|
Joss Paper
Joss paper, also known as incense papers, are papercrafts or sheets of paper made into burnt offerings common in Chinese ancestral worship (such as the veneration of the deceased family members and relatives on holidays and special occasions). Worship of deities in Chinese folk religion also uses a similar type of joss paper. Joss paper, as well as other papier-mâché items, are also burned or buried in various Asian funerals, "to ensure that the spirit of the deceased has sufficient means in the afterlife". In Taiwan alone, the annual revenue that temples received from burning joss paper was US$400 million (NT$13 billion) as of 2014. Use Spirit money is most often used for venerating those departed but has also been known to be used for other purposes such as a gift from a groom's family to the bride's ancestors. Spirit money has been said to have been given for the purpose of enabling their deceased family members to have all they will need or want in the afterlife. It ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papercraft
Paper models, also called card models or papercraft, are Physical model, models constructed mainly from sheets of heavy paper, paperboard, card stock, or foam. Details This may be considered a broad category that contains origami and card modeling. Origami is the process of making a paper model by folding a single piece of paper without using glue or cutting while the variation kirigami does. Card modeling is making scale models from sheets of cardstock on which the parts were printed, usually in full color. These pieces would be cut out, folded, scored, and glued together. Papercraft is the art of combining these model types to build complex creations such as wearable suits of armor, life-size characters, and accurate weapon models. Sometimes the model pieces can be punched out. More frequently the printed parts must be cut out. Edges may be scored to aid folding. The parts are usually glued together with polyvinyl acetate Adhesive, glue ("white glue", "PVA"). In this kind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chongyang Festival
The Double Ninth Festival is a traditional Chinese holiday observed on the ninth day of the ninth month in the Chinese calendar. According to Wu Jun, it dates back to the Eastern Han dynasty (25–220 AD). According to the ''I Ching'', ''nine'' is a yang number; the ninth day of the ninth month in the Chinese calendar (or double nine) has extra '' yang'' (a traditional Chinese spiritual concept) and is thus an auspicious date. Hence, the day is also called "Double Yang Festival" (). It is customary to climb a mountain, drink chrysanthemum liquor, and wear the ''zhuyu'' () plant (''Cornus officinalis''). Both chrysanthemum and ''zhuyu'' are considered to have cleansing qualities and are used on other occasions to air out houses and cure illnesses. On this holiday, some Chinese also visit the graves of their ancestors to pay their respects. In Hong Kong and Macau, whole extended families head to ancestral graves to clean them, repaint inscriptions and lay out food offerings such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pagoda
A pagoda is a tiered tower with multiple eaves common to Thailand, Cambodia, Nepal, India, China, Japan, Korea, Myanmar, Vietnam, and other parts of Asia. Most pagodas were built to have a religious function, most often Buddhist, but sometimes Taoist or Hindu, and were often located in or near viharas. The pagoda traces its origins to the stupa, while its design was developed in ancient India. Chinese pagodas () are a traditional part of Chinese architecture. In addition to religious use, since ancient times Chinese pagodas have been praised for the spectacular views they offer, and many classical poems attest to the joy of scaling pagodas. The oldest and tallest pagodas were built of wood, but most that survived were built of brick or stone. Some pagodas are solid with no interior. Hollow pagodas have no higher floors or rooms, but the interior often contains an altar or a smaller pagoda, as well as a series of staircases for the visitor to climb to see the view from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimney
A chimney is an architectural ventilation structure made of masonry, clay or metal that isolates hot toxic exhaust gases or smoke produced by a boiler, stove, furnace, incinerator, or fireplace from human living areas. Chimneys are typically vertical, or as near as possible to vertical, to ensure that the gases flow smoothly, drawing air into the combustion in what is known as the stack, or chimney effect. The space inside a chimney is called the '' flue''. Chimneys are adjacent to large industrial refineries, fossil fuel combustion facilities or part of buildings, steam locomotives and ships. In the United States, the term '' smokestack industry'' refers to the environmental impacts of burning fossil fuels by industrial society, including the electric industry during its earliest history. The term ''smokestack'' (colloquially, ''stack'') is also used when referring to locomotive chimneys or ship chimneys, and the term ''funnel'' can also be used. The height of a chim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
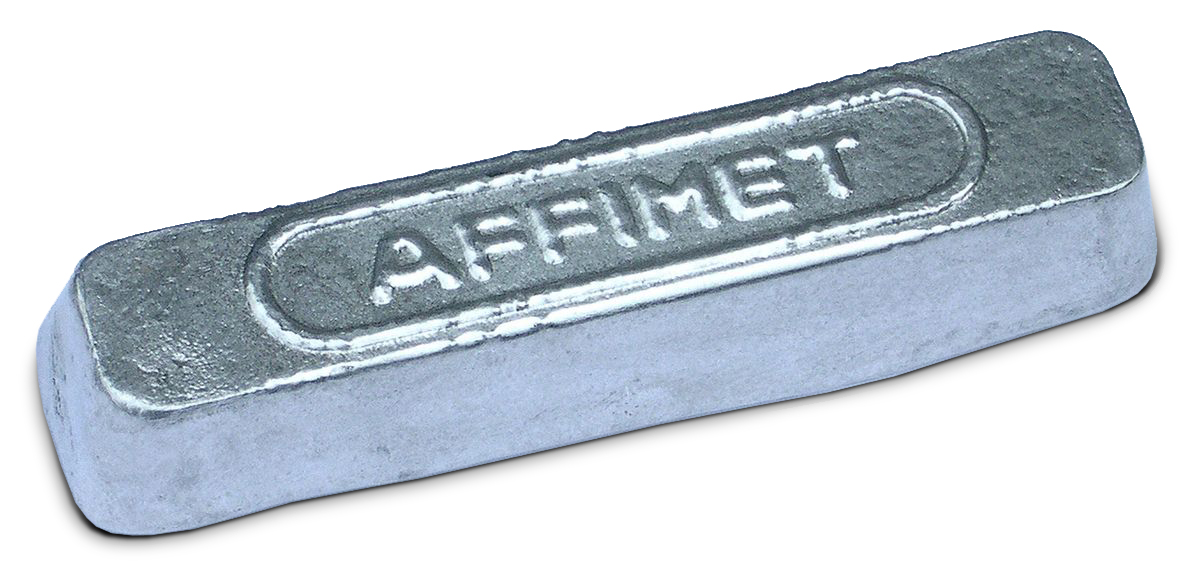
Ingot
An ingot is a piece of relatively pure material, usually metal, that is Casting, cast into a shape suitable for further processing. In steelmaking, it is the first step among semi-finished casting products. Ingots usually require a second procedure of shaping, such as cold/hot working, cutting, or milling to produce a useful final product. Non-metallic and semiconductor materials prepared in bulk form may also be referred to as ingots, particularly when cast by mold based methods. Precious metal ingots can be used as currency (with or without being processed into other shapes), or as a currency reserve, as with gold bars. Types Ingots are generally made of metal, either pure or alloy, heated past its melting point and cast into a bar or block using a mold chill method. A special case are polycrystalline or single crystal ingots made by pulling from a molten melt. Single crystal Single crystal ingots (called boule (crystal), boules) of materials are grown (crystal growth) using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macau
Macau or Macao is a special administrative regions of China, special administrative region of the People's Republic of China (PRC). With a population of about people and a land area of , it is the most List of countries and dependencies by population density, densely populated region in the world. Formerly a Portuguese Empire, Portuguese colony, the territory of Portuguese Macau was first leased to Portugal by the Ming dynasty as a trading post in 1557. Portugal paid an annual rent and administered the territory under Chinese sovereignty until 1887, when Portugal gained perpetual colonial rights with the signing of the Sino-Portuguese Treaty of Peking. The colony remained under Portuguese rule until the 1999 handover to China. Macau is a Special administrative regions of China, special administrative region of China, which maintains separate governing and economic systems from those of mainland China under the principle of "one country, two systems".. The unique blend of Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the China, People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. It has an area of , with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its Urbanization by country, highly urbanized population is concentrated. The combined Free area of the Republic of China, territories under ROC control consist of list of islands of Taiwan, 168 islands in total covering . The Taipei–Keelung metropolitan area, largest metropolitan area is formed by Taipei (the capital), New Taipei City, and Keelung. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated countries. Tai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantonese
Cantonese is the traditional prestige variety of Yue Chinese, a Sinitic language belonging to the Sino-Tibetan language family. It originated in the city of Guangzhou (formerly known as Canton) and its surrounding Pearl River Delta. While the term ''Cantonese'' specifically refers to the prestige variety, in linguistics it has often been used to refer to the entire Yue subgroup of Chinese, including related but partially mutually intelligible varieties like Taishanese. Cantonese is viewed as a vital and inseparable part of the cultural identity for its native speakers across large swaths of southeastern China, Hong Kong and Macau, as well as in overseas communities. In mainland China, it is the ''lingua franca'' of the province of Guangdong (being the majority language of the Pearl River Delta) and neighbouring areas such as Guangxi. It is also the dominant and co-official language of Hong Kong and Macau. Furthermore, Cantonese is widely spoken among overseas Chinese in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ink Seal
Ink is a gel, sol, or solution that contains at least one colorant, such as a dye or pigment, and is used to color a surface to produce an image, text, or design. Ink is used for drawing or writing with a pen, brush, reed pen, or quill. Thicker inks, in paste form, are used extensively in letterpress and lithographic printing. Ink can be a complex medium, composed of solvents, pigments, dyes, resins, lubricants, solubilizers, surfactants, particulate matter, fluorescents, and other materials. The components of inks serve many purposes; the ink's carrier, colorants, and other additives affect the flow and thickness of the ink and its dry appearance. History Many ancient cultures around the world have independently discovered and formulated inks due to the need to write and draw. The recipes and techniques for the production of ink are derived from archaeological analyses or from written texts itself. The earliest inks from all civilizations are believed to have been made w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
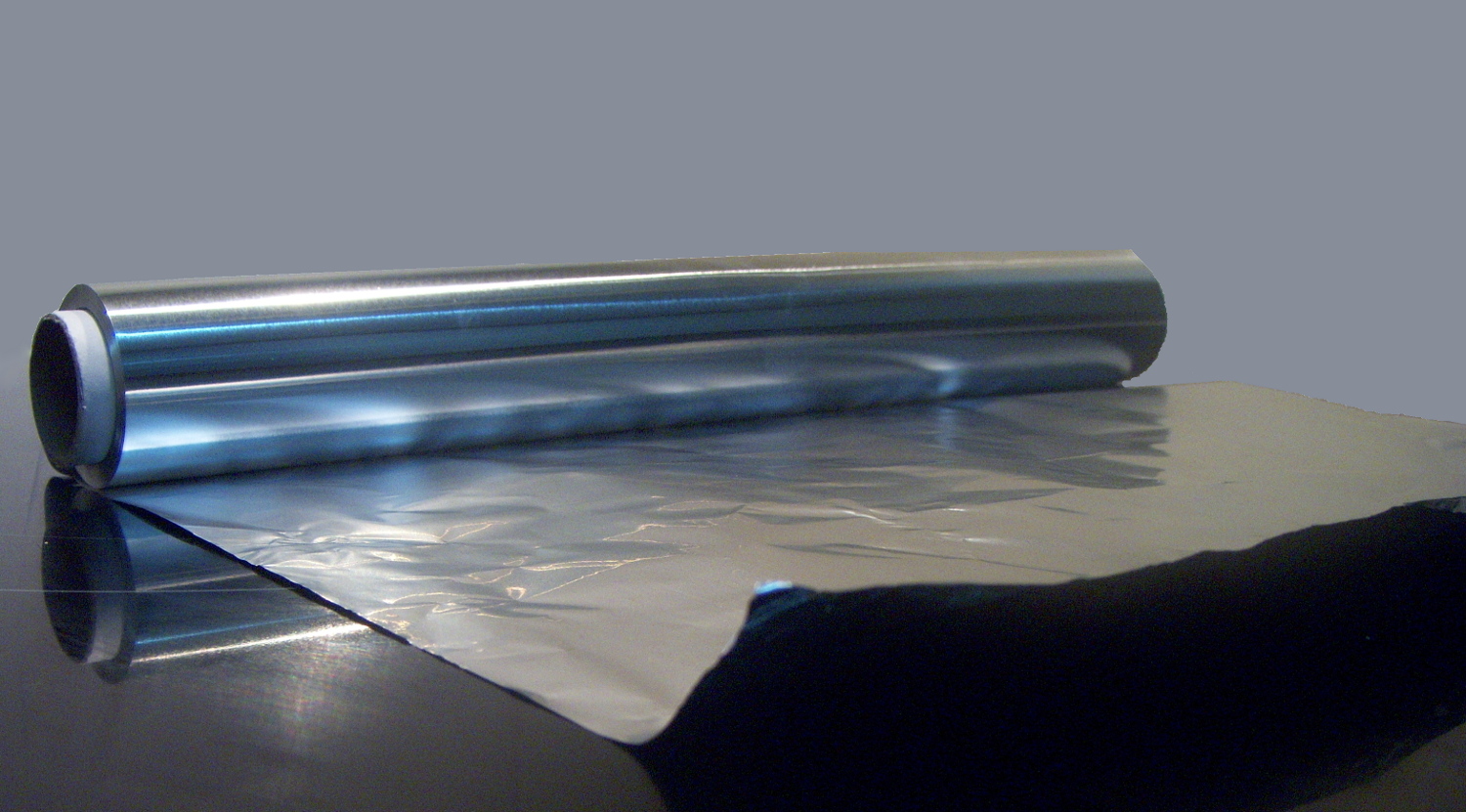
Metal Foil
A foil is a very thin sheet of metal, typically made by hammering or rolling. Foils are most easily made with malleable metal, such as aluminium, copper, tin, and gold. Foils usually bend under their own weight and can be torn easily. For example, aluminium foil is usually about , whereas gold (more malleable than aluminium) can be made into foil only a few atoms thick, called gold leaf. Extremely thin foil is called metal leaf. Leaf tears very easily and must be picked up with special brushes. See also * Aluminium foil * Copper foil * Tin foil * Gold leaf * Metal leaf A metal leaf, also called composition leaf or schlagmetal, is a thin foil used for gilding and other forms of decoration. Metal leaves can come in many different shades, due to the composition of the metal within the metal leaf. Examples of this ... References Metalworking {{Metalworking-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funeral Ceremonies
A funeral is a ceremony connected with the Disposal of human corpses, final disposition of a corpse, such as a burial or cremation, with the attendant observances. Funerary customs comprise the complex of beliefs and practices used by a culture to remember and respect the dead, from interment, to various monuments, prayers, and rituals undertaken in their honour. Customs vary between cultures and Religion, religious groups. Funerals have both normative and legal components. Common secular motivations for funerals include mourning the deceased, celebrating their life, and offering support and sympathy to the bereaved; additionally, funerals may have religious aspects that are intended to help the soul of the deceased reach the afterlife, resurrection or reincarnation. The funeral usually includes a ritual through which the corpse receives a final disposition. Depending on culture and religion, these can involve either the destruction of the body (for example, by cremation, sky bur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joss Paper Burner
--> , typing = , scope = Lexical , programming language = assembly language , discontinued = Yes , platform = JOHNNIAC, PDP-6 , operating system = , influenced by = , influenced = TELCOMP, CAL, FOCAL, MUMPS , website = JOSS (acronym for JOHNNIAC Open Shop System) was one of the first interactive, time-sharing programming languages. It pioneered many features that would become common in languages from the 1960s into the 1980s, including use of line numbers as both editing instructions and targets for branches, statements predicated by Boolean decisions, and a built-in source-code editor that can perform instructions in direct or immediate mode, what they termed a ''conversational user interface''. JOSS was initially implemented on the JOHNNIAC machine at RAND Corporation and put online in 1963. It proved very popular, and the users quickly bogged the machine down. By 1964, a replacement was sought with higher performance. JOHNNIAC was retired in 1966 and replace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |