|
Japyx
''Japyx'' is a genus of diplurans belonging to the family Japygidae. These eyeless, predatory hexapods largely shun direct sunlight, remaining under stones and among detritus In biology, detritus ( or ) is organic matter made up of the decomposition, decomposing remains of organisms and plants, and also of feces. Detritus usually hosts communities of microorganisms that colonize and decomposition, decompose (Reminera ..., where they use pincer-like cerci to catch their tiny prey. Species * ''Japyx akiyamae'' (Silvestri, 1928) * ''Japyx albanica'' (Stach, 1922) * ''Japyx angulosus'' (Silvestri, 1918) * ''Japyx arnoldii'' (Ionescu, 1959) * ''Japyx barnardi'' (Silvestri, 1935) * ''Japyx beccarii'' (Silvestri, 1931) * ''Japyx beneserratus'' (Kuwayama, 1928) * ''Japyx biangulatus'' (Silvestri, 1931) * ''Japyx bidens'' (Cook, 1899) * ''Japyx biproductus'' (Silvestri, 1908) * ''Japyx bolivari'' (Silvestri, 1929) * ''Japyx brachycerus'' (Silvestri, 1930) * ''Japyx cavicola'' (Josep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
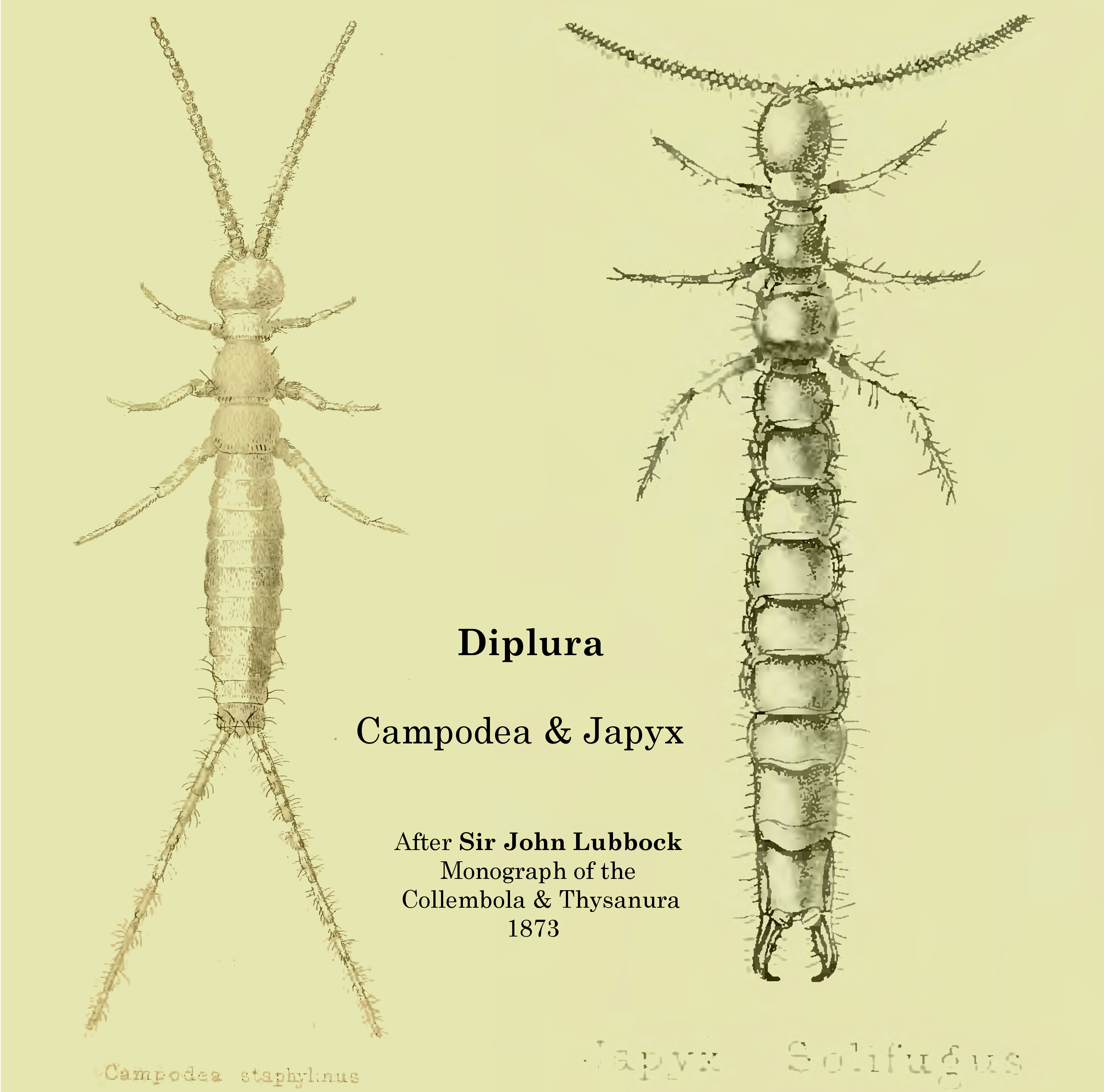
Diplura
The order Diplura ("two-pronged bristletails") is one of three orders of non-insect hexapods within the class Entognatha (alongside Collembola (springtails) and Protura). The name "diplura", or "two tails", refers to the characteristic pair of caudal appendages or filaments at the terminal end of the body. Around 800 species of diplurans have been described. Anatomy Diplurans are typically long, with most falling between . However, some species of '' Japyx'' may reach . They have no eyes and, apart from the darkened cerci in some species, they are unpigmented. Diplurans have long antennae with 10 or more bead-like segments projecting forward from the head. The abdomens of diplurans bear eversible vesicles, which seem to absorb moisture from the environment and help with the animal's water balance. The body segments themselves may display several types of setae, or scales and setae. Diplurans possess a characteristic pair of cerci projecting backwards from the last of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japygidae
thumb The japygids (family Japygidae) are a taxon of hexapods, of the order Diplura, commonly known as forcepstails. In this family, the paired cerci at the end of their abdomens are pincer-like (superficially similar to the unrelated earwigs) and are used to catch their tiny prey. Seventy genera are recognised, divided among seven subfamilies. Extant genera *'' Abjapyx'' Silvestri, 1948 *''Afrojapyx'' Silvestri, 1948 *'' Allojapyx'' Silvestri, 1948 *'' Allurjapyx'' Silvestri, 1930 *'' Atlasjapyx'' Chou & Huang, 1986 *'' Austrjapyx'' Silvestri, 1948 *'' Burmjapyx'' Silvestri, 1931 *'' Catajapyx'' Silvestri, 1933 *'' Centrjapyx'' Silvestri, 1948 *'' Chiljapyx'' Smith, 1962 *''Choujapyx'' Huang, 2001 *'' Congjapyx'' Pagés, 1954 *'' Ctenjapyx'' Silvestri, 1948 *'' Deutojapyx'' Paclt, 1957 *'' Dipljapyx'' Silvestri, 1948 *'' Ectasjapyx'' Silvestri, 1929 *'' Eojapyx'' Smith, 1960 *'' Epijapyx'' Silvestri, 1933 *''Evalljapyx ''Evalljapyx'' is a genus of diplurans in the family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cercus
Cerci (: cercus) are paired appendages usually on the rear-most segments of many arthropods, including insects and symphylans. Many forms of cerci serve as sensory organs, but some serve as pinching weapons or as organs of copulation. In many insects, they simply may be functionless vestigial structures. In basal arthropods, such as silverfish, the cerci originate from the eleventh abdominal segment. As segment eleven is reduced or absent in the majority of arthropods, in such cases, the cerci emerge from the tenth abdominal segment. It is not clear that other structures so named are homologous. In the Symphyla they are associated with spinnerets. Morphology and functions Most cerci are segmented and jointed, or filiform (threadlike), but some take very different forms. Some Diplura, in particular ''Japyx'' species, have large, stout forcipate (pincer-like) cerci that they use in capturing their prey. The Dermaptera, or earwigs, are well known for the forcipate cerci that most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Henry Haliday
Alexander Henry Haliday (1806–1870, also known as Enrico Alessandro Haliday, Alexis Heinrich Haliday, or simply Haliday) was an Ireland, Irish entomologist. He is primarily known for his work on Hymenoptera, Diptera, and Thysanoptera, but worked on all insect orders and on many aspects of entomology. Haliday was born in Carnmoney, County Antrim later living in Holywood, County Down, Holywood, County Down, Ireland. A boyhood friend of Robert Templeton, he divided his time between Ireland and Lucca, where he co-founded the La Società Entomologica Italiana, Italian Entomological Society with Camillo Rondani and Adolfo Targioni Tozzetti. He was a member of the Royal Irish Academy, the Belfast Natural History Society, the Royal Microscopical Society, Microscopical Society of London, and the Galileiana Academy of Arts and Science, as well as a fellow of the (now Royal) Royal Entomological Society, Entomological Society of London. Alexander Haliday was among the greatest dipterists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predation
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common List of feeding behaviours, feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the Host (biology), host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from Scavenger, scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with Herbivore, herbivory, as Seed predation, seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predation behavior varies significantly depending on the organism. Many predators, especially carnivores, have evolved distinct hunting strategy, hunting strategies. Pursuit predation involves the active search for and pursuit of prey, whilst ambush predation, ambush predators instead wait for prey to present an opportunity for capture, and often use stealth or aggressive mimicry. Other predators are opportunism, opportunistic or om ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexapoda
The subphylum Hexapoda (from Greek for 'six legs') or hexapods comprises the largest clade of arthropods and includes most of the extant arthropod species. It includes the crown group class Insecta (true insects), as well as the much smaller clade Entognatha, which includes three classes of wingless arthropods that were once considered insects: Collembola (springtails), Protura (coneheads) and Diplura (two-pronged bristletails). The insects and springtails are very abundant and are some of the most important pollinators, basal consumers, scavengers/ detritivores and micropredators in terrestrial environments. Hexapods are named for their most distinctive feature: a three-part body plan with a consolidated thorax and three pairs of legs. Most other arthropods have more than three pairs of legs. Most recent studies have recovered Hexapoda as a subgroup of Pancrustacea. Morphology Hexapods have bodies ranging in length from 0.5 mm to over 300 mm which are divided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detritus (biology)
In biology, detritus ( or ) is organic matter made up of the decomposition, decomposing remains of organisms and plants, and also of feces. Detritus usually hosts communities of microorganisms that colonize and decomposition, decompose (Remineralisation, remineralise) it. Such microorganisms may be decomposers, detritivores, or coprophages. In terrestrial ecosystems detritus is present as plant litter and other organic matter that is intermixed with soil, known as soil organic matter. The detritus of aquatic ecosystems is organic substances suspended in the water and accumulated in depositions on the floor of the body of water; when this floor is a seabed, such a deposition is called marine snow. Theory The remains of decaying plants or animals, or their tissue parts, and feces gradually lose their form due to physical processes and the action of decomposers, including grazers, bacteria, and fungi. Decomposition, the process by which organic matter is decomposed, occurs in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |