|
Jiāng (state)
Jiang (), also known as Hong () during the Shang dynasty or Qiong () in some historical sources, was a vassal state in China that encompasses the southeastern Henan from 1101 BCE to 623 BCE. The nation was ruled by the Ying family (), and the state name is widely believed to be the origin of the Chinese surname Jiang. The swan goose was the totem of the state. History Early history (before 1045 BCE) In 1101 BCE, Yu the Great, the leader of China under the Xia dynasty allocated a piece of land on the riverbanks of the Huai River to Genchu () under the Fengjian system. Genchu was the son of Boyi, a legendary tribal leader who was loyal to Yu the Great, and the allocation of the land to Genchu was mainly for rewarding Boyi's family for Boyi's exemplary achievements in controlling the Great Flood. Chinese historian Guangyue He () believes that the state was part of Dongyi, a group of tribes in eastern China during the pre- Qin era, and moved southwards to modern-day Hena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
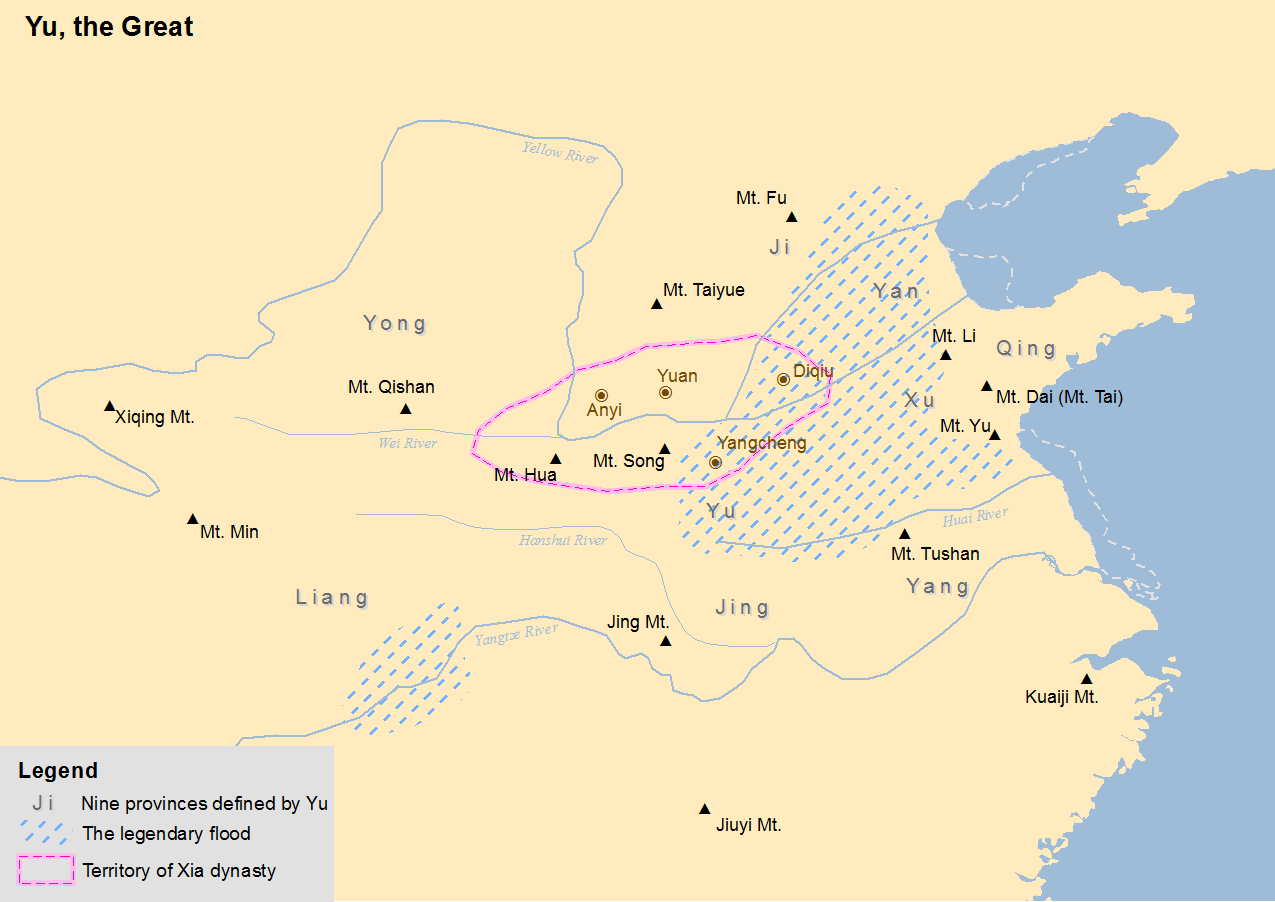
Xia Dynasty
The Xia dynasty (; ) is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, it was established by the legendary figure Yu the Great, after Emperor Shun, Shun, the last of the Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors, Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In traditional historiography, the Xia was succeeded by the Shang dynasty. There are no contemporaneous records of the Xia, and they are not mentioned in the oldest Chinese texts, the earliest oracle bone inscriptions dating from the Late Shang period (13th century BC). The earliest mentions occur in the oldest chapters of the ''Book of Documents'', which report speeches from the early Western Zhou period and are accepted by most scholars as dating from that time. The speeches justify the Zhou conquest of the Shang as the passing of the Mandate of Heaven and liken it to the succession of the Xia by the Shang. That political philosophy was promoted by the Confucian school in the Eastern Zhou period. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Flood (China)
The Great Flood of Gun-Yu, also known as the Gun-Yu myth,. was a major flood in ancient China that allegedly continued for at least two generations, which resulted in great population displacements among other disasters, such as storms and famine. People left their homes to live on the high hills and mountains, or nest on the trees. According to mythological and historical sources, it is traditionally dated to the third millennium BCE, or about 2300–2200 BCE, during the reign of Emperor Yao. However, archaeological evidence of an outburst flood at Jishi Gorge on the Yellow River, comparable to similar severe events in the world in the past 10,000 years, has been dated to about 1920 BCE (a few centuries later than the traditional beginning of the Xia dynasty which came after Emperors Shun and Yao), and is suggested to have been the basis for the myth.. Treated either historically or mythologically, the story of the Great Flood and the heroic attempts of the various human ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Cheng Of Chu
King Cheng of Chu (), personal name Xiong Yun, was a ruler of the Chu state, ruling from 671 BC to 626 BC. In 672 BC, King Cheng's older brother, Du'ao, attempted to have him killed. King Cheng escaped to the Sui state. He then attacked and killed Du'ao with the help of Sui, and succeeded Du'ao as king of Chu. Life In the summer of 648 BC, the State of Huang was annexed by the state of Chu. King Cheng's wife was Zheng Mao. Their son was possibly King Mu of Chu. The ''Shiji'' gives a detailed account of the events surrounding King Cheng's succession and untimely end. In the forty-sixth year of his reign (626 BC), Cheng wanted to make Shangchen (商臣), the future King Mu, his crown prince. Lingyin (title for prime minister of Chu) Zishang (子上) advised against this, fearing that there were many contenders for the position and that, if the king were to change his mind and act to replace the crown prince, a disturbance would ensue. He also warned the king that Shangch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qi (state)
Qi, or Ch'i in Wade–Giles romanization, was a ancient Chinese state, regional state of the Zhou dynasty in History of China#Ancient China, ancient China, whose rulers held Zhou dynasty nobility, titles of ''Hou'' (), then ''Gong (title), Gong''Gong (title), (公), before declaring themselves independent Kings (王). Its capital was Ancient Linzi, Linzi, located in present-day Shandong. Qi was founded shortly after the Zhou Battle of Muye, conquest of Shang dynasty, Shang, . Its first monarch was Jiang Ziya (Lord Tai; 1046–1015 BCE ), chancellor (China), minister of King Wen of Zhou, King Wen and a Chinese legend, legendary figure in Chinese culture. His Chinese surname#Xing, family ruled Qi for several centuries before it was Usurpation of Qi by Tian, replaced by the Tian family in 386BCE. Qi was the final surviving state to be annexed by state of Qin, Qin during its Qin's wars of unification, unification of China. History Foundation During the Zhou dynasty, Zh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song (state)
Song was an ancient Chinese state during the Zhou dynasty with its capital at Shangqiu. The state was founded soon after King Wu of Zhou conquered the Shang dynasty to establish the Zhou dynasty in 1046 BC. It was conquered by the state of Qi in 286 BC, during the Warring States period. Confucius is traditionally considered to have been a descendant of a Song nobleman who moved to the state of Lu. Origin King Zhou of Shang, King Zhou of Shang, Di Xin was the younger brother of Jizi, Zi Qi—who was said in legends to have ruled Gija Joseon in the 11th century BCE—and Zi Yan (), later rulers of Zhou's vassal state Song, father of Wu Geng. After King Wu of Zhou overthrew King Zhou of Shang, the last ruler of Shang, marking the transition to the Zhou dynasty, the victor was honor-bound by a stricture of feudal etiquette known as to allow the defeated house of Shang dynasty, Shang to continue offering sacrifices to their ancestors. As a result, for a time Shang be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huai River
The Huai River, formerly romanized as the Hwai, is a major river in East China, about long with a drainage area of . It is located about midway between the Yellow River and Yangtze River, the two longest rivers and largest drainage basins in China. Historically draining eastwards directly into the Yellow Sea, erosion from floods have changed the course of the river such that it now primarily discharges into the Yangtze. The Huai River is, to this day, notoriously vulnerable to flooding. The Qinling–Huaihe Line, formed by the Huai River and the Qin Mountains, is sometimes regarded as the geographical dividing line between northern and southern China. This line approximates the January isotherm and the isohyet in China. Course The Huai River originates in Tongbai Mountain in Henan province. It flows through southern Henan, northern Anhui, and northern Jiangsu where it pools into Lake Hongze. Nowadays the Huai River then runs southwards as the Sanhe River by w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiben
The ''Shiben'' or ''Book of Origins'' (Pinyin: ''shìběn''; Chinese; 世本; ) was an early Chinese encyclopedia which recorded imperial genealogies from the mythical Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors down to the late Spring and Autumn period (771–476 BCE), explanations of the origin of clan names, and records of legendary and historical Chinese inventors. It was written during the 2nd century BC at the time of the Han dynasty. The work was lost in the 10th century, but partially reconstructed from quotations during the Qing dynasty. Title The title combines the common Chinese words ''shì'' 世 "generation; epoch; hereditary; world" and ''běn'' 本 "root; stem; origin; fundament; wooden tablet". The personal name of Emperor Taizong of Tang (r. 627–650) was ''Shimin'' 世民, and owing to the strict naming taboo against writing an emperor's name, the ''Shiben'' 世本 title was changed to ''Xiben'' 系本 or ''Daiben'' 代本 (with the ''shi'' near-synonyms of ''xi'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Grand Historian
The ''Shiji'', also known as ''Records of the Grand Historian'' or ''The Grand Scribe's Records'', is a Chinese historical text that is the first of the Twenty-Four Histories of imperial China. It was written during the late 2nd and early 1st centuries BC by the Han dynasty historian Sima Qian, building upon work begun by his father Sima Tan. The work covers a 2,500-year period from the age of the legendary Yellow Emperor to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in the author's own time, and describes the world as it was known to the Chinese of the Western Han dynasty. The ''Shiji'' has been called a "foundational text in Chinese civilization". After Confucius and Qin Shi Huang, "Sima Qian was one of the creators of Imperial China, not least because by providing definitive biographies, he virtually created the two earlier figures." The ''Shiji'' set the model for all subsequent dynastic histories of China. In contrast to Western historiographical conventions, the ''Shiji'' does no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhongyuan
Zhongyuan (), the Central Plain(s), also known as Zhongtu (, lit. 'central land') and Zhongzhou (, lit. 'central region'), commonly refers to the part of the North China Plain surrounding the lower and middle reaches of the Yellow River, centered on the region between Luoyang and Kaifeng. It has been perceived as the birthplace of the Chinese civilization. Historically, the Huaxia people viewed Zhongyuan as 'the center of the world'. Human activities in the Zhongyuan region can be traced back to the Palaeolithic period. In prehistoric times, Huaxia, a confederation of tribes that later developed into the Han ethnicity, lived along the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River. The term 'Zhongguo' (Central State) was used to distinguish themselves from the Siyi tribes that were perceived as 'barbaric'. For a large part of Chinese history, Zhongyuan had been the political, economic, and cultural center of the Chinese civilization, as over 20 dynasties had located their cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Mu Of Zhou
King Mu of Zhou (), personal name Ji Man, was the fifth Chinese sovereign, king of the Zhou dynasty of China. The dates of his reign are 976–922 BC or 956–918 BC. Life King Mu came to the throne after his father King Zhao of Zhou, King Zhao’s death during the Zhou–Chu War, Zhou-Chu war. King Mu was perhaps the most pivotal king of the Zhou dynasty, reigning nearly 55 years, from ca. 976 BC to ca. 922 BC. Mu was more ambitious than wise, yet he was able to introduce reforms that changed the nature of the Zhou government, transforming it from a hereditary system to one that was based on merit and knowledge of administrative skills. Mu tried to stamp out invaders in the western part of China and ultimately expand Zhou’s influence to the east. In the height of his passion for conquests, he led an immense army against the Quanrong, who inhabited the western part of China. His travels allowed him to contact many tribes and swayed them to either join under the Zhou banner or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Cheng Of Zhou
King Cheng of Zhou (; 1055–1021 BC), personal name Ji Song, was the second king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty. The dates of his reign are 1042–1021 BCE or 1042/35–1006 BCE. Ji Dan, Duke of Zhou served as regent during his minority. His parents were King Wu of Zhou and Queen Yi Jiang. Life King Cheng was young when he ascended the throne. His uncle the Duke of Zhou, fearing that Shang forces might rise again under the possible weak rule of a young ruler, became the regent and supervised government affairs for several years. Duke of Zhou established the eastern capital at Luoyang and later defeated a rebellion Rebellion is an uprising that resists and is organized against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated group that seeks to gain political control over an entire state or a ... by Cheng's uncles the Three Guards Cai Shu, Guan Shu and Huo Shu.Hucker, Charles O. (1978). China to 1850: a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |