|
Joggins Fossil Cliffs
Joggins is a rural community located in western Cumberland County, Nova Scotia, Canada. On July 7, 2008 a 15-km length of the coast constituting the Joggins Fossil Cliffs was officially inscribed on the World Heritage List.UNESCO portal History The area was known to the as "Chegoggins" meaning place of the large fish weir, a name modified by French and English settlers to Joggins. Situated on the Cumberland Basin, a sub-basin of the |
Cumberland County, Nova Scotia
Cumberland County is a county in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. Cumberland was named in 1755 in honour of the Duke of Cumberland to replace Beausejour. The historic county was founded in 1759 when the English system of administration was installed to complement settlement during the Charles Lawrence governorship, and was later divided at the partitioning of the province and in 1840. The area thrived in the 19th century with the development of lumbering, shipbuilding, and coal mining, but rural outmigration and deforestation led to some communities being abandoned in the 20th century. The county spans an area of 4,271.23 km2 making it Nova Scotia's second largest county, with resources including extensive forest land, several mineral resources, and agricultural areas that concentrate on wild blueberry harvesting. As of the 2021 census, Cumberland County had a population of 30,538, with the majority residing in the Municipality of the County of Cumberland. The county in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint John, New Brunswick
Saint John () is a port#seaport, seaport city located on the Bay of Fundy in the province of New Brunswick, Canada. It is Canada's oldest Municipal corporation, incorporated city, established by royal charter on May 18, 1785, during the reign of George III. The Port of Saint John is Canada's third-largest by tonnage with a cargo base that includes dry and liquid bulk, Breakbulk cargo, break bulk, containers, and cruise. The city has a strong industrial base, including oil refining and manufacturing, matched with finance and tourism sectors and research institutions such as the New Brunswick Museum and the University of New Brunswick. Saint John was the most populous in New Brunswick until the 2016 Canadian census, 2016 census, when it was overtaken by Moncton. It is currently the second-largest city in the province, with a population of 69,895 over an area of . French explorer Samuel de Champlain landed at Saint John Harbour on June 24, 1604, the feast of St. John the Baptist, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glooscap Trail
The Glooscap Trail is a scenic roadway in the Canada, Canadian province of Nova Scotia. It is located in the central and northern part of the province around the Minas Basin and Cobequid Bay, sub-basins of the Bay of Fundy. The route connects Amherst, Nova Scotia, Amherst in Cumberland County, Nova Scotia, Cumberland County, near the interprovincial boundary with New Brunswick, with Scot's Bay, Nova Scotia, Scot's Bay in Kings County, Nova Scotia. A spur route, spur of Glooscap Trail follows Nova Scotia Trunk 2, Trunk 2 in Truro, Nova Scotia, Truro, through the Shubenacadie Valley, to Enfield, Nova Scotia, Enfield at the boundary with Halifax Regional Municipality. The Fundy Shore Scenic Drive, Fundy Shore segment branches off from the main route in Parrsboro and continues along the Minas Basin shore until reaching Advocate Harbour, where the route then follows the Chignecto Bay, outlining the Chignecto Peninsula. The main route measures , with the Shubenacadie Valley spur being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
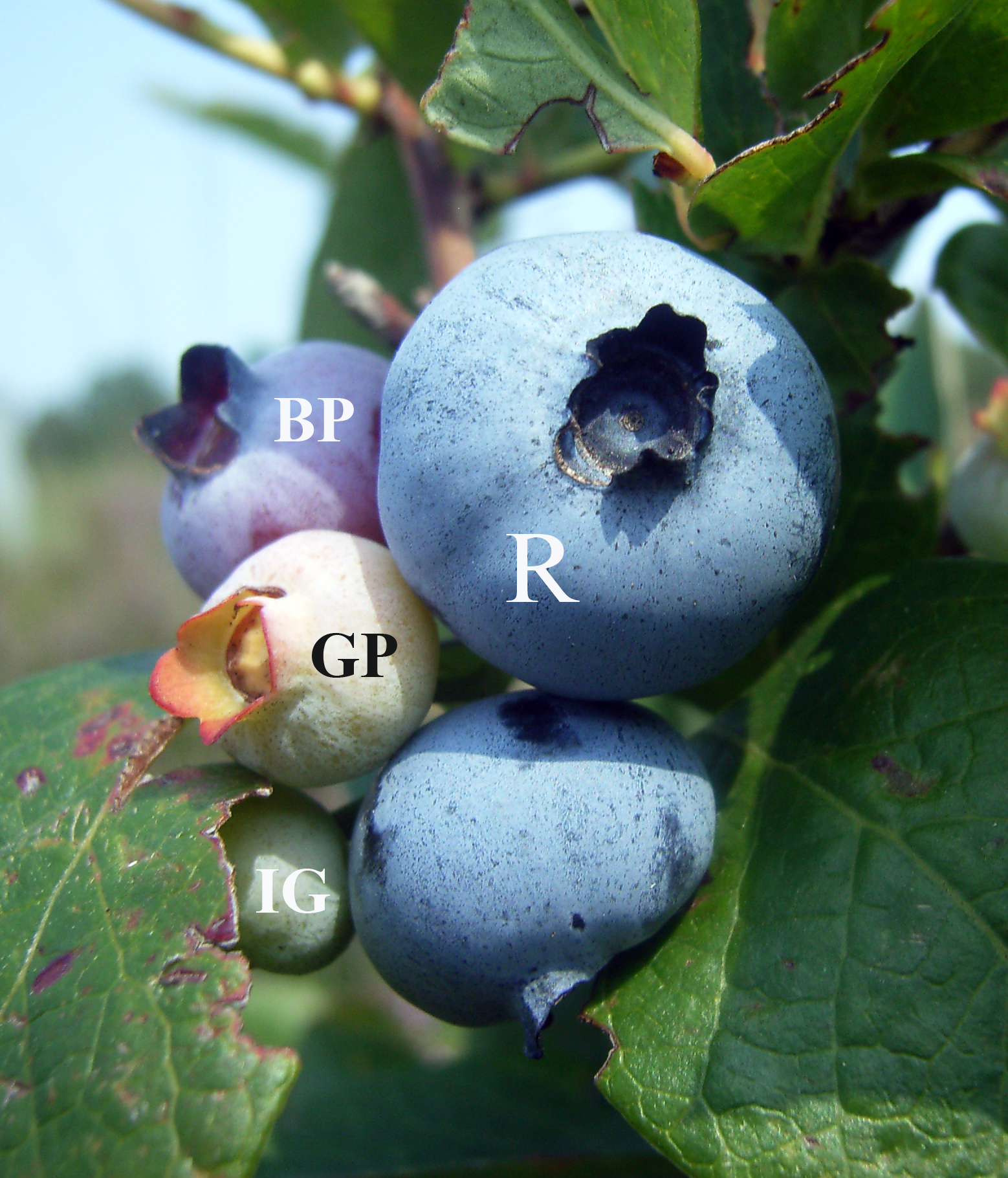
Blueberries
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' with the genus ''Vaccinium''. Commercial blueberries—both wild (lowbush) and cultivated (highbush)—are all native to North America. The highbush varieties were introduced into Europe during the 1930s. Blueberries are usually prostrate shrubs that can vary in size from to in height. In the commercial production of blueberries, the species with small, pea-size berries growing on low-level bushes are known as "lowbush blueberries" (synonymous with "wild"), while the species with larger berries growing on taller, cultivated bushes are known as "highbush blueberries". Canada is the leading producer of lowbush blueberries, while the United States produces some 40% of the world's supply of highbush blueberries. Description Many species of blueberries grow wild in North America, including '' Vaccinium myrtilloi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science), crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Limestone forms when these minerals Precipitation (chemistry), precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly Dolomite (rock), dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral Dolomite (mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springhill Mining Disaster
Springhill mining disaster may refer to any of three deadly Canadian mining disasters that occurred in 1891, 1956, and 1958 in different mines within the Springhill coalfield, near the town of Springhill in Cumberland County, Nova Scotia. In the 1891 accident, 125 died; in 1956, 39 were killed; and in 1958, 75 miners were killed. The mines in the Springhill coalfield were established in the 19th century, and by the early 1880s were being worked by the Cumberland Coal & Railway Company Ltd. and the Springhill & Parrsboro Coal & Railway Company Ltd. These entities merged in 1884 to form the Cumberland Railway & Coal Company Ltd., which its investors sold in 1910 to the industrial conglomerate Dominion Coal Company Ltd. (DOMCO). Following the third disaster in 1958, the operator Dominion Steel & Coal Corporation Ltd. (DOSCO), then a subsidiary of the A.V. Roe Canada Company Ltd., shut its mining operations in Springhill, and they were never reopened. the mine properties, am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maccan
Maccan is a small community in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia, located in Cumberland County 10 minutes away from Amherst, Nova Scotia on Route 302. The word Maccan is derived from the Mi'kmaq word 'Maakan' meaning a good place for fishing. It was a thriving coal mining, farming, railroad and river ship building community. Maccan was home of the famed Nova Scotia Intermediate baseball club, the Maccan Royals. Several books on the history of Maccan have been written. Copies are available at the Cumberland County Museum in Amherst, and in the Amherst Public Library. Several historic figures were born in Maccan, including Jonathan McCully Jonathan McCully (July 25, 1809 – January 2, 1877) was a participant at the Confederation conferences at Charlottetown, Quebec City, and in London, and is thus considered one of the Canadian Confederation, Fathers of Canadian Confederation ..., Father of Confederation. References Maccan on Destination Nova Scotia Communities in C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acadians
The Acadians (; , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French colonial empire, French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, most descendants of Acadians live in either the Northern American Acadia (region), region of Acadia, where descendants of Acadians who escaped the Expulsion of the Acadians (a.k.a. The Great Upheaval / ''Le Grand Dérangement'') re-settled, or in Louisiana, where thousands of Acadians moved in the late 1700s. Descendants of the Louisiana Acadians are most commonly known as Cajuns, the anglicized term of "Acadian". Acadia was one of the five regions of New France, located in what is now Eastern Canada's The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, as well as parts of Quebec and present-day Maine to the Kennebec River. It was ethnically, geographically and administratively different from the other French colonies such as the Canada (New France), French colony of Canada. As a result, the Acadians developed a dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Mine
Coal mining is the process of resource extraction, extracting coal from the ground or from a mine. Coal is valued for its Energy value of coal, energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to Electricity generation, generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from iron ore and for cement production. In the United Kingdom and South Africa, a coal mine and its structures are a colliery, a coal mine is called a "pit", and above-ground mining structures are referred to as a "pit head". In Australia, "colliery" generally refers to an underground coal mine. Coal mining has had many developments in recent years, from the early days of men tunneling, digging, and manually extracting the coal on carts to large Open-pit mining, open-cut and Longwall mining, longwall mines. Mining at this scale requires the use of Dragline excavator, draglines, trucks, conveyors, hydraulic jacks, and shearers. The coal mining industry has a long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Hebert, Nova Scotia
River Hebert is a village on the River Hebert in Cumberland County, Nova Scotia, Canada.It is approximately 25 kilometres southwest of Amherst. As of 2021 the population was 468. The village and the river are both named after Louis Hébert, an early French settler from Port Royal, who navigated the river. Until the late 20th century, coal mining was the major industry in the area, but the last mine closed in 1981. River Hebert is home to 1442 River Hebert Royal Canadian Army Cadet Corps, founded in 1949. River Hebert has one school that is open to students from grades pre-primary to 12, a public library, a medical centre, and it is home to Heritage Models, a tourist attraction that features scale models of local areas of interest, such as the home of Amos Peck "King" Seaman. The Village is also home to a gas station, which was burned down, but has since been replaced. Demographics In the 2021 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada Statistics Canada (Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |