|
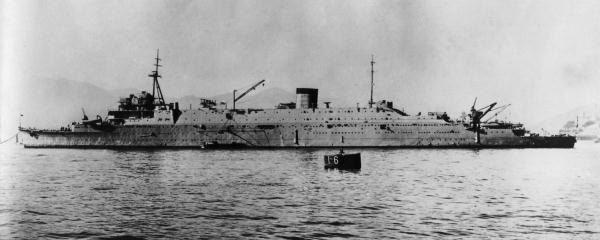
Japanese Aircraft Carrier Ryūhō
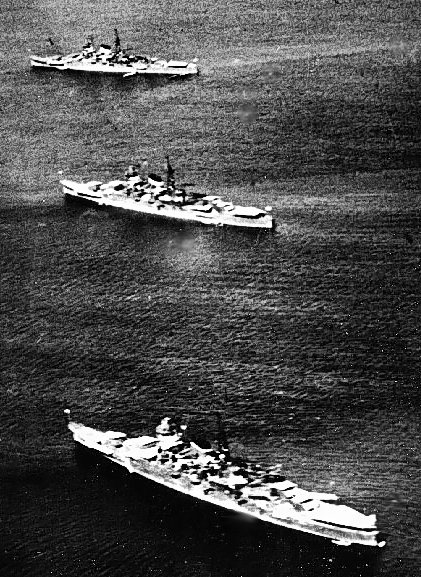
was a light aircraft carrier of the Imperial Japanese Navy. She was converted from the submarine tender , which had been used in the Second Sino-Japanese War. One of the least successful of the light aircraft carrier conversions due to her small size, slow speed and weak construction, during World War II, ''Ryūhō'' was used primarily as an aircraft transport and for training purposes, although she was also involved in a number of combat missions, including the Battle of the Philippine Sea. Background The London Naval Treaty imposed limitations on new construction of major capital warships for the major world powers. The Imperial Japanese Navy responded in part by the construction of auxiliary vessels, such as fleet oilers and submarine tenders, designed so that they could be converted quickly into aircraft carriers in time of conflict. ''Taigei'' was ordered as part of the 1st Naval Armaments Supplement Programme of 1932. Design Although ''Taigei'' was designed from the onse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Aircraft Carrier Ryūjō
''Ryūjō'' ( "Prancing Dragon") was a light aircraft carrier built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during the early 1930s. Small and lightly built in an attempt to exploit a loophole in the Washington Naval Treaty of 1922, she proved to be top-heavy and only marginally stable and was back in the shipyard for modifications to address those issues within a year of completion. With her stability improved, ''Ryūjō'' returned to service and was employed in operations during the Second Sino-Japanese War. During World War II, she provided air support for operations in the Philippines, Malaya, and the Dutch East Indies, where her aircraft participated in the Second Battle of the Java Sea. During the Indian Ocean raid in April 1942, the carrier attacked British merchant shipping with her guns and aircraft. ''Ryūjō'' next participated in the Battle of Dutch Harbor, the opening battle of the Aleutian Islands campaign, in June 1942. She was sunk by American carrier-based air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine Tender
A submarine tender, in British English a submarine depot ship, is a type of depot ship that supplies and supports submarines. Development Submarines are small compared to most oceangoing vessels, and generally cannot carry large amounts of food, fuel, torpedoes, and other supplies, or a full array of maintenance equipment and personnel. The tender carries all these, and either meets submarines at sea to replenish them or provides these services while docked at a port near the submarines' operations zone. In some navies, the tenders were equipped with workshops for maintenance, and as floating dormitories with relief crews. With the increased size and automation of modern submarines, plus in some navies the introduction of nuclear power, tenders are no longer as necessary for fuel as they once were. Canada Canada's first submarine depot ship was . Chile The term used in the Chilean Navy is "submarine mother ship", as for example the BMS (buque madre de submarinos) ''Almir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yokosuka D4Y
The is a two-seat carrier-based dive bomber developed by the Yokosuka Naval Air Technical Arsenal and operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy from 1942 to 1945 during World War II. Development of the aircraft began in 1938. The first D4Y1 was complete in November 1940 and made its maiden flight at Yokosuka the following month. While the aircraft was originally conceived as a dive bomber, the D4Y was used in other roles including reconnaissance, night fighter and special attack ( kamikaze). It made its combat debut as a reconnaissance aircraft when two pre-production D4Y1-Cs embarked aboard the ''Sōryū'' to take part in the Battle of Midway in 1942. It was not until March 1943 that it was accepted for use as a dive bomber. The early D4Y1 and D4Y2 featured the liquid-cooled Aichi Atsuta engine, a licensed version of the German Daimler-Benz DB 601, while the later D4Y3 and D4Y4 featured the Mitsubishi MK8P Kinsei radial engine. Like many other Japanese aircraft of the time, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aichi D3A
The Aichi D3A (Navy designation "Type 99 Carrier Bomber"; World War II Allied names for Japanese aircraft, Allied reporting name "Val") is a World War II carrier-borne dive bomber. It was the primary dive bomber of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) and was involved in almost all IJN actions, including the attack on Pearl Harbor. The Aichi D3A was the first Japanese aircraft to bomb American targets in the war, commencing with Pearl Harbor and U.S. bases in the Philippines, such as Clark Air Force Base. They sank more Allies of World War II, Allied warships than any other Axis powers, Axis aircraft. Design and development In mid-1936, the Japanese Navy issued the 11-Shi specification for a monoplane carrier-based dive bomber to replace the existing Aichi D1A, D1A biplane then in service. Aichi Kokuki, Aichi, Nakajima Aircraft Company, Nakajima, and Mitsubishi all submitted designs, with the former two subsequently being asked for two prototypes each. The Aichi design starte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitsubishi A6M
The Mitsubishi A6M "Zero" is a long-range carrier-capable fighter aircraft formerly manufactured by Mitsubishi Aircraft Company, a part of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. It was operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) from 1940 to 1945. The A6M was designated as the , or the Mitsubishi A6M Rei-sen. The A6M was usually referred to by its pilots as the ''Reisen'' (, zero fighter), "0" being the last digit of the imperial year 2600 (1940) when it entered service with the IJN. The official Allied reporting name was "Zeke", although the name "Zero" was used more commonly. The Zero is considered to have been the most capable carrier-based fighter in the world when it was introduced early in World War II, combining excellent maneuverability, high airspeed, strong firepower and very long range.Hawks, Chuck"The Best Fighter Planes of World War II" chuckhawks.com. Retrieved: 18 January 2007. The Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service also frequently used it as a land-based fighter. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kampon
The was the externally operating division of the Ministry of the Navy of Japan responsible for the administration of naval vessel construction. From 1923 onward, it took on the role of a research institution for the research and development of naval technologies and engineering. This included studying and investigating existing western naval technology, developing and overseeing Japan's domestic shipbuilding and arms industries, and training officers to become naval engineers and inspectors. The bureau was dismantled along with the naval ministry in November 1945 after Japan surrendered to the Allies at the end of World War II. Taishō period weapons The Department developed various weapons during the Taishō period. These were known a "Xth Year Type" weapons, with the year being the year of the Taishō Emperor's reign (dating from 30 July 1912 - 25 December 1926). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Engine
The diesel engine, named after the German engineer Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which Combustion, ignition of diesel fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to Mechanics, mechanical Compression (physics), compression; thus, the diesel engine is called a compression-ignition engine (CI engine). This contrasts with engines using spark plug-ignition of the air-fuel mixture, such as a petrol engine (gasoline engine) or a gas engine (using a gaseous fuel like natural gas or liquefied petroleum gas). Introduction Diesel engines work by compressing only air, or air combined with residual combustion gases from the exhaust (known as exhaust gas recirculation, "EGR"). Air is inducted into the chamber during the intake stroke, and compressed during the compression stroke. This increases air temperature inside the Cylinder (engine), cylinder so that atomised diesel fuel injected into the combustion chamber ignites. The torque a dies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc Welding
Arc welding is a welding process that is used to join metal to metal by using electricity to create enough heat to melt metal, and the melted metals, when cool, result in a joining of the metals. It is a type of welding that uses a welding power supply to create an electric arc between a metal stick ("electrode") and the base material to melt the metals at the point of contact. Arc welding power supplies can deliver either Direct current, direct (DC) or Alternating current, alternating (AC) current to the work, while consumable or non-consumable electrodes are used. The welding area is usually protected by some type of shielding gas (e.g. an inert gas), vapor, or slag. Arc welding processes may be manual, semi-automatic, or fully automated. First developed in the late part of the 19th century, arc welding became commercially important in shipbuilding during the Second World War. Today it remains an important process for the fabrication of steel structures and vehicles. Power supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freeboard (nautical)
In sailing and boating, a vessel's freeboard is the distance from the waterline to the upper deck level, measured at the lowest point of sheer where water can enter the boat or ship. In commercial vessels, the latter criterion measured relative to the ship's load line, regardless of deck arrangements, is the mandated and regulated meaning. In yachts, a low freeboard is often found on racing boats, for increased speed (by reducing weight and therefore drag). A higher freeboard will give more room in the cabin, but will increase weight and drag, compromising speed. A higher freeboard, such as used on ocean liners, also helps weather waves and so reduce the likelihood of being washed over by full water waves. A low-freeboard vessel is susceptible to taking in water in rough seas. Freighter ships and warships use high freeboard designs to increase internal volume, which also allows them to satisfy International Maritime Organization The International Maritime Organizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Naval Armaments Supplement Programme
The , otherwise known as the "Circle One" plan was the first of four expansion plans of the Imperial Japanese Navy between 1930 and the start of World War II. Background The London Naval Treaty placed severe restrictions on Japan's naval capabilities vis-a-vis the United States Navy and the British Royal Navy in terms of tonnage and numbers of capital warships. The response of the Imperial Japanese Navy General Staff was to initiate a construction program to build new warships to the allotted tonnage limits in each of the restricted categories, and to invest in types of warships and weaponry not specifically covered by the provisions of the treaty. The "Circle One" plan was submitted by the Naval Ministry and approved by the Cabinet in November 1930, and officially ratified by the Diet of Japan in 1931. It called for the construction of 39 new combat vessels, centering on four of the new s, and expansion of the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service to 14 Naval Air Groups. Budget ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fleet Oiler
A replenishment oiler or replenishment tanker is a naval auxiliary ship with fuel tanks and dry cargo holds which can supply both fuel and dry stores during underway replenishment (UNREP) at sea. Many countries have used replenishment oilers. The United States Navy's hull classification symbol for this type of ship was 'AOR' (Auxiliary Oil Replenishment). Replenishment oilers are slower and carry fewer dry stores than the US Navy's modern fast combat support ships, which carry the classification 'AOE'. In 2020 the US Navy began to develop a new type of ship, the 'AOL' or light replenishment oiler; construction of the first is planned for 2026. History The development of the "oiler" paralleled the change from coal- to oil-fired boilers in warships. Prior to the adoption of oil fired machinery, navies could extend the range of their ships either by maintaining coaling stations or for warships to raft together with colliers and for coal to be manhandled aboard. Though argument ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Naval Treaty
The London Naval Treaty, officially the Treaty for the Limitation and Reduction of Naval Armament, was an agreement between the United Kingdom, Empire of Japan, Japan, French Third Republic, France, Kingdom of Italy, Italy, and the United States that was signed on 22 April 1930. Seeking to address issues not covered in the 1922 Washington Naval Treaty, which had created tonnage limits for each nation's Surface combatant, surface warships, the new agreement regulated submarine warfare, further controlled cruisers and destroyers, and limited naval shipbuilding. Ratifications were exchanged in London on 27 October 1930, and the treaty went into effect on the same day, but it was largely ineffective. The treaty was registered in ''Treaty series#League of Nations, League of Nations Treaty Series'' on 6 February 1931. Conference The signing of the treaty remains inextricably intertwined with the ongoing negotiations, which began before the official start of the London Naval Confer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |