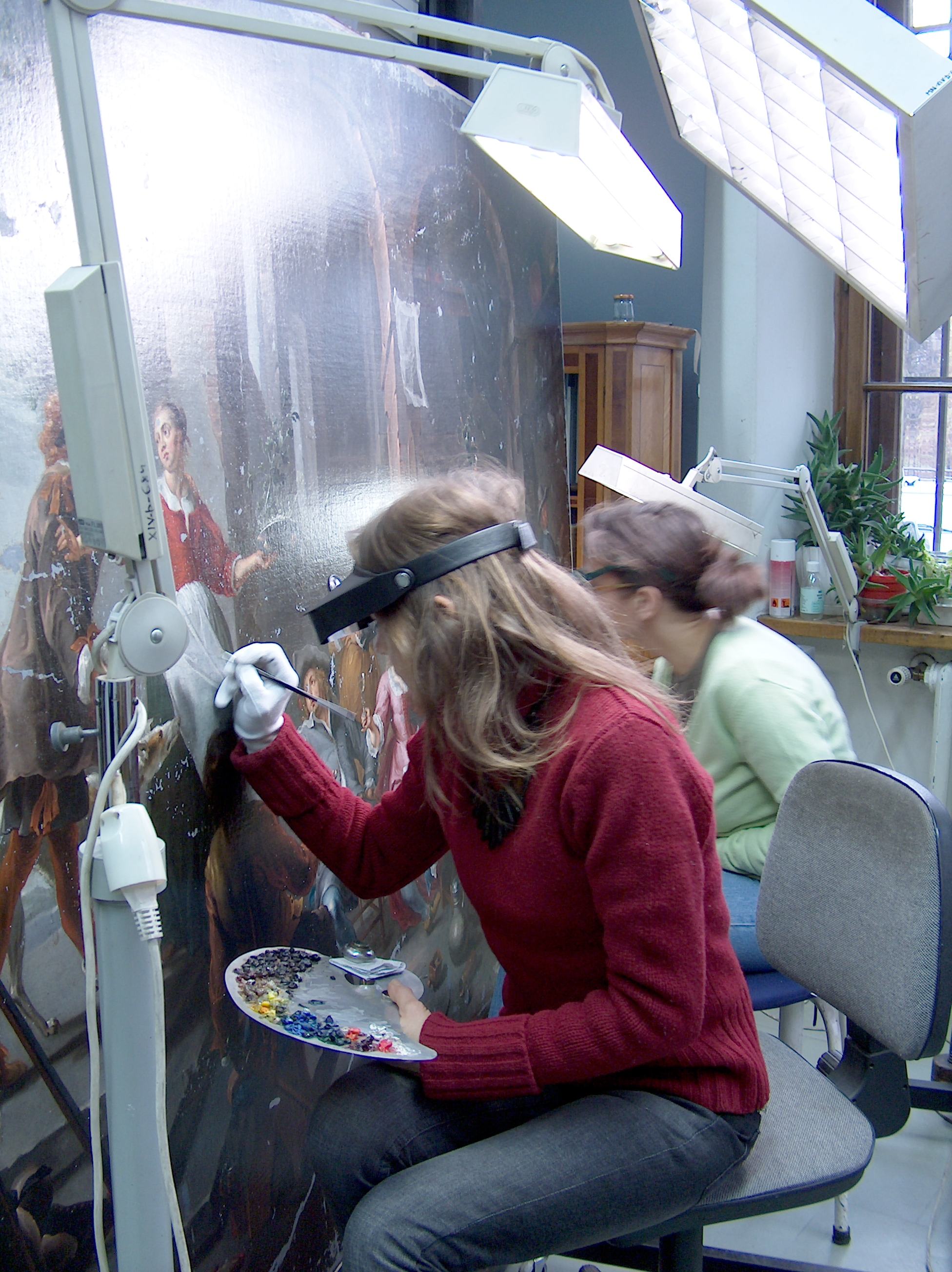|
Joseph-Désiré Court
Joseph-Désiré Court (14 September 1797, Rouen – 23 January 1865, Paris) was a French painter of historical subjects and portraits. Life and work He was a descendant of the portrait painter Hyacinthe Rigaud and displayed an early interest in art. His first studies were with , at a drawing school established by Descamps' father, Jean-Baptiste. Following that, he worked at the studios of Antoine-Jean Gros in Paris. His allowance from his family was not quite enough for his needs, so he painted small pictures, which he sold through an agent. Despite this, he was unable to save enough money to continue his studies in Rome. Hoping that he could go at the expense of the state, he competed for the Prix de Rome and, in 1821, was awarded a prize for his depiction of Samson and Delilah. During his stay there, he continued to send works back to Paris for exhibition. His painting, " The Death of Caesar", was acquired by the Musée du Luxembourg in 1827. In 1828, the Académie de Rouen na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine, in northwestern France. It is in the prefecture of Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of the largest and most prosperous cities of medieval Europe, the population of the metropolitan area () is 702,945 (2018). People from Rouen are known as ''Rouennais''. Rouen was the seat of the Exchequer of Normandy during the Middle Ages. It was one of the capitals of the Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman and Angevin kings of England, Angevin dynasties, which ruled both England and large parts of modern France from the 11th to the 15th centuries. From the 13th century onwards, the city experienced a remarkable economic boom, thanks in particular to the development of textile factories and river trade. Claimed by both the French and the English during the Hundred Years' War, it was on its soil that Joan of Arc was tried and burned alive on 30 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
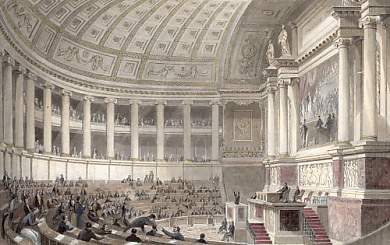
Chamber Of Deputies (France)
The Chamber of Deputies (, ) was the lower house of parliament in France at various times in the 19th and 20th centuries: * 1814–1848 during the Bourbon Restoration in France, Bourbon Restoration and the July Monarchy, the Chamber of Deputies was the lower house of the French Parliament, elected by census suffrage. * 1875–1940 during the French Third Republic, the Chamber of Deputies was the legislative assembly of the French Parliament, elected by two-round system with universal male suffrage. When reunited with the Senate (France), Senate in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, the French Parliament was called the National Assembly (France), National Assembly (''Assemblée nationale'') and carried out the election of the President of France, president of the French Republic. During the Bourbon Restoration Created by the Charter of 1814 and replacing the Corps législatif, which existed under the First French Empire, the Chamber of Deputies was composed of individuals electe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy-Victor Duperré
Admiral of France Guy-Victor Duperré (20 February 1775 – 2 November 1846) was a French Navy officer. He is known for commanding French naval forces in the Mauritius campaign of 1809–1811 and was victorious in the Battle of Grand Port, where he was wounded. Later he had a command in the Mediterranean and continued to serve during and after the Bourbon Restoration. He commanded the naval elements of the expeditionary force that carried out the Invasion of Algiers in 1830 and went on to become Minister of the Navy three times. Early years and education Duperré was born on 20 February 1775 in La RochelleB. Barbiche, ''Les institutions de la monarchie française à l'époque moderne'', Presses universitaires de France, 1999. to Jean Augustin Duperré, counselor of the king and financer for war, and Marie-Gabrielle Prat-Desprez. He spent a few years with the Oratory of Saint Philip Neri at the Collège de Juilly, before enlisting at 16 on the ''Henri IV'', a French East Indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
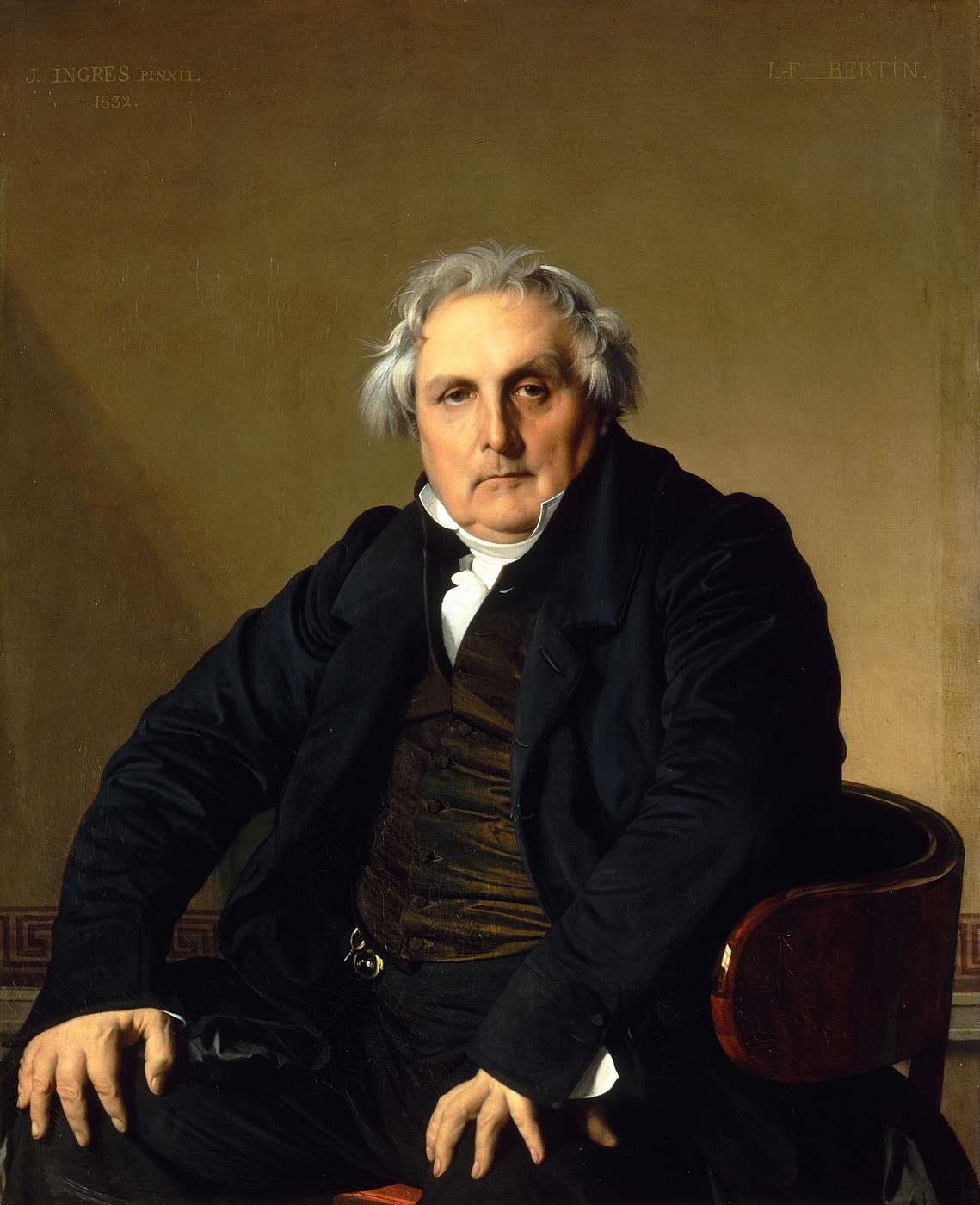
The Death Of Caesar
Julius Caesar, the Roman dictator, was assassinated on the Ides of March (15 March) 44 BC by a group of senators during a Senate session at the Curia of Pompey, located within the Theatre of Pompey in Rome. The conspirators, numbering between 60 and 70 individuals and led by Marcus Junius Brutus, Gaius Cassius Longinus, and Decimus Junius Brutus Albinus, stabbed Caesar approximately 23 times. They justified the act as a preemptive defense of the Roman Republic, asserting that Caesar's accumulation of lifelong political authority—including his perpetual dictatorship and other honors—threatened republican traditions. The assassination failed to achieve its immediate objective of restoring the Republic's institutions. Instead, it precipitated Caesar's posthumous deification, triggered the Liberators' civil war (43–42 BC) between his supporters and the conspirators, and contributed to the collapse of the Republic. These events ultimately culminated in the rise of the Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Léonore
''Base Léonore'', or the Léonore database, is a French database that lists the records of the members of the National Order of the Legion of Honor. The database lists the records of those inducted into the Legion of Honor The National Order of the Legion of Honour ( ), formerly the Imperial Order of the Legion of Honour (), is the highest and most prestigious French national order of merit, both military and civil. Currently consisting of five classes, it was ... since its 1802 inception and who died before 1977. , the database contained 390,000 records. References External links * Archives in France History websites of France Online databases Recipients of the Legion of Honour {{database-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legion Of Honor
The National Order of the Legion of Honour ( ), formerly the Imperial Order of the Legion of Honour (), is the highest and most prestigious French national order of merit, both military and civil. Currently consisting of five classes, it was originally established in 1802 by Napoleon Bonaparte, and it has been retained (with occasional slight alterations) by all later French governments and regimes. The order's motto is ' ("Honour and Fatherland"); its seat is the Palais de la Légion d'Honneur next to the Musée d'Orsay, on the left bank of the Seine in Paris. Since 1 February 2023, the Order's grand chancellor has been retired General François Lecointre, who succeeded fellow retired General Benoît Puga in office. The order is divided into five degrees of increasing distinction: ' (Knight), ' (Officer), ' (Commander), ' (Grand Officer) and ' (Grand Cross). History Consulate During the French Revolution, all of the French orders of chivalry were abolished and repla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rouen Monumental Cemetery
The Rouen Monumental Cemetery () is the most important cemetery of the Norman city of Rouen, opened in 1828 and situated to the North-East of the town-centre. The entrance gate, the chapel and the monumental cross are the work of Charles Felix Maillet du Boullay. Buried people * Charles Angrand * Henry Barbet * Albert Beaucamp * Michel Bérégovoy * Édouard de Bergevin * François Adrien Boieldieu (cœur) * Georges Bouctot * Louis Bouilhet * Louis Auguste de Bourbel de Montpinçon * Jean-Baptiste Cécille * Marcel Couchaux * Joseph-Désiré Court * Pierre Chirol * Jean Benoît Désiré Cochet * Georges Dubosc * Marcel Duchamp * Suzanne Duchamp * Raymond Duchamp-Villon * Gustave Flaubert * Jean Pierre Louis Girardin * Jacques Hébertot * Auguste Houzeau * Eustache-Hyacinthe Langlois * Albert Lebourg * Théodore-Éloi Lebreton * Léon-Jules Lemaître * Valérius Leteurtre * Juste Lisch * Ferdinand Marrou * Georges Métayer * Étienne Nétien * Émile Frédér ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservator-restorer
A conservator-restorer is a professional responsible for the Conservation-restoration of cultural heritage, preservation of artistic and cultural artifacts, also known as cultural heritage. Conservators possess the expertise to preserve cultural heritage in a way that retains the integrity of the object, building or site, including its historical significance, context and aesthetic or visual aspects.Defining the Conservator: Essential Competencies. (2003). Retrieved from http://www.conservation-us.org/docs/default-source/governance/defining-the-conservator-essential-competencies.pdf. This kind of preservation is done by analyzing and assessing the condition of cultural property, understanding processes and evidence of deterioration, planning collections care or site management strategies that prevent damage, carrying out conservation treatments, and conducting research.Careers in Conservation. (2014). Retrieved from http://www.conservation-us.org/publications-resources/careers-in- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
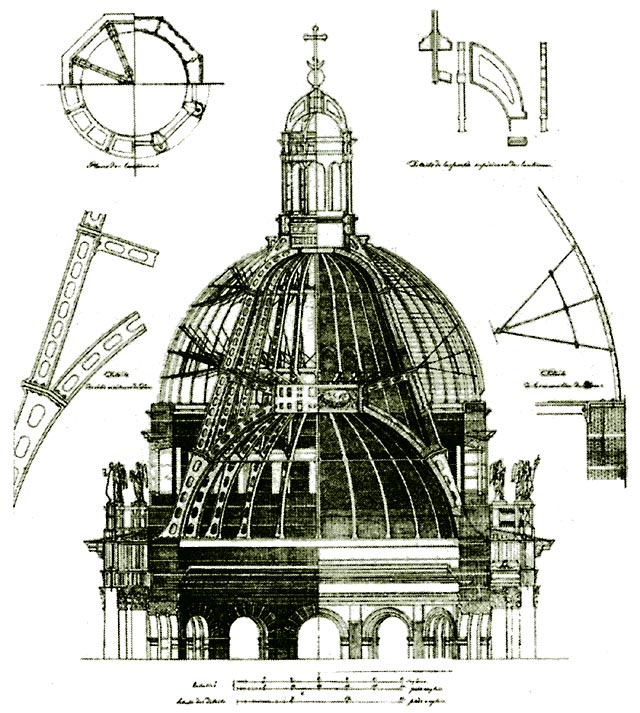
Saint Isaac's Cathedral
Saint Isaac's Cathedral () is a large architectural landmark cathedral that currently functions as a museum with occasional church services in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is dedicated to Saint Isaac of Dalmatia, a patron saint of Peter the Great, who had been born on the feast day of that saint. It was originally built as a cathedral but was turned into a museum by the Soviet government in 1931 and has remained a museum ever since, with church services held in a side chapel since the 1990s. In 2017, the Governor of Saint Petersburg offered to transfer the cathedral back to the Russian Orthodox Church, but this was not accomplished due to the protests of St Petersburg citizens opposing the offer. History The church on St Isaac's Square was ordered by Tsar Alexander I, to replace an earlier structure by Vincenzo Brenna, and was the fourth consecutive church standing at this place. A specially appointed commission examined several designs, including that of the French-born a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hôtel De Ville, Paris
The (, ''City hall (administration), City Hall'') is the city hall of Paris, France, standing on the in the 4th arrondissement of Paris, 4th arrondissement. The south wing was originally constructed by Francis I of France, Francis I beginning in 1535 until 1551. The north wing was built by Henry IV of France, Henry IV and Louis XIII between 1605 and 1628. It was burned by the Paris Commune, along with all the city archives that it contained, during the Semaine Sanglante, the Commune's final days, in May 1871. The outside was rebuilt following the original design, but larger, between 1874 and 1882, while the inside was considerably modified. It has been the headquarters of the municipality of Paris since 1357. It serves multiple functions, housing the Council of Paris, local government council, since 1977 the Mayor of Paris, mayors of Paris and their cabinets, and also serves as a venue for large receptions. It was designated a ''monument historique'' by the French government in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musée Des Beaux-Arts De Rouen
The Musée des Beaux-Arts de Rouen () is an art museum in Rouen, in Normandy in north-western France. It was established by Napoléon Bonaparte in 1801, and is housed in a building designed by and built between 1877, and 1888. Its collections include paintings, sculptures, drawings and objets d'art. History The museum was established by Napoléon Bonaparte in 1801. The museum building was built between 1877, and 1888 to designs by . The collections include paintings, sculptures, drawings and objets d'art from the Renaissance to the present day, including a collection of Russian icons dating from the fifteenth to the early nineteenth century, and some 8000 drawings. The Depeaux collection of Impressionist works was donated to the museum in 1909. The Rouen Museum of Fine Arts is one of the main regional museums in France6. It is located in the heart of the city, opposite Square Verdrel, in a building whose complete renovation was completed in 1994. In addition to the prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salon Of 1833
The Salon of 1833 was an art exhibition held at the Louvre in Paris which opened on the 1 March 1833. It was held during the July Monarchy of Louis Philippe I and the first Salon to be staged since the failed Paris Uprising of 1832 against his rule. The critic Heinrich Heine, reviewing the Salon, observed that Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres was the dominant figure of the Salon. "Like Louis-Philippe in politics, M. Ingres was this year the king in art: as the former reigned at the Tuileries, he reigned at the Louvre". Eugene Delacroix who had enjoyed success at the Salon of 1831 with ''Liberty Leading the People'', was away in Morocco in 1832 and short of time he submitted a few watercolours and portraits rather than the history paintings he had become known for. Amongst the works on display was ''The Nation Is in Danger'', a large patriotic painting commissioned by Louis Philippe I from Auguste-Hyacinthe Debay of which only a fragment now survives. Joseph-Désiré Court exhibited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |