|
Jaén, Spain
Jaén () is a Municipalities in Spain, municipality of Spain and the capital of the Jaén Province, Spain, province of Jaén, in the autonomous community of Andalusia. The city of Jaén is the administrative and industrial centre for the province. Industrial establishments in the city include chemical works, tanneries, distilleries, cookie factories, textile factories, as well as agricultural and olive oil processing machinery industry. The layout of Jaén is determined by its position on the foothills of the Cerro de Santa Catalina, with steep, narrow streets, in the historic core. Its population is 112,757 (2020), about one-sixth of the population of the province. Jaén had an increase in cultural tourism in the mid-2010s, having received 604,523 tourists in 2015, 10% more than in 2014. Etymology The name is most likely derived from the Roman name ''Villa Gaiena'' (Villa of Gaius). It was called Jayyān during the time of Al-Andalus. The inhabitants of the city are known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Spain
The municipality (, , , , , )In other languages of Spain: *Catalan language, Catalan/Valencian (), grammatical number, sing. . *Galician language, Galician () or (), grammatical number, sing. /. *Basque language, Basque (), grammatical number, sing. . *Asturian language, Asturian (), grammatical number, sing. . is one of the two fundamental territorial divisions in Spain, the other being the Provinces of Spain, provinces. Organisation Although provinces of Spain, provinces are groupings of municipality, municipalities, there is no implied hierarchy or primacy of one over the other. Instead the two entities are defined according to the authority or jurisdiction of each (). Some autonomous communities also group municipalities into entities known as ''comarcas of Spain, comarcas'' (districts) or ''mancomunidades'' (commonwealths). The governing body in most municipalities is called ''Ayuntamiento (Spain), ayuntamiento'' (municipal council or municipal corporation, corpora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaén Province, Spain
Jaén may refer to: Places Peru *Jaén Province, Peru, a province in Cajamarca Region, Peru ** Jaén District, one of twelve districts of the province Jaén in Peru *** Jaén, Peru, a city in Peru, capital of the Jaén Province Philippines * Jaen, Nueva Ecija, a municipality in the Philippines Spain *Kingdom of Jaén, a territorial jurisdiction of the Crown of Castile from 1246 to 1833 *Province of Jaén (Spain), a province in southern Spain ** Jaén (Congress of Deputies constituency), the electoral district used for the Spanish Congress of Deputies, corresponding to the province of Jaén **Jaén, Spain, a city in south-central Spain, capital of the province of Jaén *** Roman Catholic Diocese of Jaén, a diocese located in the city of Jaén in the ecclesiastical province of Granada * Taifa of Jaén, a medieval kingdom in 1145 and 1168 People *Jaén (surname), a Spanish surname * Andrés González Jaén (born 1993), Spanish footballer * Jaime Jaen (born 1978), Panamanian baseba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civitas Stipendaria
A or , meaning "tributary state/community", was the lowest and most common type of towns and local communities under Roman rule. Each Roman province comprised a number of communities of different status. Alongside Roman colonies or , whose residents held the Roman citizenship or Latin citizenship, a province was largely formed by self-governing communities of natives (''peregrini''), which were distinguished according to the level of autonomy they had: the were the lowest grade, after the ("allied states") which were bound to Rome by formal treaty (), and the ("free states"), which were granted specific privileges. The were by far the most common of the three—for example, in 70 BC in Sicily Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ... there were 65 such cities, as opp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
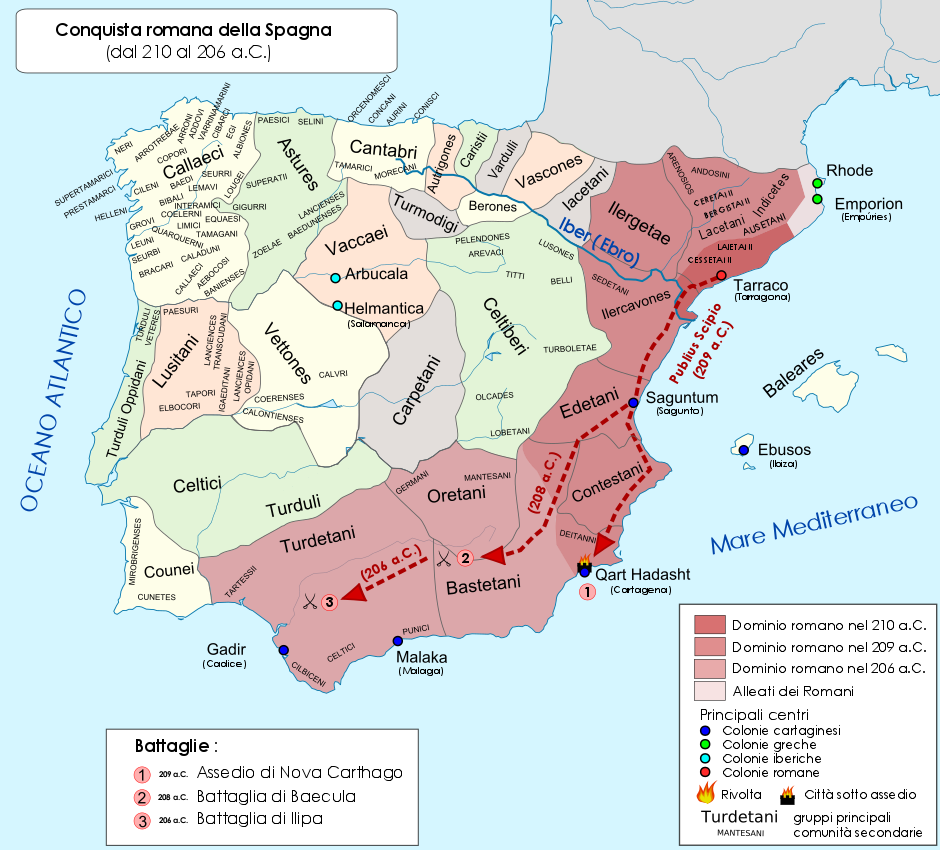
Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of Punic Wars, three wars fought between Ancient Carthage, Carthage and Roman Republic, Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Roman Italy, Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were once again defeated. Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonia, Kingdom of Syracuse, Syracuse and several Numidians, Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Celtiberians, Iberian and Gauls, Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main Theater (military), military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal (Barcid), Hasdru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Carthage
Ancient Carthage ( ; , ) was an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic civilisation based in North Africa. Initially a settlement in present-day Tunisia, it later became a city-state, and then an empire. Founded by the Phoenicians in the ninth century BC, Carthage reached its height in the fourth century BC as one of the largest ''metropoleis'' in the world.George Modelski, ''World Cities: –3000 to 2000'', Washington DC: FAROS 2000, 2003. . Figures in main tables are preferentially cited. Part of former estimates can be read at Evolutionary World Politics Homepage Archived 2008-12-28 at the Wayback Machine It was the centre of the Carthaginian Empire, a major power led by the Punic people who dominated the ancient western and central Mediterranean Sea. Following the Punic Wars, Carthage was Siege of Carthage (Third Punic War), destroyed by the Romans in 146 BC, who later rebuilt Roman Carthage, the city lavishly. Carthage Phoenician settlement of No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scipio Africanus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus (, , ; 236/235–) was a Roman general and statesman who was one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Ancient Carthage, Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the greatest military commanders and strategists of all time, his greatest military achievement was the defeat of Hannibal at the Battle of Zama in 202 BC. This victory in Africa earned him the honorific epithet ''Africanus'', literally meaning 'the African', but meant to be understood as a conqueror of Africa (Roman province), Africa. Scipio's conquest of Carthaginian Iberia culminated in the Battle of Ilipa in 206 BC against Hannibal's brother Mago Barca. Although considered a hero by the Roman people, primarily for his victories against Carthage, Scipio had many opponents, especially Cato the Elder, who hated him deeply. In 187 BC, he was tried in a show trial alongside his brother for bribes they supposedly received from the Seleucid king Antiochus III ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El País
(; ) is a Spanish-language daily newspaper in Spain. is based in the capital city of Madrid and it is owned by the Spanish media conglomerate PRISA. It is the second-most circulated daily newspaper in Spain . is the most read newspaper in Spanish online and one of the Madrid dailies considered to be a national newspaper of record for Spain (along with '' El Mundo'' and '' ABC)''. In 2018, its number of daily sales were 138,000. Its headquarters and central editorial staff are located in Madrid, although there are regional offices in the principal Spanish cities (Barcelona, Seville, Valencia, Bilbao, and Santiago de Compostela) where regional editions were produced until 2015. also produces a world edition in Madrid that is available online in English and in Spanish (Latin America). History was founded in May 1976 by a team at PRISA which included Jesus de Polanco, José Ortega Spottorno and Carlos Mendo. The paper was designed by Reinhard Gade and Julio Alonso. It wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcolithic
The Chalcolithic ( ) (also called the Copper Age and Eneolithic) was an archaeological period characterized by the increasing use of smelted copper. It followed the Neolithic and preceded the Bronze Age. It occurred at different periods in different areas, but was absent in some parts of the world, such as Russia, where there was no well-defined Copper Age between the Stone and Bronze Ages. Stone tools were still predominantly used during this period. The Chalcolithic covers both the early cold working (hammering) of near pure copper ores, as exhibited by the likes of North American Great Lakes Old Copper complex, from around 6,500 BC, through the later copper smelting cultures. The archaeological site of Belovode, on Rudnik mountain in Serbia, has the world's oldest securely dated evidence of copper smelting at high temperature, from . The transition from Copper Age to Bronze Age in Europe occurred between the late 5th and the late In the Ancient Near East the Copper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaén - Muralla Calcolítica
Jaén may refer to: Places Peru *Jaén Province, Peru, a province in Cajamarca Region, Peru ** Jaén District, one of twelve districts of the province Jaén in Peru ***Jaén, Peru, a city in Peru, capital of the Jaén Province Philippines * Jaen, Nueva Ecija, a municipality in the Philippines Spain *Kingdom of Jaén, a territorial jurisdiction of the Crown of Castile from 1246 to 1833 *Province of Jaén (Spain), a province in southern Spain ** Jaén (Congress of Deputies constituency), the electoral district used for the Spanish Congress of Deputies, corresponding to the province of Jaén **Jaén, Spain, a city in south-central Spain, capital of the province of Jaén *** Roman Catholic Diocese of Jaén, a diocese located in the city of Jaén in the ecclesiastical province of Granada * Taifa of Jaén, a medieval kingdom in 1145 and 1168 People *Jaén (surname), a Spanish surname *Andrés González Jaén (born 1993), Spanish footballer *Jaime Jaen (born 1978), Panamanian baseball ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most of the peninsula as well as Septimania under Umayyad rule. These boundaries changed through a series of conquests Western historiography has traditionally characterized as the ''Reconquista'',"Para los autores árabes medievales, el término Al-Andalus designa la totalidad de las zonas conquistadas – siquiera temporalmente – por tropas arabo-musulmanas en territorios actualmente pertenecientes a Portugal, España y Francia" ("For medieval Arab authors, Al-Andalus designated all the conquered areas – even temporarily – by Arab-Muslim troops in territories now belonging to Spain, Portugal and France"), García de Cortázar, José Ángel. ''V Semana de Estudios Medievales: Nájera, 1 al 5 de agosto de 1994'', Gobie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villa
A villa is a type of house that was originally an ancient Roman upper class country house that provided an escape from urban life. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became small farming compounds, which were increasingly fortified in Late Antiquity, sometimes transferred to the Church for reuse as a monastery. They gradually re-evolved through the Middle Ages into elegant upper-class country homes. In the early modern period, any comfortable detached house with a garden near a city or town was likely to be described as a villa; most surviving villas have now been engulfed by suburbia. In modern parlance, "villa" can refer to various types and sizes of residences, ranging from the suburban semi-detached double villa to, in some countries, especially around the Mediterranean, residences of above average size in the countryside. Roman Roman villas included: * the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |