|
Jimsar
Jimsar County is a county in Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang, China. It contains an area of . According to the 2002 census, it has a population of 130,000. Near the town of Jimsar are the ruins of the ancient city of Beiting ( zh, c=北庭, p=Běitíng) or Ting Prefecture ( zh, c=庭州, p=Tíngzhōu), the headquarters of the Beiting Protectorate during the 8th century. It was later known as Beshbalik ( zh, c=别失八里) and became one of the capitals of the Uyghur Khaganate and then the Kingdom of Qocho. History The name Beshbalik first appears in history in the description of the events of 713 in the Turkic Kul Tigin inscription. It was one of the largest of five towns in the Uyghur Khaganate. The Tibetans briefly held the city in 790. Established in 1902 as a county, it was known as Fuyuan (孚远) until 1952, when its name was changed to Jimsar. The modern city Jimsar is located at 43°59'N, 89°4'East; It is a location of the Uyghur ancient southern cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture
Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture ( zh, s=昌吉回族自治州; ) is an autonomous prefecture for Hui people in the middle north of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, Western China. The prefecture has an area of and its seat is Changji City. Subdivisions Changji directly controls 2 county-level cities, 4 counties and 1 autonomous county. * Defunct: Miquan (county-level city) Demographics According to the 2010 census, Changji had a population of 1,428,587 inhabitants, with a population density of 19.4 inhabitants per km2. Its population in the 2000 census was 1,503,097. Part of the change in population is due to boundary changes, for example, the formerly county-level city Miquan was merged into Midong District and became part of Ürümqi in 2007. The population in 2000 minus Miquan was 1,322,145. Sister cities * Barnaul, Altai Krai Altai Krai (, ) is a federal subject of Russia (a krai). It borders, clockwise from the west, Kazakhstan ( East Kazakhstan Region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beshbalik
Beshbalik ( zh, t=別失八里, s=别失八里, first=t) is an ancient Turkic archaeological site, now located in Jimsar County, Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang, China. The ancient city was initially called Beiting () or Ting Prefecture (), and was the headquarters of the Beiting Protectorate during the 8th century. It was later known as Beshbalik (Old Uyghur: ''beš balık'' “five cities”) and became one of the capitals of the Uyghur Khaganate and then the Kingdom of Qocho. Etymology The name of ''tíng'' 庭 (“court”) comes from this place of being a royal residence of the Further Jūshī 車師 people. Its Old Turkic name, Bešbalık “five cities” (''beš'' ”five” + ''balık'' “city”), comes from the fact that it was composed of five cities. This is made clear by a passage in the Old Book of Tang: 金滿流沙州北,前漢烏孫部舊地,方五千里。後漢車師後王庭。胡故庭有五城,俗號「五城之地」。貞觀十� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beiting Protectorate
The Beiting Protectorate-General, initially the Beiting Protectorate, was a Chinese protectorate established by the Tang dynasty in 702 to control the Beiting region north of Gaochang in contemporary Xinjiang. Wu Zetian set up the Beiting Protectorate in Ting Prefecture ( Jimsar County) and granted it governorship over Yi Prefecture (Hami) and Xi Prefecture (Gaochang). The Beiting Protectorate ended in 790 when Tingzhou was conquered by the Tibetan Empire. The ruins, along with other sites along the Silk Road, were inscribed in 2014 on the UNESCO World Heritage List as the Silk Roads: the Routes Network of Chang'an-Tianshan Corridor World Heritage Site. History In 702 Wu Zetian set up the Beiting Protectorate in Ting Prefecture ( Jimsar County) and granted it governorship over Yi Prefecture (Hami) and Xi Prefecture (Gaochang). In 715 the Tibetan Empire attacked the Beiting Protectorate. In 735 the Türgesh attacked Ting Prefecture. In 755 the An Lushan Rebellion occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
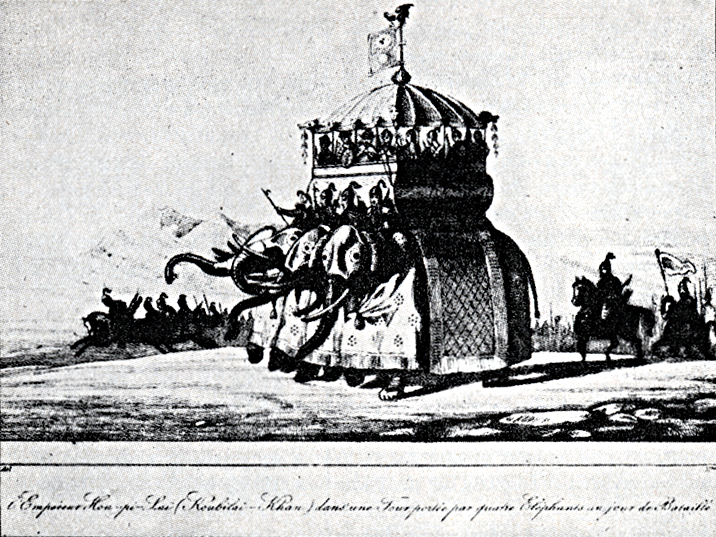
Kublai Khan
Kublai Khan (23 September 1215 – 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder and first emperor of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty of China. He proclaimed the dynastic name "Great Yuan" in 1271, and ruled Yuan China until his death in 1294. Kublai was the second son of Tolui by his chief wife Sorghaghtani Beki, and a grandson of Genghis Khan. He was almost 12 when Genghis Khan died in 1227. He had succeeded his older brother Möngke as Khagan in 1260, but had to defeat his younger brother Ariq Böke in the Toluid Civil War lasting until 1264. This episode marked the beginning of the division of the Mongol Empire. Kublai's real power was limited to the Yuan Empire, even though as Khagan he still influenced the Ilkhanate and, to a significantly lesser degree, the Golden Horde. In 1271, Kublai established the Yuan dynasty and formally claimed orthodox succession from prior Chinese dynasties. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counties Of China
Counties ( zh, s=县, labels=no) are found in the County-level divisions of China, third level of the administrative hierarchy in Provinces of China, provinces and Autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions and the second level in Direct-controlled municipality#People's Republic of China, municipalities and Hainan, a level that is known as "county level" and also contains autonomous county, autonomous counties, county-level city, county-level cities, Banners of Inner Mongolia, banners, Banners of Inner Mongolia#Autonomous banners, autonomous banners and District (China)#Ethnic districts, city districts. There are 1,355 counties in mainland China out of a total of 2,851 county-level divisions. The term ''xian'' is sometimes translated as "district" or "prefecture" when put in the context of History of China, Chinese history. History ''Xian'' have existed since the Warring States period and were set up nationwide by the Qin dynasty. The number of counties in China proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, extending northward into parts of the Arctic; eastward and southward into parts of the Indian subcontinent, mounting invasions of Southeast Asia, and conquering the Iranian plateau; and reaching westward as far as the Levant and the Carpathian Mountains. The Mongol Empire emerged from the unification of several nomad, nomadic tribes in the Mongol heartland under the leadership of Temüjin, known by the title of Genghis Khan (–1227), whom a council proclaimed as the ruler of all Mongols in 1206. The empire grew rapidly under his rule and that of his descendants, who sent out Mongol invasions, invading armies in every direction. The vast transcontinental empire connected the Eastern world, East with the Western world, West, and the Pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
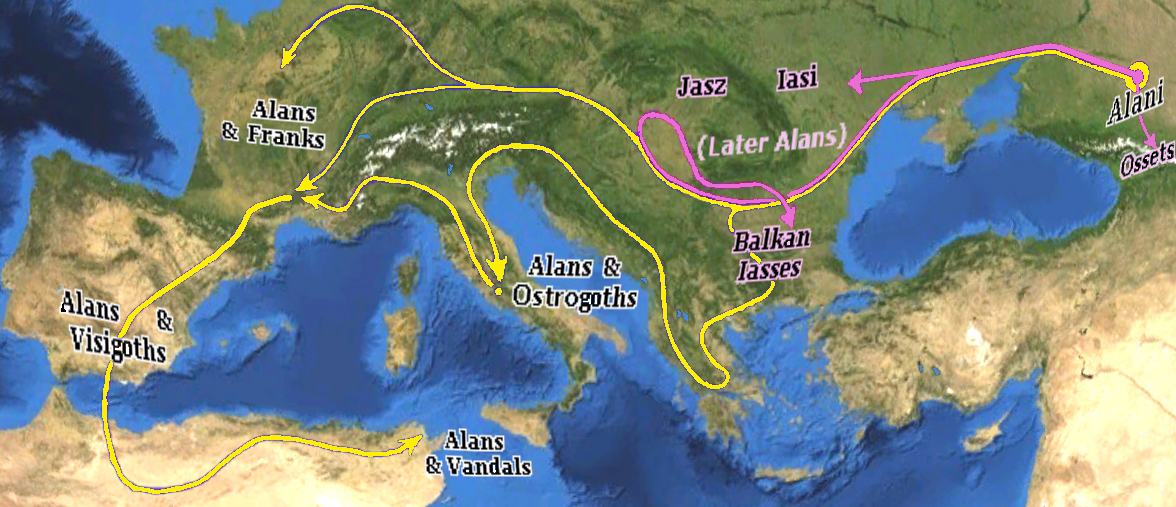
Alans
The Alans () were an ancient and medieval Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, nomadic pastoral people who migrated to what is today North Caucasus – while some continued on to Europe and later North Africa. They are generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of China, Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Ancient Rome, Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the South Caucasus provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe, thereby assimilating a sizeable portion of the associated Alans. Upon the Huns, Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asud
The Asud ( Mongolian Cyrillic: , IPA: //) were a military group of Alani origin. The Mongol clan Asud is the plural of As, the Arabic name for the Alans. Against the Alans and the Cumans (Kipchaks), the Mongols used divide and conquer tactics by first telling the Cumans to stop allying with the Alans and after the Cumans followed their suggestion the Mongols then attacked the Cumans after defeating the Alans. Alans were recruited into the Mongol forces with one unit called "Right Alan Guard" which was combined with "recently surrendered" soldiers, Mongols, and Chinese soldiers stationed in the area of the former Kingdom of Qocho and in Besh Balikh the Mongols established a Chinese military colony led by Chinese general Qi Kongzhi (Ch'i Kung-chih). Alan and Kipchak guards were used by Kublai Khan. In 1368 at the end of the Yuan dynasty in China Toghan Temür was accompanied by his faithful Alan guards. ''Mangu enlisted in his bodyguard half the troops of the Alan prince, Arslan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chagatai Khanate
The Chagatai Khanate, also known as the Chagatai Ulus, was a Mongol and later Turkification, Turkicized khanate that comprised the lands ruled by Chagatai Khan, second son of Genghis Khan, and his descendants and successors. At its height in the late 13th century the khanate extended from the Amu Darya south of the Aral Sea to the Altai Mountains in the border of modern-day Mongolia and China, roughly corresponding to the area once ruled by the Qara Khitai (Western Liao dynasty). Initially, the rulers of the Chagatai Khanate recognized the supremacy of the Great Khan, but by the reign of Kublai Khan, Ghiyas-ud-din Baraq no longer obeyed the emperor's orders. From 1363, the Chagatais progressively lost Transoxiana to the Timurids. The reduced realm came to be known as Moghulistan, which lasted until the late 15th century, when it broke off into the Yarkent Khanate and Turpan Khanate. In 1680, the remaining Chagatai domains lost their independence to the Dzungar Khanate. Finally, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Yuan
The ''History of Yuan'' (), also known as the ''Yuanshi'', is one of the official Chinese historical works known as the '' Twenty-Four Histories'' of China. Commissioned by the court of the Ming dynasty, in accordance to political tradition, the text was composed in 1370 by the official Bureau of History of the Ming dynasty, under direction of Song Lian (1310–1381). The compilation formalized the official history of the preceding Yuan dynasty. Under the guidance of Song Lian, the official dynastic history broke with the old Confucian historiographical tradition, establishing a new historical framework asserting that the influence of history was equal in influence to the great Confucian classics in determining the course of human affairs. Layout and contents The historical work consists of 210 chapters chronicling the history of the Yuan dynasty from the time of Genghis Khan (c. 1162–1227) to the flight of the last Yuan emperor, Toghon Temür ("Emperor Huizong", 1333– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and conquests, a series of military campaigns, conquering large parts of Mongol conquest of China, China and Mongol invasion of Central Asia, Central Asia. Born between 1155 and 1167 and given the name Temüjin, he was the eldest child of Yesugei, a Mongol chieftain of the Borjigin, Borjigin clan, and his wife Hö'elün. When Temüjin was eight, his father died and his family was abandoned by its tribe. Reduced to near-poverty, Temüjin killed Behter, his older half-brother to secure his familial position. His charismatic personality helped to attract his first followers and to form alliances with two prominent Eurasian Steppe, steppe leaders named Jamukha and Toghrul; they worked together to retrieve Temüjin's newlywed wife Börte, who had b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |