|
John Bidwell
John Bidwell (August 5, 1819 – April 4, 1900), known in Spanish as Don Juan Bidwell, was an American pioneer, politician, and soldier. Bidwell is known as the founder of the city of Chico, California. Born in New York, he emigrated at the age of 22 to Alta California (then a part of Mexico) as part of the Bartleson–Bidwell Party, one of the first expeditions of American emigrants along the California Trail. In California, he became a Mexican citizen and a prominent landowner, receiving multiple rancho grants from the governors of Alta California. Following the U.S. Conquest of California, Bidwell went on to serve in the California Senate and then in the U.S. House of Representatives. Early life Bidwell was born in 1819 in Chautauqua County, New York. His Bidwell ancestors immigrated to North America in the colonial era. His family moved to Erie, Pennsylvania, in 1829, and then to Ashtabula County, Ohio, in 1831. At age 17, he attended and shortly thereafter became princi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mathew Brady
Mathew B. Brady ( – January 15, 1896) was an American photographer. Known as one of the earliest and most famous photographers in American history, he is best known for his scenes of the American Civil War, Civil War. He studied under inventor Samuel Morse, who pioneered the daguerreotype technique in America. Brady opened his own studio in New York City in 1844, and went on to photograph President of the United States, U.S. presidents John Quincy Adams, Abraham Lincoln, Millard Fillmore, Martin Van Buren, and other public figures. When the Civil War began, Brady's use of a mobile studio and darkroom enabled thousands of vivid War photography, battlefield photographs to bring home the reality of war to the public. He also photographed generals and politicians on both sides of the conflict, though most of these were taken by his assistants rather than by Brady himself. After the end of the Civil War, these pictures went out of fashion, and the government did not purchase the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bidwell Mansion State Historic Park
Bidwell Mansion State Historic Park was a historic building with surrounding land in Chico, California, United States. It is listed as a California Historical Landmark #329 under the name "Rancho Chico And Bidwell Adobe" in 1939; and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places under the name "Bidwell Mansion" on March 24, 1972. On December 11, 2024, the building was destroyed by arson. History Bidwell Mansion was the home of General John Bidwell and Annie Bidwell from late 1868 until 1900, when Gen. Bidwell died. Annie continued to live there until her death in 1918. John Bidwell began construction of the mansion on his Rancho del Arroyo Chico in 1865, during his courtship of Annie Ellicott Kennedy. After their marriage in 1868, the three-story, 26-room Victorian house became the social and cultural center of the upper Sacramento Valley. The mansion was a $60,000 project, and was finished in May 1868. When constructed, Bidwell Mansion featured modern plumbing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Conquest Of California
The Conquest of California, also known as the Conquest of Alta California or the California Campaign, was a military campaign during the Mexican–American War carried out by the United States in Alta California (modern-day California), then part of Mexico, lasting from 1846 to 1847, and ending with signing of the Treaty of Cahuenga by military leaders from both the Californios and Americans. Background When war was declared on May 13, 1846, between the United States and Mexico, it took almost three months for definitive word of Congress' declaration of war to reach the Pacific coast. U.S. consul Thomas O. Larkin, stationed in the pueblo of Monterey, California, Monterey, was concerned about the increasing possibility of war and worked to prevent bloodshed between the Americans and the small Mexican military garrison at the Presidio of Monterey, California, Presidio of Monterey, commanded by José Castro. United States Army Captain John C. Frémont, on a United States Army Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ranchos Of California
In Alta California (now known as California) and Baja California, ranchos were concessions and land grants made by the Viceroyalty of New Spain, Spanish and History of Mexico, Mexican governments from 1775 to 1846. The Spanish concessions of land were made to retired soldiers as an inducement for them to settle in the frontier. These concessions reverted to the Spanish crown upon the death of the recipient. After independence, the Mexican government encouraged settlement in these areas by issuing much larger land grants to both native-born and naturalized Mexican citizens. The grants were usually two or more square league (unit), leagues, or in size. Unlike Spanish Concessions, Mexican land grants provided permanent, unencumbered ownership rights. Most ranchos granted by Mexico were located along the California coast around San Francisco Bay, inland along the Sacramento River, and within the San Joaquin Valley. When the Missions were secularized per the Mexican Secularizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
California Trail
The California Trail was an emigrant trail of about across the western half of the North American continent from Missouri River towns to what is now the state of California. After it was established, the first half of the California Trail followed the same corridor of networked river valley trails as the Oregon Trail and the Mormon Trail, namely the valleys of the Platte, North Platte, and Sweetwater rivers to Wyoming. The trail has several splits and cutoffs for alternative routes around major landforms and to different destinations, with a combined length of over . Introduction By 1847, two former fur trading frontier forts marked trailheads for major alternative routes through Utah and Wyoming to Northern California. The first was Jim Bridger's Fort Bridger (est. 1842) in present-day Wyoming on the Green River, where the Mormon Trail turned southwest over the Wasatch Range to the newly established Salt Lake City, Utah. From Salt Lake the Salt Lake Cutoff (est. 1848 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bartleson–Bidwell Party
In 1841, the Bartleson–Bidwell Party of thirty-two men and one woman, and her baby daughter, was led by Captain John Bartleson and John Bidwell. They became the first American emigrants to succeed in a wagon crossing from Missouri to California. No lives were lost in their difficult trip. Beginnings In the winter of 1840, the Western Emigration Society was founded in Missouri, with a few dozen men, women and children ready to go to what they thought was a very prosperous utopia in Mexican California. Members included Baldridge, Barnett, Bartleson, Bidwell and Nye. Organized on 18 May 1841, Talbot H. Green was elected president, John Bidwell secretary, and John Bartleson captain. The group joined Father Pierre Jean De Smet's Jesuit missionary group, led by Thomas F. Fitzpatrick, westward across South Pass along the Oregon Trail. That trail took them past Courthouse and Jail Rocks, Chimney Rock, Scotts Bluff, Fort Laramie, and Independence Rock. The Bartleson-Bidwell party ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
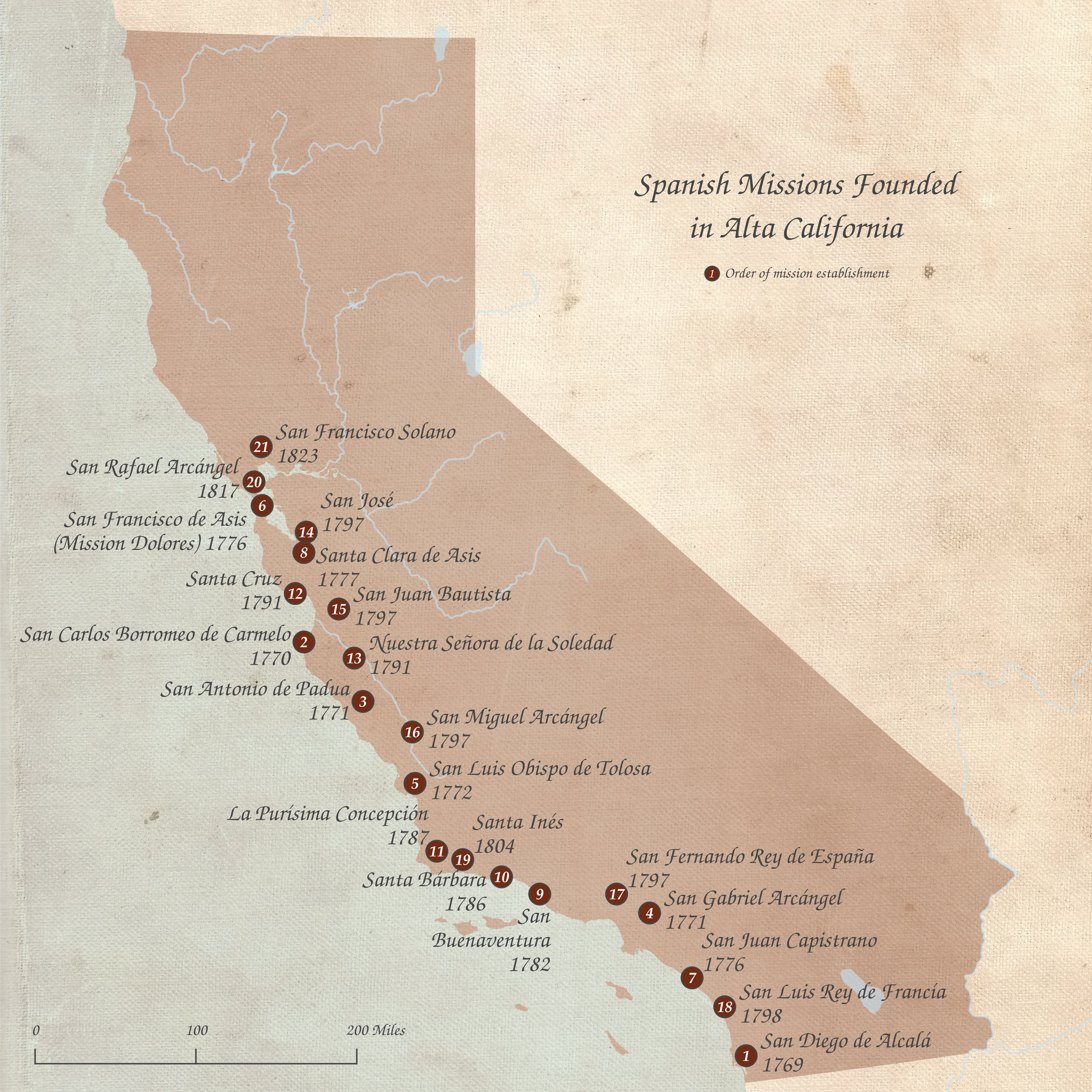
Alta California
Alta California (, ), also known as Nueva California () among other names, was a province of New Spain formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but was made a separate province in 1804 (named ). Following the Mexican War of Independence, it became a territory of First Mexican Empire, Mexico in April 1822 and was renamed in 1824. The territory included all of the present-day U.S. states of California, Nevada, and Utah, and parts of Arizona, Wyoming, and Colorado. The territory was with Baja California Territory, Baja California (as a single ) in Mexico's 1836 ''Siete Leyes'' (Seven Laws) constitutional reform, granting it more autonomy. That change was undone in 1846, but rendered moot by the outcome of the Mexican–American War in 1848, when most of the areas formerly comprising Alta California Mexican Cession, were ceded to the U.S. in Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, the treaty which ended the war. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spanish Language
Spanish () or Castilian () is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin spoken on the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. Today, it is a world language, global language with 483 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain, and about 558 million speakers total, including second-language speakers. Spanish is the official language of List of countries where Spanish is an official language, 20 countries, as well as one of the Official languages of the United Nations, six official languages of the United Nations. Spanish is the world's list of languages by number of native speakers, second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's list of languages by total number of speakers, fourth-most spoken language overall after English language, English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani language, Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, (April 25, 1846 – February 2, 1848) was an invasion of Second Federal Republic of Mexico, Mexico by the United States Army. It followed the 1845 American annexation of Texas, which Mexico still considered its territory because it refused to recognize the Treaties of Velasco, signed by President Antonio López de Santa Anna after he was captured by the Texian Army during the 1836 Texas Revolution. The Republic of Texas was ''de facto'' an independent country, but most of its Anglo-American citizens who had moved from the United States to Texas after 1822 wanted to be annexed by the United States. Sectional politics over slavery in the United States had previously prevented annexation because Texas would have been admitted as a slave state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
California Battalion
The California Battalion (also called the first California Volunteer Militia and U.S. Mounted Rifles) was formed during the Mexican–American War (1846–1848) in present-day California, United States. It was led by U.S. Army Brevet (military), Brevet Lieutenant Colonel John C. Frémont and composed of his cartographers, scouts and hunters and the Rebel Californian Volunteer Militia formed during the Bear Flag Revolt. The battalion's formation was officially authorized by Commodore (United States), Commodore Robert F. Stockton, commanding officer of the U.S. Navy Pacific Squadron. Formation Hostilities between U.S. and Mexican forces had been History of Texas, underway in Texas since April 1846 resulting in a formal declaration of war on 13 May 1846, by the U.S. Congress. On 17 May 1846, unofficial word reached the U.S. Navy fleet of four vessels at anchor in the harbor of Mazatlán, Mexico, and that hostilities had begun between Mexico and the United States. Commodore (United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Brigadier General (United States)
In the United States Armed Forces, a brigadier general is a one-star general officer in the United States Army, Marine Corps, Air Force, and Space Force. A brigadier general ranks above a colonel and below a Major general (United States), major general. The U.S. uniformed services pay grades, pay grade of brigadier general is O-7. It is equivalent to the rank of Rear admiral (United States)#Rear admiral (lower half), rear admiral (lower half) in the other United States Uniformed services of the United States, uniformed services which use Naval officer ranks, naval ranks. It is abbreviated as BG in the Army, BGen in the Marine Corps, and Brig Gen in the Air Force and Space Force. The Civil Air Patrol also uses this grade for its National Vice Commander and some past National commanders. History The rank of brigadier general has existed in the U.S. military since the inception of the Continental Army in June 1775. To prevent mistakes in recognizing officers, a general ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |