|
Joseph-Étienne Richard
Joseph-Étienne Richard (known as 'Richard de la Sarthe') (28 September 1761 La Flèche - 17 August 1834 Saintes), was a French politician. Under the Republic Before the French Revolution he was admitted to the bar in 1788 and in 1790 was elected 'procureur syndic' of the commune of La Flèche, later becoming its public prosecutor. On 4 September 1791, he was elected député for Sarthe to the Legislative Assembly, the seventh of ten elected, with 248 votes from 346 voters. On 3 September 1792 he was re-elected to the National Convention, this time at the head of the list, with a plurality of votes. At the trial of Louis XVI he voted for the king’s death. He was first sent as a représentant en mission to Sarthe and Maine-et-Loire where he took part in several victories over the Vendée rebels, establishing the first military commission (16 June 1793) and surveillance committee (18 October 1793) at Tours Tours ( ; ) is the largest city in the region of Centre-Val de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Etienne Richard - AD14
Joseph is a common male name, derived from the Hebrew (). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef (given name), Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the modern-day Nordic countries. In Portuguese language, Portuguese and Spanish language, Spanish, the name is "José". In Arabic, including in the Quran, the name is spelled , . In Kurdish language, Kurdish (''Kurdî''), the name is , Persian language, Persian, the name is , and in Turkish language, Turkish it is . In Pashto the name is spelled ''Esaf'' (ايسپ) and in Malayalam it is spelled ''Ousep'' (ഔസേപ്പ്). In Tamil language, Tamil, it is spelled as ''Yosepu'' (யோசேப்பு). The name has enjoyed significant popularity in its many forms in numerous countries, and ''Joseph'' was one of the two names, along with ''Robert'', to have remained in the top 10 boys' names list in the US from 1925 to 1972. It is especiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobins
The Society of the Friends of the Constitution (), renamed the Society of the Jacobins, Friends of Freedom and Equality () after 1792 and commonly known as the Jacobin Club () or simply the Jacobins (; ), was the most influential List of political groups in the French Revolution, political club during the French Revolution of 1789. The period of its political ascendancy includes the Reign of Terror, during which well over 10,000 people were put on trial and executed in France, many for "political crimes". Initially founded in 1789 by Criticism of monarchy, anti-royalist deputies from Duchy of Brittany, Brittany, the club grew into a nationwide Republicanism, republican movement with a membership estimated at a half million or more. The Jacobin Club was heterogeneous and included both prominent parliamentary factions of the early 1790s: The Mountain and the Girondins. In 1792–93, the Girondins were more prominent in leading France when they French Revolutionary Wars, declared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baron De L'Empire
As Emperor of the French, Napoleon I created titles in a newly established ' (imperial nobility) to institute a stable elite in the First French Empire, after the instability resulting from the French Revolution. Like many others, both before and since, Napoleon found that the ability to confer titles was also a useful tool of patronage which cost the state little. In all, about 2,200 titles were created by Napoleon: * Princes and dukes: ** Princes of the imperial family *** The Prince Imperial (Napoleon's son and heir apparent, who was later styled as Napoleon II) *** Princes of France (8 close family members) ** Sovereign princes (3) ** Dukes of large fiefs (20) ** Victory princes (4) ** Victory dukedoms (10) ** Other dukedoms (3) * Counts (251) * Barons (1,516) * Knights (385) Napoleon also established a new knightly order in 1802, the Legion of Honour, which is still in existence today. The Grand Dignitaries of the French Empire ranked, regardless of noble title, imme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legion Of Honour
The National Order of the Legion of Honour ( ), formerly the Imperial Order of the Legion of Honour (), is the highest and most prestigious French national order of merit, both military and Civil society, civil. Currently consisting of five classes, it was originally established in 1802 by Napoleon, Napoleon Bonaparte, and it has been retained (with occasional slight alterations) by all later French governments and regimes. The order's motto is ' ("Honour and Fatherland"); its Seat (legal entity), seat is the Palais de la Légion d'Honneur next to the Musée d'Orsay, on the left bank of the Seine in Paris. Since 1 February 2023, the Order's grand chancellor has been retired General François Lecointre, who succeeded fellow retired General Benoît Puga in office. The order is divided into five degrees of increasing distinction: ' (Knight), ' (Officer), ' (Commander (order), Commander), ' (Grand Officer) and ' (Grand Cross). History Consulate During the French Revolution, all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career of Napoleon, a series of military campaigns across Europe during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars from 1796 to 1815. He led the French First Republic, French Republic as French Consulate, First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then ruled the First French Empire, French Empire as Emperor of the French from 1804 to 1814, and briefly again in 1815. He was King of Italy, King of Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Italy from 1805 to 1814 and Protector of the Confederation of the Rhine, Protector of the Confederation of the Rhine from 1806 to 1813. Born on the island of Corsica to a family of Italian origin, Napoleon moved to mainland France in 1779 and was commissioned as an officer in the French Royal Army in 1785. He supported the French Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Rochelle
La Rochelle (, , ; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''La Rochéle'') is a city on the west coast of France and a seaport on the Bay of Biscay, a part of the Atlantic Ocean. It is the capital of the Charente-Maritime Departments of France, department. With 78,535 inhabitants in 2021, La Rochelle is the most populated commune in the department and ranks fourth in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region after Bordeaux, the regional capital, Limoges and Poitiers. Situated on the edge of the Atlantic Ocean the city is connected to the Île de Ré by a bridge completed on 19 May 1988. Since the Middle Ages the harbour has opened onto a protected strait, the Pertuis d'Antioche and is regarded as a "Door océane" or gateway to the ocean because of the presence of its three ports (fishing, trade and yachting). The city has a strong commercial tradition, having an active port from very early on in its history. The city traces its origins to the Gallo-Roman culture, Gallo-Roman period, attested by the rema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charente-Maritime
Charente-Maritime (; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Chérente-Marine''; ) is a Departments of France, department in the French Regions of France, region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine, on the country's west coast. Named after the river Charente (river), Charente, its Prefectures in France, prefecture is La Rochelle. As of 2019, it had a population of 651,358 with an area of 6,864 square kilometres (2,650 sq mi). History The history of the department begins with a decree from the National Constituent Assembly (France), Constituent Assembly on December 22, 1789, which took effect on March 4, 1790, creating it as one of the 83 original departments during the French Revolution. Named “Charente-Inférieure” after the lower course of the Charente (river), Charente, it was renamed Charente-Maritime on September 4, 1941, during World War II, reflecting its Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast identity. The department encompasses most of the former province of County of Saintonge, Saintonge (excluding Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
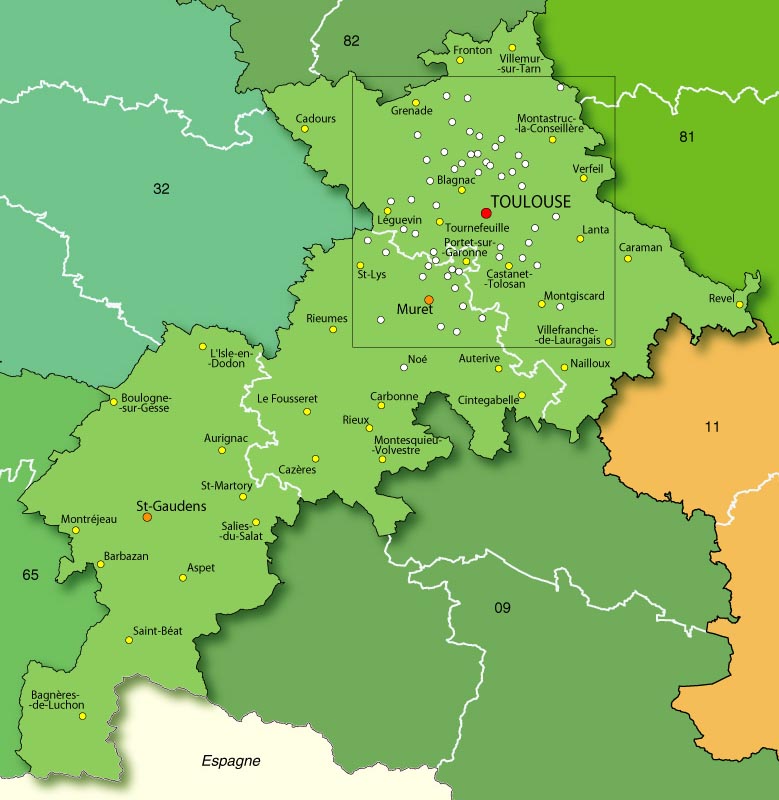
Haute-Garonne
Haute-Garonne (; , ; ''Upper Garonne'') is a department in the southwestern French region of Occitanie. Named after the river Garonne, which flows through the department. Its prefecture and main city is Toulouse, the country's fourth-largest. In 2019, it had a population of 1,400,039.Populations légales 2019: 31 Haute-Garonne INSEE History Haute-Garonne is one of the original 83 departments created during the French Revolution on 4 March 1790. It was created from part of the former provinces of and |
Prefect (France)
A prefect (, plural , both ) in France is the State's representative in a Departments of France, department or Regions of France, region. Regional prefects are ''ex officio'' the departmental prefects of the regional Prefectures in France, prefecture. Prefects are tasked with upholding the law in the department they serve in, including controlling the actions of local authorities. Prefects are appointed by decree by the President of France when presiding over the Government of France, government's Council of Ministers, following a proposal by the Prime Minister of France, Prime Minister and the Minister of the Interior (France), Minister of the Interior. They serve at the government's discretion and can be replaced at any meeting of the Council of Ministers. To uphold the law, they are authorised to undertake a wide variety of actions, such as coordinating police forces, enforcing immigration rules, controlling authorities' finances, as well as suing local collectivities in the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batavian Republic
The Batavian Republic (; ) was the Succession of states, successor state to the Dutch Republic, Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. It was proclaimed on 19 January 1795 after the Batavian Revolution and ended on 5 June 1806, with the accession of Louis Bonaparte to the Kingdom of Holland, Dutch throne. From October 1801 onward, it was known as the Batavian Commonwealth (). Both names refer to the Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe of the Batavi (Germanic tribe), ''Batavi'', representing both the Dutch ancestry and their ancient quest for liberty in their Nationalism, nationalist lore. In early 1795, intervention by the French First Republic, French Republic led to the downfall of the old Dutch Republic. The new republic enjoyed widespread support from the Dutch populace and was the product of a genuine popular revolution. However, it was founded with the armed support of the French Revolutionary Army. The Batavian Republic became a client state, the first of the "sister repu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breda
Breda ( , , , ) is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the southern part of the Netherlands, located in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of North Brabant. The name derived from ''brede Aa'' ('wide Aa' or 'broad Aa') and refers to the confluence of the rivers Mark (Dintel), Mark and Aa of Weerijs, Aa. Breda has 185,072 inhabitants on 13 September 2022 and is part of the Brabantse Stedenrij; it is the tenth largest city/municipality in the country, and the third largest in North Brabant after Eindhoven and Tilburg. It is equidistant from Rotterdam and Antwerp. As a Defensive wall, fortified city, it was of strategic military and political significance. Although a direct fiefdom of the Holy Roman Emperor, the city obtained a City rights in the Low Countries, municipal charter; the acquisition of Breda, through marriage, by the House of Orange-Nassau, House of Nassau ensured that Breda would be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |