|
Jin Xi (Han)
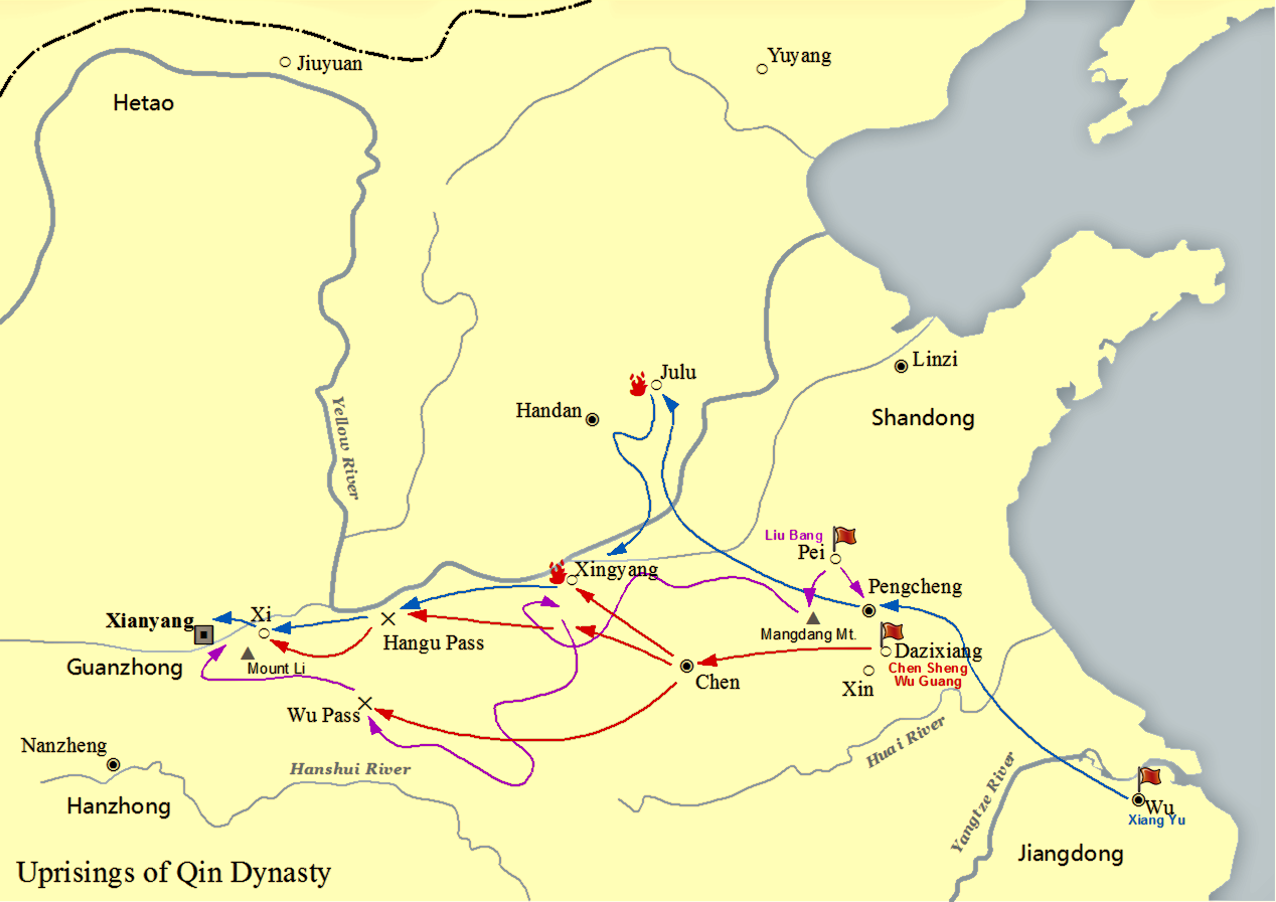
Jin Xi (; died 182 BC) was a general under Emperor Liu Bang. In 209 BC, Jin "joined in the attack on Qin forces, defeating Li You", for which Jin received various titles and honors from Liu Bang including being named Commandant of Cavalry.Michael Loewe, ''A Biographical Dictionary of the Qin, Former Han and Xin Periods, 221 BC - AD 24'' (2000), p. 198. In this capacity, in 206 BC, Jin "took part in the pacification of the Qin metropolitan area", and in 202 BC, during the Chu–Han Contention, Jin conquered the Kingdom of Linjiang of the Eighteen Kingdoms, capturing its ruler, Gong Wei, who was then escorted to Luoyang and executed. Jin was further rewarded for this and other military victories in the period, being "nominated as Marquis of Xinwu (lit. honest and martial)". References * Sima Qian. ''Records of the Grand Historian''. * Ban Gu et al. ''Book of Han The ''Book of Han'' is a history of China finished in 111 CE, covering the Western, or Former Han dynasty fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jin (Chinese Surname)
Jin is the Hanyu pinyin transliteration of a number of Chinese surnames. The most common one, Jīn , literally means "gold" and is 29th in the list of " Hundred Family Surnames". As of 2006, it is ranked the 64th most common Chinese surname and is sometimes transliterated as Chin. The other, less common, surnames that are "Jin" in pinyin include Jìn (/) and Jìn (). 金 (Jīn) Mythology Jin is an ancient surname, dating back over 4,000 years. It was first mentioned during the period ruled by the Yellow Emperor, a legendary Chinese sovereign and cultural hero, who is considered in Chinese mythology to be the ancestor of all Han Chinese. The legend behind the Jin surname is as follows: The Yellow Emperor's son, Yi Zhi ( Shaohao), eventually succeeded him. On the same day he was installed as leader, a golden phoenix flew down and perched on top of a house exactly opposite of where he sat. His followers reckoned it was an auspicious beginning. They decided to use gold as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Gaozu Of Han
Emperor Gaozu of Han (2561 June 195 BC), also known by his given name Liu Bang, was the founder and first emperor of the Han dynasty, reigning from 202 to 195 BC. He is considered by traditional Chinese historiography to be one of the greatest emperors in history, credited with establishing the first Pax Sinica, one of China's longest golden ages. Liu Bang was among the few dynastic founders to have been born in a peasant family. He initially entered the Qin dynasty bureaucracy as a minor law enforcement officer in his home town in Pei County, within the conquered state of Chu. During the political chaos following the death of Qin Shi Huang, who had been the first emperor in Chinese history, Liu Bang renounced his civil service position and became a rebel leader, taking up arms against the Qin dynasty. He outmanoeuvred rival rebel leader Xiang Yu to invade the Qin heartland and forced the surrender of the Qin ruler Ziying in 206 BC. After the fall of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty Legacy of the Qing dynasty, assembled the territoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li You (fl
Li You is the name of: * Emperor Muzong of Tang (795–824), Tang dynasty emperor, known as Li You before 812 * Li You (general) (died 829), Tang dynasty general and military governor * Li Yu, Prince of De (died 905), Tang dynasty prince, known as Li You before 897 {{human name disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chu–Han Contention
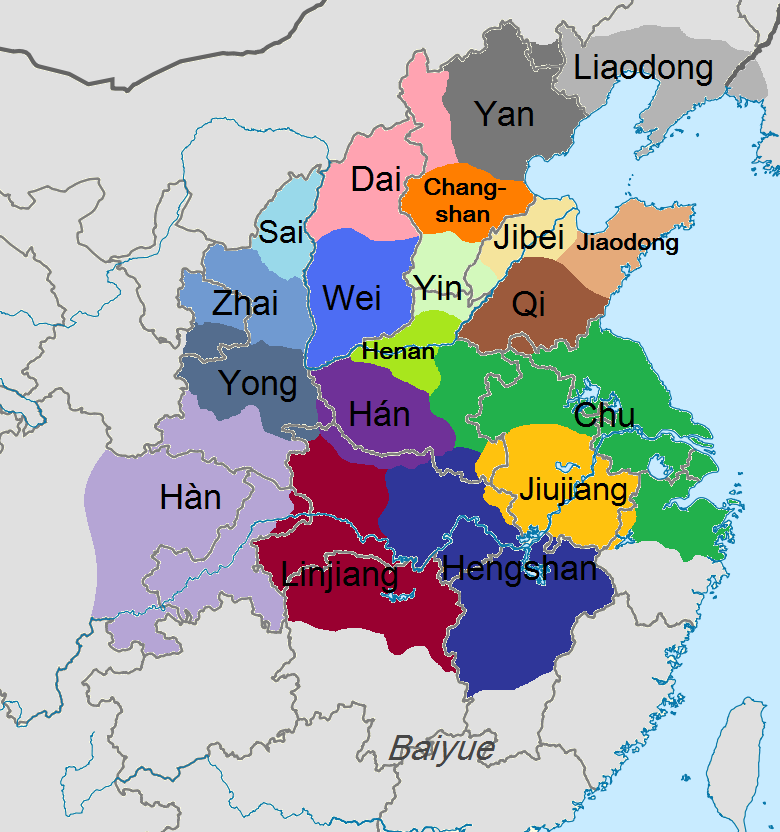
The Chu–Han Contention (), also known as the Chu–Han War (), was an interregnum in Imperial China between the fall of the Qin dynasty and the establishment of the Han dynasty. After the Qin dynasty was overthrown in 206 BCE, the empire was divided into the Eighteen Kingdoms ruled by enfeoffed rebel leaders and surrendered Qin generals according to arrangement by Xiang Yu, the hegemon warlord. Due to dissatisfaction among the rebels, a civil war soon broke out, most prominently between two major powersXiang Yu and Liu Bang, who were the rulers of the Western Chu and Han kingdoms, respectively. Other contending kingdoms also waged war against Chu and Han and among themselves, but these were largely insignificant compared to the Chu-Han conflict. The war ended with a total victory to Han at the Battle of Gaixia in 202 BCE, during which Xiang Yu committed suicide after losing all his men in a last stand. Liu subsequently proclaimed himself emperor of the newly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighteen Kingdoms
The historiographical term "Eighteen Kingdoms" ( zh, t=十八國), also translated as "Eighteen States", refers to the eighteen '' fengjian'' states in China created by military leader Xiang Yu in 206 BCE, after the collapse of the Qin dynasty.林达礼,中华五千年大事记, 台南大孚书局, 1982, p. 56 The establishment and abolishment of the Eighteen Kingdoms marked the beginning and end of a turbulent interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention. The details of the feudal division are as follows: The Eighteen Kingdoms were short-lived. Almost immediately rebellion broke out in Qi, after which Tian Rong conquered Jiaodong and Jibei, reuniting the old Qi state. Meanwhile, Xiang Yu had Emperor Yi of Chu and King Han Cheng of Hán killed. Thereafter, Liu Bang of Hàn conquered the lands of the Three Qins, thereby formally starting the Chu–Han Contention. Following many battles and changing alliances, Han defeated Chu and subdued all other kingdoms, where Liu Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gong Wei
Gong Wei (; died 202 BC) was a ruler of the Kingdom of Linjiang of the Eighteen Kingdoms during the Chu–Han Contention, an interregnum between the Qin dynasty and the Han dynasty. Gong Wei's father Gong Ao received his fief and the title of "King of Linjiang" (臨江國) from Xiang Yu in 206 BC when Xiang divided the former Qin Empire into the Eighteen Kingdoms after the fall of the Qin dynasty. Gong Wei succeeded his father in 204 BC when the latter died. During the Chu–Han Contention, Gong Wei remained on Xiang Yu's side but did not participate in the conflict. In 202 BC, Xiang was defeated by Liu Bang in the Battle of Gaixia and committed suicide. Seven months later, Gong Wei's Linjiang kingdom was conquered by Liu Bang's general Jin Xi (靳歙). Gong Wei was captured and escorted to Luoyang and executed. References * Sima Qian. ''Records of the Grand Historian''. * Ban Gu et al. ''Book of Han The ''Book of Han'' is a history of China finished in 111 CE, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luoyang
Luoyang ( zh, s=洛阳, t=洛陽, p=Luòyáng) is a city located in the confluence area of the Luo River and the Yellow River in the west of Henan province, China. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyang to the south, Sanmenxia to the west, Jiyuan to the north, and Jiaozuo to the northeast. As of December 31, 2018, Luoyang had a population of 6,888,500 inhabitants with 2,751,400 people living in the built-up (or metro) area made of the city's five out of six urban districts (except the Jili District not continuously urbanized) and Yanshi District, now being conurbated. By the end of 2022, Luoyang Municipality had jurisdiction over 7 municipal districts, 7 counties and 1 development zone. The permanent population is 7.079 million. Situated on the central plain of China, Luoyang is among the oldest cities in China and one of the cradles of Chinese civilization. It is the earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sima Qian
Sima Qian () was a Chinese historian during the early Han dynasty. He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for the ''Shiji'' (sometimes translated into English as ''Records of the Grand Historian''), a general history of China covering more than two thousand years from the rise of the legendary Yellow Emperor and formation of the first Chinese polity to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han, during which Sima wrote. As the first universal history of the world as it was known to the ancient Chinese, the ''Shiji'' served as a model for official histories for subsequent dynasties across the Sinosphere until the 20th century. Sima Qian's father, Sima Tan, first conceived of the ambitious project of writing a complete history of China, but had completed only some preparatory sketches at the time of his death. After inheriting his father's position as court historian in the imperial court, he was determined to fulfill his father's dying wish of composing and putting together th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Grand Historian
The ''Shiji'', also known as ''Records of the Grand Historian'' or ''The Grand Scribe's Records'', is a Chinese historical text that is the first of the Twenty-Four Histories of imperial China. It was written during the late 2nd and early 1st centuries BC by the Han dynasty historian Sima Qian, building upon work begun by his father Sima Tan. The work covers a 2,500-year period from the age of the legendary Yellow Emperor to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in the author's own time, and describes the world as it was known to the Chinese of the Western Han dynasty. The ''Shiji'' has been called a "foundational text in Chinese civilization". After Confucius and Qin Shi Huang, "Sima Qian was one of the creators of Imperial China, not least because by providing definitive biographies, he virtually created the two earlier figures." The ''Shiji'' set the model for all subsequent dynastic histories of China. In contrast to Western historiographical conventions, the ''Shiji'' does no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ban Gu
Ban Gu (AD32–92) was a Chinese historian, poet, and politician best known for his part in compiling the ''Book of Han'', the second of China's 24 dynastic histories. He also wrote a number of '' fu'', a major literary form, part prose and part poetry, which is particularly associated with the Han era. A number of Ban's ''fu'' were collected by Xiao Tong in the '' Wen Xuan''. Family background The Ban family was one of the most distinguished families of the Eastern Han dynasty. They lived in the state of Chu during the Warring States period but, during the reign of the First Emperor, a man named Ban Yi ( or ''Bān Yī'') fled north to the Loufan ( t s ''Lóufán'') near the Yanmen Pass in what is now northern Shanxi Province. By the early Han Dynasty, Ban Gu's ancestors gained prominence on the northwestern frontier as herders of several thousand cattle, oxen, and horses, which they traded in a formidable business and encouraged other families to move to the front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Han
The ''Book of Han'' is a history of China finished in 111 CE, covering the Western, or Former Han dynasty from the first emperor in 206 BCE to the fall of Wang Mang in 23 CE. The work was composed by Ban Gu (32–92 CE), an Eastern Han court official, with the help of his sister Ban Zhao, continuing the work of their father, Ban Biao. They modelled their work on the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (), a cross-dynastic general history, but theirs was the first in this annals-biography form to cover a single dynasty. It is the best source, sometimes the only one, for many topics such as literature in this period. The ''Book of Han'' is also called the ''Book of the Former Han'' () to distinguish it from the '' Book of the Later Han'' () which covers the Eastern Han period (25–220 CE), and was composed in the fifth century by Fan Ye (398–445 CE). Contents This history developed from a continuation of Sima Qian's ''Records of the Grand Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |