|
Jean Tarde
Jean Tarde (b. La Roque-Gageac 1561 or 1562, d. La Roque-Gageac 1636) was Vicar general of Sarlat, famous for his chronicles of the diocese. He was a Frenchman and was an early adopter of Copernican theory. Tarde was born into a semi wealthy family in the bourgeois community in La Roque-Gageac, near Sarlat, France. He received his doctorate of law from the University of Cahors and then went on to the University of Paris to continue his studies. Throughout his younger adult life, he held a number of different religious positions such as canon theologian, and almoner where during his free time he studied various sciences including mathematics, astronomy, physics, and geography. He is most famous for his work with sunspots which he concluded were small satellites of the sun. Biography Jean Tarde belonged to an established family of Sarlat dating to a least the 14th century. The family had two branches, the du Ponts, to which Jean Tarde belonged, and the de Lisles. He studied at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Roque-Gageac
La Roque-Gageac (; oc, La Ròca de Gajac) is a commune in the Dordogne department Department may refer to: * Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility Government and military *Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ... in Nouvelle-Aquitaine, southwestern France. Perched above the river Dordogne, the village is a member of the '' Les Plus Beaux Villages de France'' ("The most beautiful villages of France") association. Population See also * Communes of the Dordogne department References Image:La roque gageac.jpg File:La Roque Gageac (9).JPG, La Roque-Gageac File:La Roque-Gageac - rue.jpg File:F07.La Roque-Gageac.0005.JPG, File:La Roque-Gageac - Panorama.jpg Communes of Dordogne Plus Beaux Villages de France {{Dordogne-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avignon
Avignon (, ; ; oc, Avinhon, label=Provençal or , ; la, Avenio) is the prefecture of the Vaucluse department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of Southeastern France. Located on the left bank of the river Rhône, the commune had a population of 93,671 as of the census results of 2017, with about 16,000 (estimate from Avignon's municipal services) living in the ancient town centre enclosed by its medieval walls. It is France's 35th largest metropolitan area according to INSEE with 336,135 inhabitants (2019), and France's 13th largest urban unit with 458,828 inhabitants (2019). Its urban area was the fastest-growing in France from 1999 until 2010 with an increase of 76% of its population and an area increase of 136%. The Communauté d'agglomération du Grand Avignon, a cooperation structure of 16 communes, had 192,785 inhabitants in 2018. Between 1309 and 1377, during the Avignon Papacy, seven successive popes resided in Avignon and in 1348 Pope Clement VI b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
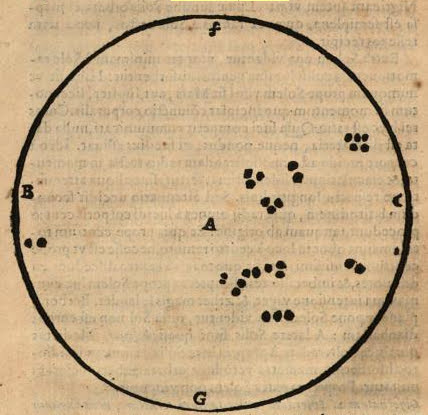
Diagram Of Sunspots From Borbonia Sidera
A diagram is a symbolic representation of information using visualization techniques. Diagrams have been used since prehistoric times on walls of caves, but became more prevalent during the Enlightenment. Sometimes, the technique uses a three-dimensional visualization which is then projected onto a two-dimensional surface. The word '' graph'' is sometimes used as a synonym for diagram. Overview The term "diagram" in its commonly used sense can have a general or specific meaning: * ''visual information device'' : Like the term "illustration", "diagram" is used as a collective term standing for the whole class of technical genres, including graphs, technical drawings and tables. * ''specific kind of visual display'' : This is the genre that shows qualitative data with shapes that are connected by lines, arrows, or other visual links. In science the term is used in both ways. For example, Anderson (1997) stated more generally: "diagrams are pictorial, yet abstract, represent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christoph Grienberger
Christoph (Christophorus) Grienberger (also variously spelled Gruemberger, Bamberga, Bamberger, Banbergiera, Gamberger, Ghambergier, Granberger, Panberger) (2 July 1561 – 11 March 1636) was an Austrian Jesuit astronomer, after whom the crater Gruemberger on the Moon is named. Biography Born in Hall in Tirol, in 1580 Christoph Grienberger joined the Jesuits. He studied in Prague and Vienna, and subsequently succeeded his tutor, Christopher Clavius, as professor of mathematics at the Collegio Romano in 1612. In 1610, Jesuit and high church officials had turned to Grienberger, as well as Clavius, Paolo Lembo, and Odo Van Maelcote, the other mathematicians on the faculty of the Collegio Romano, for their opinion on the new phenomena Galileo had discovered with his telescope. Grienberger sympathized with Galileo's theory of motion. However, he was asked to defend the Aristotelian view of the universe by Claudio Acquaviva, the Father General of the Jesuits. Grienber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidereus Nuncius
''Sidereus Nuncius'' (usually ''Sidereal Messenger'', also ''Starry Messenger'' or ''Sidereal Message'') is a short astronomical treatise (or ''pamphlet'') published in New Latin by Galileo Galilei on March 13, 1610. It was the first published scientific work based on observations made through a telescope, and it contains the results of Galileo's early observations of the imperfect and mountainous Moon, the hundreds of stars that were unable to be seen in either the Milky Way or certain constellations with the naked eye, and the Medicean Stars (later Galilean moons) that appeared to be circling Jupiter.Raphael, Renée. ''Sidereus nuncius; or, A Sidereal Message, by Galileo Galilei''. Isis, Vol. 101, No. 3 (September 2010), pp. 644-645. Published by: The University of Chicago Press on behalf of The History of Science Society. The Latin word ''nuncius'' was typically used during this time period to denote ''messenger''; however, it was also (though less frequently) rendered as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Balfour (philosopher)
Robert Balfour (c. 1553–1621; known also as Balforeus) was a Scottish philosopher. He was educated at the University of St Andrews and the University of Paris. He was for many years principal of the College of Guienne at Bordeaux. Works His great work is his ''Commentarii in Organum Logicum Aristotelis'' (Bordeaux, 1618); the copy in the British Museum contains a number of highly eulogistic poems in honour of Balfour, who is described as ''Graium aemulus acer.'' Balfour was one of the scholars who contributed to spread over Europe the fame of the ''praefervidum ingenium Scotorum.'' His contemporary, Thomas Dempster, called him the "phoenix of his age, a philosopher profoundly skilled in the Greek and Latin languages, and a mathematician worthy of being compared with the ancients." His ''Cleomedis meteora,'' with notes and Latin translation, was reprinted at Leiden Leiden (; in English and archaic Dutch also Leyden) is a city and municipality in the province of South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was born in the city of Pisa, then part of the Duchy of Florence. Galileo has been called the "father" of observational astronomy, modern physics, the scientific method, and modern science. Galileo studied speed and velocity, gravity and free fall, the principle of relativity, inertia, projectile motion and also worked in applied science and technology, describing the properties of pendulums and " hydrostatic balances". He invented the thermoscope and various military compasses, and used the telescope for scientific observations of celestial objects. His contributions to observational astronomy include telescopic confirmation of the phases of Venus, observation of the four largest satellites of Jupiter, observation of Satur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considered fundamental principles of liberal democracy, while phrases like '' liberté, égalité, fraternité'' reappeared in other revolts, such as the 1917 Russian Revolution, and inspired campaigns for the abolition of slavery and universal suffrage. The values and institutions it created dominate French politics to this day. Its causes are generally agreed to be a combination of social, political and economic factors, which the ''Ancien Régime'' proved unable to manage. In May 1789, widespread social distress led to the convocation of the Estates General, which was converted into a National Assembly in June. Continuing unrest culminated in the Storming of the Bastille on 14 July, which led to a series of radical measures by the Assemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri IV Of France
Henry IV (french: Henri IV; 13 December 1553 – 14 May 1610), also known by the epithets Good King Henry or Henry the Great, was King of Navarre (as Henry III) from 1572 and King of France from 1589 to 1610. He was the first monarch of France from the House of Bourbon, a cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty. He was assassinated in 1610 by François Ravaillac, a Catholic zealot, and was succeeded by his son Louis XIII. Henry was the son of Jeanne III of Navarre and Antoine de Bourbon, Duke of Vendôme. He was baptised as a Catholic but raised in the Protestant faith by his mother. He inherited the throne of Navarre in 1572 on his mother's death. As a Huguenot, Henry was involved in the French Wars of Religion, barely escaping assassination in the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre. He later led Protestant forces against the French royal army. Henry became king of France in 1589 upon the death of Henry III, his brother-in-law and distant cousin. He was the first French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rome
, established_title = Founded , established_date = 753 BC , founder = King Romulus ( legendary) , image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg , map_caption = The territory of the ''comune'' (''Roma Capitale'', in red) inside the Metropolitan City of Rome (''Città Metropolitana di Roma'', in yellow). The white spot in the centre is Vatican City. , pushpin_map = Italy#Europe , pushpin_map_caption = Location within Italy##Location within Europe , pushpin_relief = yes , coordinates = , coor_pinpoint = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Italy , subdivision_type2 = Regions of Italy, Region , subdivision_name2 = Lazio , subdivision_type3 = Metropolitan cities of Italy, Metropolitan city , subdivision_name3 = Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, Rome Capital , government_footnotes= , government_type = Mayor–council gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrant (instrument)
A quadrant is an instrument used to measure angles up to 90°. Different versions of this instrument could be used to calculate various readings, such as longitude, latitude, and time of day. Its earliest recorded usage was in ancient India in Rigvedic times by Rishi Atri to observe a solar eclipse. It was then proposed by Ptolemy as a better kind of astrolabe. Several different variations of the instrument were later produced by medieval Muslim astronomers. Mural quadrants were important astronomical instruments in 18th-century European observatories, establishing a use for positional astronomy. Etymology The term ''quadrant'', meaning one fourth, refers to the fact that early versions of the instrument were derived from astrolabes. The quadrant condensed the workings of the astrolabe into an area one fourth the size of the astrolabe face; it was essentially a quarter of an astrolabe. History During Rigvedic times in ancient India, quadrants called 'Tureeyam's were use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |