|
John Henry Hutton
John Henry Hutton FRAI (27 June 1885 – 23 May 1968) was an English-born anthropologist and an administrator in the Indian Civil Service (ICS) during the period of the British Raj. The period that he spent with the ICS in Assam evoked an interest in tribal cultures of that region that was of seminal importance. His research work was recognised subsequently with his appointment to the chair of William Wyse Professor of Social Anthropology at the University of Cambridge and with various honours. Early life John Henry Hutton was the son of a Church of England clergyman. He was born on 27 June 1885 at West Heslerton, then in the East Riding of Yorkshire and now in North Yorkshire. He attended Chigwell School in Essex and then obtained a third-class degree in modern history from Worcester College, Oxford in 1907. Career Hutton joined the ICS in 1909, spending most of his career in India in Assam. He held positions as a Political Officer and as a Deputy Commissioner, for which h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Anthropological Institute Of Great Britain And Ireland
The Royal Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland (RAI) is a long-established anthropological organisation, and Learned Society, with a global membership. Its remit includes all the component fields of anthropology, such as biological anthropology, evolutionary anthropology, social anthropology, cultural anthropology, visual anthropology and medical anthropology, as well as sub-specialisms within these, and interests shared with neighbouring disciplines such as human genetics, archaeology and linguistics. It seeks to combine a tradition of scholarship with services to anthropologists, including students. The RAI promotes the public understanding of anthropology, as well as the contribution anthropology can make to public affairs and social issues. It includes within its constituency not only academic anthropologists, but also those with a general interest in the subject, and those trained in anthropology who work in other fields. History The institute's fel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Philip Mills
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kathleen Gough
Eleanor Kathleen Gough Aberle (16 August 1925 – 8 September 1990) was a British anthropologist and feminist who was known for her work in South Asia and South-East Asia. As a part of her doctorate work, she did field research in Malabar district from 1947 to 1949. She did further research in Tanjore district from 1950 to 1953 and again in 1976, and in Vietnam in 1976 and 1982. In addition, some of her work included campaigning for: nuclear disarmament, the civil rights movement, women's rights, the third world and the end of the Vietnam War. She was known for her Marxist leanings and was on an FBI watchlist. Early life and education Kathleen Gough was born on 16 August 1925 in Hunsingore, a village near Wetherby in Yorkshire, England, that then had a population of 100, no electricity and no piped water. She had a brother and a half-sister. Her father, Albert, was a blacksmith who became involved in the introduction of agricultural machinery to the area and has been des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frazer Lecture
The Sir James George Frazer Memorial Lectureship in Social Anthropology is a British academic lecture series. In 1920 a sum of £675 was raised by a Committee of the University of Cambridge for the purpose of commemorating Sir James Frazer's contributions to learning. In accordance with the wishes of the subscribers, a Frazer Lectureship in Anthropology was founded, the annual income of the fund being assigned to the University of Oxford, University of Cambridge, University of Glasgow and University of Liverpool , mottoeng = These days of peace foster learning , established = 1881 – University College Liverpool1884 – affiliated to the federal Victoria Universityhttp://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukla/2004/4 University of Manchester Act 200 ... in rotation for this purpose. Lectures Oxford Lectures Cambridge Lectures Glasgow Lectures Liverpool Lectures References *''Oxford University Gazette'' *''Cambridge University Reporter'' *''University of Liverpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Arts
The Royal Society for the Encouragement of Arts, Manufactures and Commerce (RSA), also known as the Royal Society of Arts, is a London-based organisation committed to finding practical solutions to social challenges. The RSA acronym is used more frequently than the full legal name (The Royal Society for the Encouragement of Arts, Manufactures and Commerce). The RSA's mission expressed in the founding charter was to "embolden enterprise, enlarge science, refine art, improve our manufacturers and extend our commerce", but also of the need to alleviate poverty and secure full employment. On its website, the RSA characterises itself as "an enlightenment organisation committed to finding innovative practical solutions to today's social challenges". Notable past fellows (before 1914, members) include Charles Dickens, Benjamin Franklin, Stephen Hawking, Karl Marx, Adam Smith, Marie Curie, Nelson Mandela, David Attenborough, Judi Dench, William Hogarth, John Diefenbaker, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Sheriff Of Radnorshire
History The office of High Sheriff is over 1000 years old, with its establishment before the Norman Conquest. The Office of High Sheriff remained first in precedence in the counties until the reign of Edward VII when an Order in Council in 1908 gave the Lord-Lieutenant the prime office under the Crown as the Sovereign's personal representative. The High Sheriff remains the Sovereign's representative in the County for all matters relating to the Judiciary and the maintenance of law and order. The office of High Sheriff for Radnorshire ceased with local government re-organisation in 1974, when it was combined with the High Sheriffs of Brecknockshire and Montgomeryshire as the High Sheriff of Powys. List of officeholders 16th century 17th century 18th century 19th century 20th century References *Sheriffs:Radnorshire - Powys Local History Encyclopaedia {{High Shrievalties Radnorshire , HQ = Presteigne , Government = Radnorshire Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Indian Empire
The Most Eminent Order of the Indian Empire is an order of chivalry founded by Queen Victoria on 1 January 1878. The Order includes members of three classes: #Knight Grand Commander ( GCIE) #Knight Commander ( KCIE) #Companion ( CIE) No appointments have been made since 1947, the year that British India gained independence as the Union of India and Dominion of Pakistan. With the death of the last surviving knight, the Maharaja Meghrajji III of Dhrangadhra, the order became dormant in 2010. The motto of the Order is ''Imperatricis auspiciis'', (Latin for "Under the auspices of the Empress"), a reference to Queen Victoria, the first Empress of India. The Order is the junior British order of chivalry associated with the British Indian Empire; the senior one is The Most Exalted Order of the Star of India. History The British founded the Order in 1878 to reward British and native officials who served in British India. The Order originally had only one class (Companion), b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
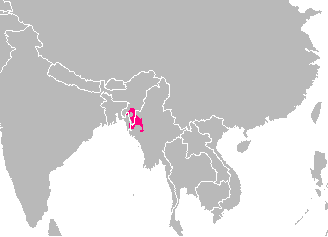
Kuki People
The Kuki people are an ethnic group native to the Mizo Hills (formerly Lushai), a mountainous region in the southeastern part of Mizoram and Manipur in India. The Kuki constitute one of several hill tribes within India, Bangladesh, and Myanmar. In Northeast India, they are present in all states except Arunachal Pradesh. Some fifty tribes of Kuki peoples in India are recognised as scheduled tribes, based on the dialect spoken by that particular Kuki community as well as their region of origin. The Chin people of Myanmar and the Mizo people of Mizoram are kindred tribes of the Kukis. Collectively, they are termed the Zo people. History Early history The early history of the Kukis is obscure. The origin of the word "Kuki" is uncertain; it is an exonym: it was not originally as a self-designation by the tribes that are now called Kukis. According to the colonial British writer Adam Scott Reid, the earliest reference to the word Kuki can be dated to 1777 CE, when it first appea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christoph Von Fürer-Haimendorf
Christoph von Fürer-Haimendorf or Christopher von Fürer-Haimendorf FRAI (22 June 1909 – 11 June 1995) was an Austrian ethnologist and professor at the School of Oriental and African Studies at London. He spent forty years studying tribal cultures in Northeast India, in the central region of what is now the state of Telangana and in Nepal. He was married to British ethnologist of India and Nepal, Betty Barnardo. Biography Christoph von Fürer-Haimendorf was born in an Austrian aristocratic family. Very early he developed an interest in Indian culture, having read Rabindranath Tagore as a young man. He studied anthropology and archaeology in Vienna and there he was most influenced by Robert von Heine-Geldern. He wrote his thesis on the tribal social organization of the peoples of Assam and northwestern Burma (''Staat und Gesellschaft bei den Völkern Assams und des nordwestlichen Birmas'') and in later years was inspired by John Henry Hutton, a fellow rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Radnor
New Radnor ( cy, Maesyfed) is a village in Powys, Wales, to the south of Radnor Forest, and was the county town of Radnorshire. In the 2001 census, the community's population of 410 was split evenly between male and female, in 192 households. The population at the 2011 Census was 409. The community includes the village of Llanfihangel Nant Melan. Medieval planned layout The village lies by the Radnor Forest and has been said to have been built to replace Old Radnor. It was a planned medieval walled town with streets laid out in a grid pattern. It was linked to other settlements nearby and regionally such as Builth, Presteigne and Kington Castle and later Huntington Castle near Gladestry. The castle Attractions in the town include a significant castlebr>mound of a Norman architecture, Norman mottebr> New Radnor castle was originally called Trefaesyfed and was once a considerable fortress and a significant border castle in the Welsh Marches and played its part in the tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalithic Culture
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea. The word was first used in 1849 by the British antiquarian Algernon Herbert in reference to Stonehenge and derives from the Ancient Greek words "mega" for great and "lithos" for stone. Most extant megaliths were erected between the Neolithic period (although earlier Mesolithic examples are known) through the Chalcolithic period and into the Bronze Age. At that time, the beliefs that developed were dynamism and animism, because Indonesia experienced the megalithic age or the great stone age in 2100 to 4000 BC. So that humans ancient tribe worship certain objects that are considered to have supernatural powers. Some relics of the megalithic era are menhirs (stone monuments) and dolmens (stone tables). Types and definitions While "megalith" is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)
.jpg)
