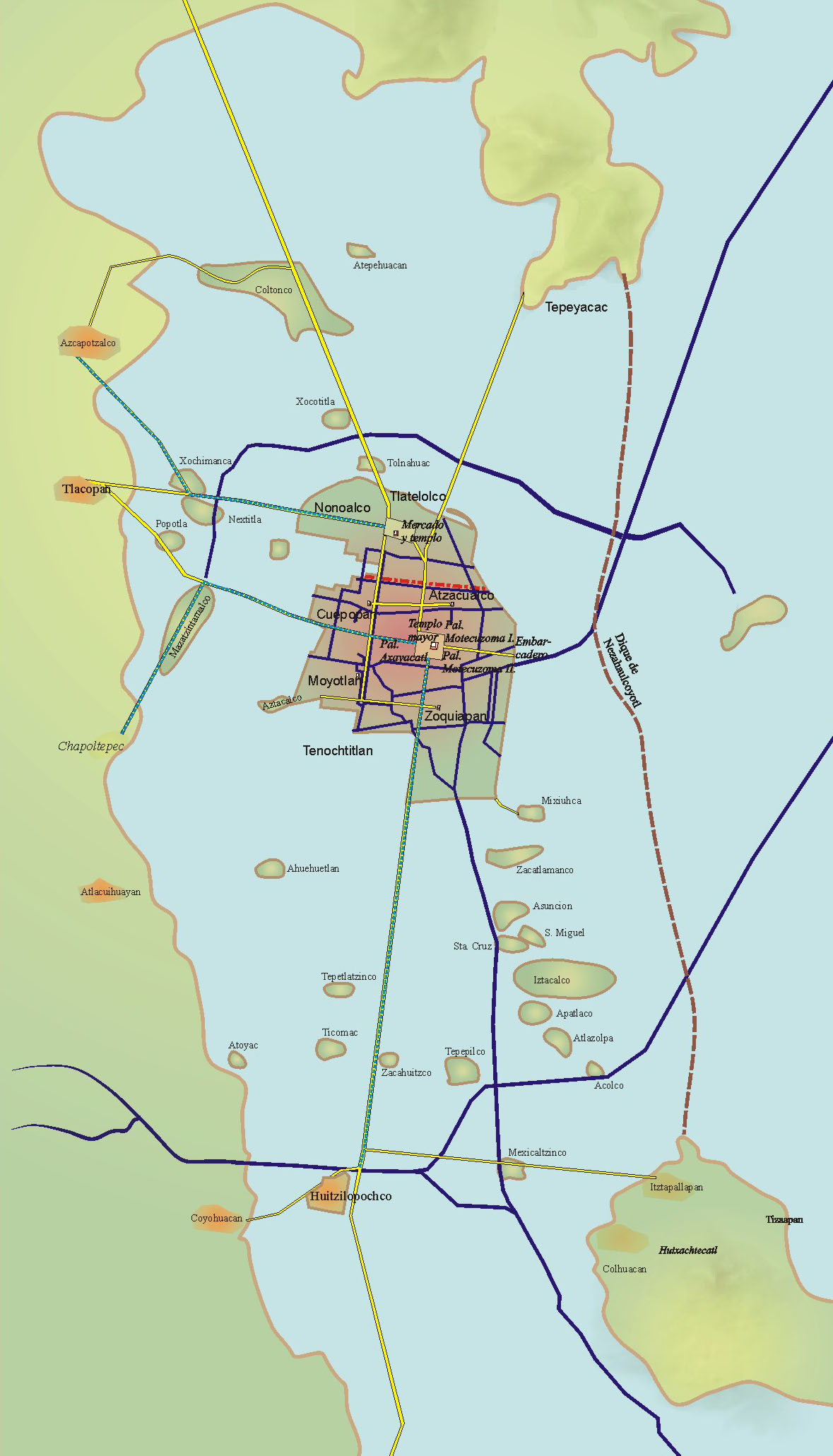
Tenochtitlan
, also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear, but the date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th anniversary of the city. The city was built on an island in what was then Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. The city was the capital of the expanding Aztec Empire in the 15th century until it was Fall of Tenochtitlan, captured by the Tlaxcaltec and the Spanish in 1521. At its peak, it was the largest city-state, city in the pre-Columbian Americas. It subsequently became a ''Municipalities of Mexico, cabecera'' of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Today, the ruins of are in the historic center of the Mexican capital. The World Heritage Site of contains what remains of the geography (water, boats, Chinampa, floating gardens) of the Mexica capital. was one of two Mexica (city-states or Polity, polities) on the island, the other being . Etymol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztecs
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states ('' altepetl''), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec Empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427: Tenochtitlan, the capital city of the Mexica or Tenochca, Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahua polities or peoples of central Mexico in the prehispanic era, as well as the Spanish colonial era (1521–1821). The definitions of Azt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |