|
John Bugas
John Stephen Bugas (April 26, 1908 – December 2, 1982) was the second in command at Ford Motor Company during the presidency and chairmanship reign of Henry Ford II (the oldest grandson of founder Henry Ford). He is best known for taking control of the company away from Harry Bennett so that John could be in command of it—including drawing pistols on each other—following the death of Edsel Ford. As the ''Detroit Free Press'' wrote of Bugas: Early life The Bugas family originated from Slovakia. The parents of Jack Bugas, Andrew (Andrej) P. Bugas (born in 1867) and Helena L. Bugas (the name "Bugas" was then spelled "Bugos"), were both born in eastern Slovakia, in the village Lučina near Prešov. Andrew Bugas immigrated to the United States in 1882 (following his father, John P. Bugos, who immigrated in 1878, though died back in Slovakia, at that time part of Austria-Hungary, in 1902) and became a naturalized U.S. citizen at age 26 in 1891.Men of Wyoming. ''Slovak Inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Springs, Wyoming
Rock Springs is a city in Sweetwater County, Wyoming, United States. The population was 23,036 at the 2010 census, making it the fifth most populated city in the state of Wyoming, and the most populous city in Sweetwater County. Rock Springs is the principal city of the Rock Springs micropolitan statistical area, which has a population of 37,975. Rock Springs is known as the Home of 56 Nationalities because of the influx of immigrants from all over the world who came to work in the coal mines that supplied the fuel to power the steam engines of the Union Pacific Railroad. The city's rich cultural heritage is celebrated each summer on International Day, a festival where the foods, costumes, and traditions of residents' ancestors are recreated and enjoyed at Bunning Park in downtown Rock Springs. Rock Springs is the site of Western Wyoming Community College and Wyoming's Big Show, a yearly event with a carnival and concerts which is held at the Sweetwater County Events Complex. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wyoming Legislature
The Wyoming State Legislature is the legislative branch of the U.S. State of Wyoming. It is a bicameral state legislature, consisting of a 60-member Wyoming House of Representatives, and a 30-member Wyoming Senate. The legislature meets at the Wyoming State Capitol in Cheyenne. There are no term limits for either chamber. The Republican Party holds a supermajority in the current legislature, which began meeting in 2019; 51 of the 60 seats in the House and 28 of the 30 seats in the Senate are held by Republicans. History The Wyoming State Legislature began like other Western states as a territorial legislature, with nearly (though with not all) the parliamentary regulations that guide other fully-fledged state legislatures. Women's Suffrage During its territorial era, the Wyoming Legislature played a crucial role in the Suffragette Movement in the United States. In 1869, only four years following the American Civil War, and another 35 years before women's suffrage became a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lindbergh Kidnapping
On March 1, 1932, Charles Augustus Lindbergh Jr. (born June 22, 1930), the 20-month-old son of aviators Charles Lindbergh and Anne Morrow Lindbergh, was abducted from his crib in the upper floor of the Lindberghs' home, Highfields, in East Amwell, New Jersey, United States. On May 12, the child's corpse was discovered by a truck driver by the side of a nearby road. In September 1934, a German immigrant carpenter named Bruno Richard Hauptmann was arrested for the crime. After a trial that lasted from January 2 to February 13, 1935, he was found guilty of first-degree murder and sentenced to death. Despite his conviction, he continued to profess his innocence, but all appeals failed and he was executed in the electric chair at the New Jersey State Prison on April 3, 1936. Newspaper writer H. L. Mencken called the kidnapping and trial "the biggest story since the Resurrection". Legal scholars have referred to the trial as one of the "trials of the century". The crime spurred Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoll Kidnapping
The Stoll kidnapping was a 1934 crime in Louisville, Kentucky that made the front page of national newspapers and magazines as an FBI investigation under the Federal Kidnapping Act. In 2016, ''Louisville Magazine'' writer Brian Hunt called the Stoll kidnapping "Louisville's crime of the century." Alice Speed-Stoll, wife of oil company executive Berry V. Stoll, was kidnapped in October 1934 and held in Indianapolis for a $50,000 ransom by Thomas H. Robinson, Jr. While the kidnapper's wife was apprehended by the FBI almost immediately, Robinson was not arrested until May 11, 1936, when he was taken at gunpoint in Glendale, California by FBI agents including John Bugas. Robinson was convicted, served time in prison, was retried and sentenced to death, had his death sentence commuted by President Harry S. Truman Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. A leader of the Democratic Party, he previously s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Enemy
"Public enemy" is a term which was first widely used in the United States in the 1930s to describe individuals whose activities were seen as criminal and extremely damaging to society, though the phrase had been used for centuries to describe pirates, vikings, highwaymen, bandits, mobsters, and similar outlaws. Origin and usage The expression dates back to Roman times. The Senate declared emperor Nero a ''hostis publicus'' in AD 68. Its direct translation is "public enemy". Whereas "public" is currently used in English in order to describe something related to collectivity at large, with an implication towards government or the State, the Latin word "publicus" could, in addition to that meaning, also refer directly to people, making it the equivalent of the genitive of ''populus'' ("people"), ''populi'' ("popular" or "of the people"). Thus, "public enemy" and " enemy of the people" are, etymologically, near-synonyms. The words "'' ennemi du peuple''" were extensively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Nazi Germany. During Hitler's rise to power in 1930s Europe, it was frequently referred to as Hitlerism (german: Hitlerfaschismus). The later related term "neo-Nazism" is applied to other far-right groups with similar ideas which formed after the Second World War. Nazism is a form of fascism, with disdain for liberal democracy and the parliamentary system. It incorporates a dictatorship, fervent antisemitism, anti-communism, scientific racism, and the use of eugenics into its creed. Its extreme nationalism originated in pan-Germanism and the ethno-nationalist ''Völkisch movement, Völkisch'' movement which had been a prominent aspect of German nationalism since the late 19th century, and it was strongly i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
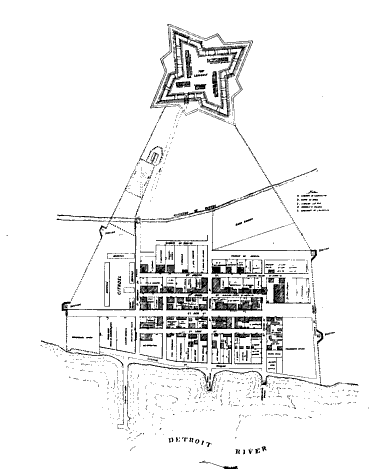
Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at the 2020 census, making it the 27th-most populous city in the United States. The metropolitan area, known as Metro Detroit, is home to 4.3 million people, making it the second-largest in the Midwest after the Chicago metropolitan area, and the 14th-largest in the United States. Regarded as a major cultural center, Detroit is known for its contributions to music, art, architecture and design, in addition to its historical automotive background. '' Time'' named Detroit as one of the fifty World's Greatest Places of 2022 to explore. Detroit is a major port on the Detroit River, one of the four major straits that connect the Great Lakes system to the Saint Lawrence Seaway. The City of Detroit anchors the second-largest regional econ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Bureau Of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice, the FBI is also a member of the U.S. Intelligence Community and reports to both the Attorney General and the Director of National Intelligence. A leading U.S. counterterrorism, counterintelligence, and criminal investigative organization, the FBI has jurisdiction over violations of more than 200 categories of federal crimes. Although many of the FBI's functions are unique, its activities in support of national security are comparable to those of the British MI5 and NCA; the New Zealand GCSB and the Russian FSB. Unlike the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), which has no law enforcement authority and is focused on intelligence collection abroad, the FBI is primarily a domestic agency, maintaining 56 field offices in major cities thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma Alpha Epsilon
Sigma Alpha Epsilon (), commonly known as SAE, is a North American Greek-letter social college Fraternities and sororities in North America, fraternity. It was founded at the University of Alabama on March 9, 1856. Of all existing national social fraternities today, Sigma Alpha Epsilon is the only one founded in the Antebellum Age, Antebellum Southern United States, South. Its national headquarters, the Levere Memorial Temple, was established on the campus of Northwestern University in Evanston, Illinois, in 1929. The fraternity's mission statement is "To promote the highest standards of friendship, scholarship and service for our members based upon the ideals set forth by our Founders and as specifically enunciated in our creed." The fraternity has chapters and colonies in 50 states and provinces as of 2011. The creed of Sigma Alpha Epsilon, ''The True Gentleman'', must be memorized and recited by all prospective members. In March 2014, the fraternity announced that it was elimi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1933–34 Wyoming Cowboys Basketball Team
The 1933–34 Wyoming Cowboys basketball team represented the University of Wyoming during the 1933–34 NCAA men's basketball season in the United States. The head coach was Willard Witte, coaching in his fourth season with the Cowboys. The team finished the season with a 26–4 record and were named national champions by the Helms Athletic Foundation. Schedule and results , - !colspan=9, Regular season ''Source'' References {{DEFAULTSORT:1933-34 Wyoming Cowboys Basketball Team Wyoming Cowboys basketball seasons Wyoming Wyoming () is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the southwest, and Colorado to the sou ... NCAA Division I men's basketball tournament championship seasons Wyoming Cowboys Basketball Team Wyoming Cowboys Basketball Team ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willard Witte
Willard A. "Dutch" Witte (April 3, 1906 – February 13, 1966) was the head men's basketball and football coach of the University of Wyoming from 1930–31 through 1938–39 (basketball) and 1933 through 1938 (football). He led the Cowboys basketball team to an overall record of 134–51 in his tenure. His 1933–34 team, led by his younger brother and two-time consensus All-American Les Witte, finished 26–4 and were retroactively named national champions by the Helms Athletic Foundation. He died in 1966 at a hospital in Fremont, Nebraska."Death Claims Former Coach for Cowboys", United Press International United Press International (UPI) is an American international news agency whose newswires, photo, news film, and audio services provided news material to thousands of newspapers, magazines, radio and television stations for most of the 20th ..., February 15, 1966 He also coached Wyoming to three division titles and two outright conference championships. He was induc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |