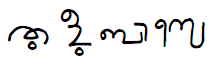|
Jeppu
Jeppu is a locality in Mangalore city, Karnataka, India. It is situated on the southern part of Mangalore. Jeppu is on the bank of Nethravathi River. The National Highway 17 (India) passes through this locality. Jeppu means sleep in local Tulu language. Tulu is the main language, which is spoken and understood by everyone in this locality. Beary And Dakhini Urdu is Spoken By Muslims in Jeppu. Konkani is another language that is commonly used. Jeppu is predominantly a residential area. However, there are several educational institutions run by Christian missionaries. Occupation Jeppu is a low lying locality and is on the bank of the river Netravathi, and thus naturally agriculture and fishing have become the predominant occupations. Rice is the major crop grown here. However, in recent past people have stopped agriculture and now all the barren fields used by real estate can be seen. You can also find wood industries and tile factories in this locality. Educational Institu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cascia High School
Cascia High School is located in Jeppu near Mangaladevi Temple in Mangalore run by the Cascia St Rita's Church, Jeppu. Mahanavami Katta (of Mangala Devi) is located within the school compound. It recently completed 60 years of its service to the society in 2006. It offers high school education in both English & Kannada mediums under the Karnataka board of secondary education. This school has around 800 students History This school was established by parish priest of St Rita’s church Fr F X Fernandes on 3 June 1946. Monsignor F X Fernandes, Fr A J D'Silva, Fr J M Menezes, Fr Thomas D'Sa, Fr J I Saldanha, Fr Robert M Pinto, Fr Aloysius P D'Souza (the present Bishop of Mangalore Diocese) and Fr Denis D'Souza have served as school conveners for this great institute. Its first headmaster was Manjeshwar Purushottam Kini, followed by Fr Fredrick Fernandes and Kateel Govind Pai. In 1950, it became a full-fledged high school and within a years time built a four-class room buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Of India
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions. History Pre-independence The Indian subcontinent has been ruled by many different ethnic groups throughout its history, each instituting their own policies of administrative division in the region. The British Raj The British Raj (; from Hindi language, Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Q ... mostly retained the administrative structure of the preceding Mughal Empire. India was divided into provinces (also called Presidencies), directly governed by the British, and princely states, which were nominally controlled by a local prince or raja loyal to the British Empire, which held ''de f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nethravathi River
The Netravati River or Netravathi Nadi has its origins at Bangrabalige valley, Yelaneeru Ghat in Kudremukh in Chikkamagaluru district of Karnataka, India. This river flows through the famous pilgrimage place Dharmasthala and is considered one of the holy rivers of India. It merges with the Kumaradhara River at Uppinangadi before flowing to the Arabian Sea, south of Mangalore city. This river is the main source of water to Bantwal and Mangalore. The Netravati railway bridge is one of the known bridges which serve as the gateway to Mangalore. Earlier in the last century it was known as the Bantwal River; the important town of Bantwal is seen on its banks. A reference to the River Netravati, as unfordable during the South-West Monsoon, can be seen in the ''Gazetteer of Southern India,'', published in 1855. It has an apparent breadth of about 200 yards with a bed encumbered by large rocky masses, chiefly of hornblende rock, containing spangles of mica and small garnets. Sie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navratri
Navaratri is an annual Hindu festival observed in the honour of the goddess Durga. It spans over nine nights (and ten days), first in the month of Chaitra (March/April of the Gregorian calendar), and again in the month of Sharada. It is observed for different reasons and celebrated differently in various parts of the Hindu Indian cultural sphere. Theoretically, there are four seasonal ''Navaratri''. However, in practice, it is the post-monsoon autumn festival called Sharada Navaratri. The festival is celebrated in the bright half of the Hindu calendar month Ashvin, which typically falls in the Gregorian months of September and October. Etymology and nomenclature The word ''Navaratri'' means 'nine nights' in Sanskrit, ''nava'' meaning nine and ''ratri'' meaning nights. Dates and celebrations In the eastern and northeastern states of India, the Durga Puja is synonymous with ''Navaratri'', wherein goddess Durga battles and emerges victorious over the buffalo demon Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mangaladevi
The Mangaladevi Temple is a Hindu temple at Bolara in the city of Mangalore in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is situated about three kilometres southwest of the city centre. The temple is dedicated to the Hindu goddess Shakti in the form of Mangaladevi, the presiding deity from whom the city derives its name. The temple is of significant antiquity and is believed to have been built during the 9th century by Kundavarman, the most noted king of the Alupa dynasty, under the patronage of Matsyendranath. As per another legend, the temple is believed to have been built by Parashurama, one of the ten avatars of Hindu god Vishnu and later expanded by Kundavarman. The temple is built in Architecture of Kerala, Kerala style architecture, which is common in all temples in the South Indian state of Kerala and Western Ghats, with most of its structure made of wood. The presiding deity, Mangaladevi in the central shrine is in a seated posture. There are shrines around the sanctum fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roshni Nilaya - College Of Social Work
The School of Social Work Roshni Nilaya, managed by the Institute of Social Service Mangalore of Karnataka State. It believes in the dictum – "Small is Beautiful". It is situated on a six-acre campus, wherein besides the college of social work Social work is an academic discipline and practice-based profession concerned with meeting the basic needs of individuals, families, groups, communities, and society as a whole to enhance their individual and collective well-being. Social work ..., there are service centers such as Kindergarten, Family Service Agency, Family Counselling Centre and CHILDLINE. The Institute has adopted as its motto, the words of Tagore – "LOVE IS MADE FRUITFUL IN SERVICE"- Serving God by serving human persons is the principle that guides its action. History Established in 1960 in Mangalore by the Society of Daughters of the Heart of Mary, an International Catholic Religious Society, founded in France in 1790 during the French Revolution. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Bhogi In Red
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beary
The Beary (also known as Byari) is a community concentrated along the southwest coast of India, mostly in the Mangalore district of the south Indian state of Karnataka. They are an ethnic group of Indian Muslims with their own distinct culture and identity along with other Muslims of the coastal India, like ''Nawayaths'' of the North Canara, Moplahs of the Malabar region & the Labbay of the Coromandel. Bearys incorporate the local Tulu culture of Magalore and diverse traditions of the Moplahs of the Malabar coast. The Beary community of Maikala is one among the earliest Muslim inhabitants of India, with a clear history of more than 950 years. One mosque, Masjid Zeenath Baksh was built in the Bunder area of Mangalore by Malik Deenar, an Arab Da'ee, in 644Ahmed Noori, Maikala, II edition, p.11 (1997) Etymology The word 'Beary' is said to be derived from the Tulu word 'Byara', which means trade or business. Since the major portion of the community was involved in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulu Language
Tulu () in Kannada script, ml, തുളു ഭാഷെ in Malayalam script. ''bhāṣe'', , ''bhāśe'', and ''bāśe'' are alternative spellings for the Tulu word ''bāse'' in the Kannada script. The correct spelling for the word "language" in Kannada is kn, ಭಾಷೆ ''bhāṣe'', but that is not necessarily true in Tulu. Männer's ''Tulu-English and English-Tulu Dictionary'' (1886) says, " bāšè, bāsè, ''see'' ." (vol. 1, p. 478), " bhāšè, bhāshè, ''s''. Speech, language." (vol. 1, p. 508), meaning that the four spellings are more or less acceptable. The word is actually pronounced ''bāse'' in Tulu. Note that š and sh in his dictionary correspond to ''ś'' and ''ṣ'', respectively, in ISO 15919 is a Dravidian language whose speakers are concentrated in Dakshina Kannada and the southern part of Udupi of Karnataka in south-western India and in the northern parts of the Kasaragod district of Kerala. The native speakers of T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)