|
Janissary
A janissary (, , ) was a member of the elite infantry units that formed the Ottoman sultan's household troops. They were the first modern standing army, and perhaps the first infantry force in the world to be equipped with firearms, adopted during the reign of Murad II (r. 1421–1444, 1446–1451). The corps was established under either Orhan or Murad I, and dismantled by Mahmud II in 1826. Janissaries began as elite corps made up through the ''devşirme'' system of Ghilman, child levy enslavement, by which Ethnic groups in Europe, indigenous European Christians, Christian boys, chiefly from the Balkans, were taken, levied, subjected to forced circumcision and Forced conversion#Islam, forced conversion to Islam, and incorporated into the Ottoman army in the 15th–19th centuries, Ottoman army. They became famed for internal cohesion cemented by strict discipline and order. Unlike typical History of slavery in the Muslim world, slaves, they were paid regular salaries. Forbidden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agha Of The Janissaries
The Agha of the Janissaries or Janissary Agha (; ) was a top Ottoman Empire, Ottoman military official and courtier, and the commander of the Janissary corps. Apart from the commander-general of the entire corps, the title of "Agha of the Janissaries" was also borne by the commanders of provincial garrisons of Janissaries. Appointment and duties The Agha (title), Agha was chosen by the Ottoman Sultan, but was not necessarily himself a Janissary. To secure the often uncertain loyalty of the corps, Bayezid II () stopped the practice of appointing the (the commander of the regiments) to the post, and instead nominated a member of his own household to the post. These were usually pages who had been recruited, like the Janissaries, via the system, but then had been educated in the palace school, then proven their ability in the inner, private palace service (), before being appointed to senior posts in the palace's outer service (). At the same time, Bayezid founded the () regiment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Army In The 15th–19th Centuries
The Ottoman army was the military structure established by Mehmed II () during his reorganization of the Ottoman state and its military. It resulted from a major reorganization of the standing army dating from the time of Sultan Orhan (), which had centred on janissaries who were paid by salary rather than rewarded with booty or fiefs. The army built by Orhan had operated during the period of the rise of the Ottoman Empire (1299 to 1453). The organization introduced by Mehmed II was twofold, central (, the household division) and peripheral (, province-level). Sultan Mahmud II forced this army to disband on 15 June 1826 in what is known as Auspicious Incident, which followed a century-long reform effort. Predecessor force The medieval Ottoman Empire had become the first country to maintain a standing army in Europe since the days of the Roman Empire. The force originated in the 14th century. The Ottoman army may have also been the first to equip with firearms, which they acqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Sultan
The sultans of the Ottoman Empire (), who were all members of the Ottoman dynasty (House of Osman), ruled over the Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental empire from its perceived inception in 1299 to Dissolution of the Ottoman Empire, its dissolution in 1922. At its height, the Ottoman Empire spanned an area from Budin Eyalet, Hungary in the north to Yemen Eyalet, Yemen in the south and from Ottoman Algeria, Algeria in the west to Ottoman Iraq, Iraq in the east. Administered at first from the city of Söğüt since before 1280 and then from the city of Bursa since 1323 or 1324, the empire's capital was moved to Adrianople (now known as Edirne in English) in 1363 following Ottoman conquest of Adrianople, its conquest by Murad I and then to Constantinople (present-day Istanbul) in 1453 following Fall of Constantinople, its conquest by Mehmed the Conqueror, Mehmed II. The Rise of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Empire's early years have been the subject of varying narrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahmud II
Mahmud II (, ; 20 July 1785 – 1 July 1839) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1808 until his death in 1839. Often described as the "Peter the Great of Turkey", Mahmud instituted extensive administrative, military, and fiscal reforms. His disbandment of the conservative Janissary, Janissary Corps removed a major obstacle to his and his successors' reforms in the Empire, creating the foundations of the subsequent Tanzimat era. Mahmud's reign was also marked by further Ottoman military defeats and loss of territory as a result of nationalist uprisings and European intervention. Mahmud ascended the throne following an Ottoman coups of 1807–1808, 1808 coup that deposed his half-brother Mustafa IV. Early in his reign, the Ottoman Empire ceded Bessarabia to Russia at the end of the Russo-Turkish War (1806–1812), 1806–1812 Russo-Turkish War. Greece waged a Greek War of Independence, successful war of independence that started in 1821 with British, French and Russian su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Varna
The Battle of Varna took place on 10 November 1444 near Varna in what is today eastern Bulgaria. The Ottoman army under Sultan Murad II (who did not actually rule the sultanate at the time) defeated the Crusaders commanded by King Władysław III of Poland and Hungary, John Hunyadi (acting as commander of the combined Christian forces) and Mircea II of Wallachia. It was the final battle of the unsuccessful Crusade of Varna, a last-ditch effort to prevent further Ottoman expansion into the Balkans. Background The Hungarian Kingdom fell into crisis after the death of King Sigismund in 1437. His son-in-law and successor, King Albert, ruled for only two years and died in 1439, leaving his widow Elizabeth with an unborn child, Ladislaus the Posthumous. The Hungarian noblemen then called the young King Władysław III of Poland to the throne of Hungary, expecting his aid in defense against the Ottomans. After his Hungarian coronation, he never went back to his homeland again, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orhan
Orhan Ghazi (; , also spelled Orkhan; died 1362) was the second sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1323/4 to 1362. He was born in Söğüt, as the son of Osman I. In the early stages of his reign, Orhan focused his energies on conquering most of northwestern Anatolia. The majority of these areas were under Byzantine rule and he won his first battle at Pelekanon against the Byzantine Emperor Andronikos III Palaiologos. Orhan also occupied the lands of the Karasids of Balıkesir and the Ahis of Ankara. A series of civil wars surrounding the ascension of the nine-year-old Byzantine emperor John V Palaiologos greatly benefited Orhan. In the Byzantine civil war of 1341–1347, the regent John VI Kantakouzenos married his daughter Theodora to Orhan and employed Ottoman warriors against the rival forces of the empress dowager, allowing them to loot Thrace. In the Byzantine civil war of 1352–1357, Kantakouzenos used Ottoman forces against John V, granting them the use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
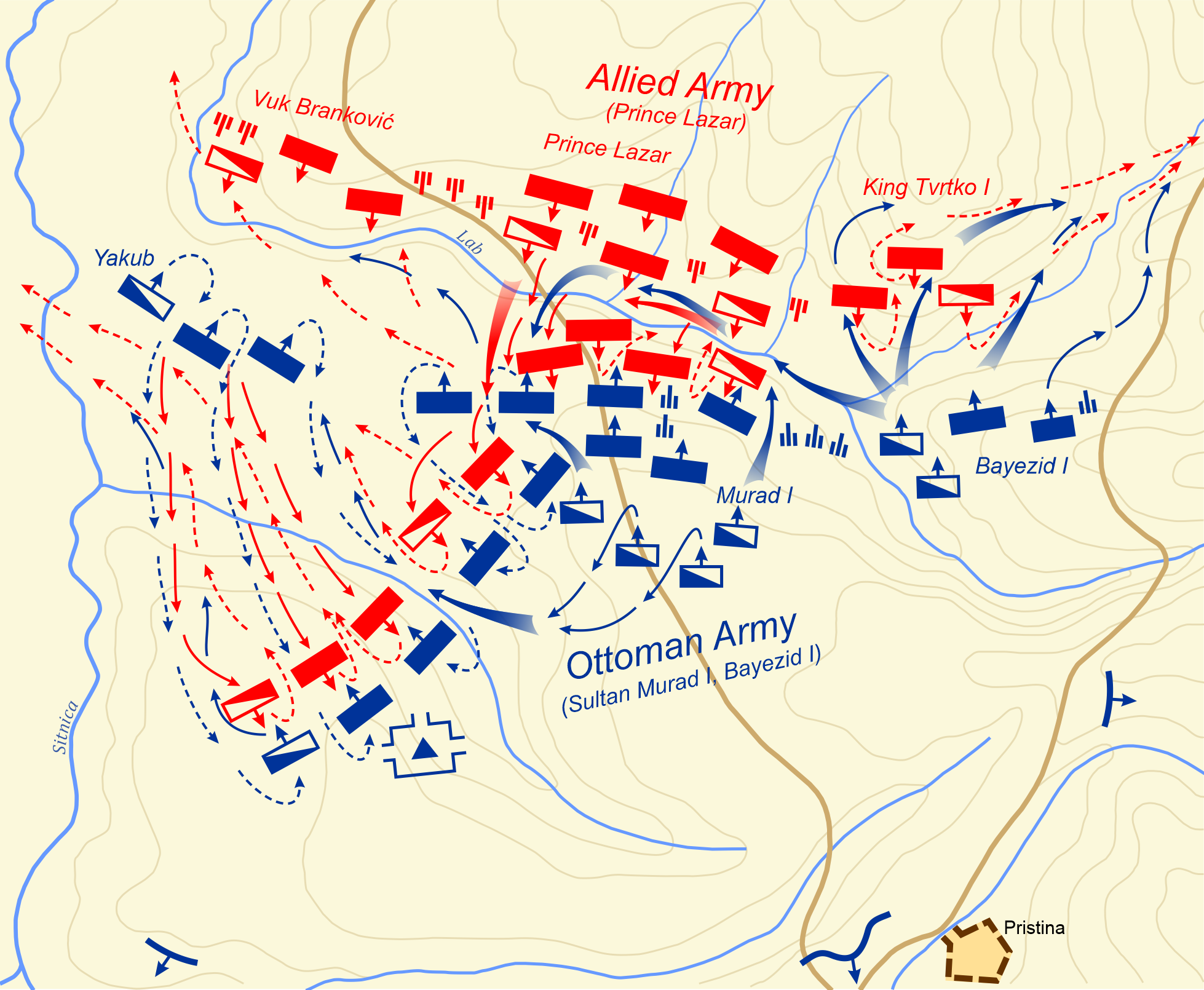
Battle Of Kosovo
The Battle of Kosovo took place on 15 June 1389 between an army led by the Serbian Prince Lazar Hrebeljanović and an invading army of the Ottoman Empire under the command of Sultan Murad I. It was one of the largest battles of the Late Middle Ages. The battle was fought on the Kosovo field in the territory ruled by Serbian nobleman Vuk Branković, in what is today Kosovo, about northwest of the modern city of Pristina. The army under Prince Lazar consisted mostly of his own troops, a contingent led by Branković, and a contingent sent from Bosnia by King Tvrtko I, commanded by Vlatko Vuković. Additionally, Lazar was also supported by a Christian coalition from various European ethnic groups. Prince Lazar was the ruler of Moravian Serbia and the most powerful among the Serbian regional lords of the time, while Branković ruled the District of Branković and other areas, recognizing Lazar as his overlord. Reliable historical accounts of the battle are scarce. The bulk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city was captured on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 55-day siege which had begun on 6 April. The attacking Army of the classical Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Army, which significantly outnumbered Constantinople's defenders, was commanded by the 21-year-old List of sultans of the Ottoman Empire, Sultan Mehmed the Conqueror, Mehmed II (later nicknamed "the Conqueror"), while the Byzantine army (Palaiologan era), Byzantine army was led by List of Byzantine emperors, Emperor Constantine XI Palaiologos. After conquering the city, Mehmed II made Constantinople the new Ottoman capital, replacing Edirne, Adrianople. The fall of Constantinople and of the Byzantine Empire was a watershed of the Late Middle Ages, marking the effective end of the Roman Empire, a state which began in roughly 27 BC and had la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murad II
Murad II (, ; June 1404 – 3 February 1451) was twice the sultan of the Ottoman Empire, from 1421 to 1444 and from 1446 to 1451. Early life Murad was born in June 1404 to Mehmed I, while the identity of his mother is disputed according to various accounts. According to 15th century historian Şükrullah, Murad's mother was a concubine. Hüseyin Hüsâmeddin Yasar, an early 20th century historian, wrote in his work ''Amasya Tarihi'' that his mother was Şahzade Hatun, daughter of Divitdar Ahmed Pasha. According to historians İsmail Hami Danişmend, and Heath W. Lowry, his mother was Emine Hatun, a Dulkadirids, Dulkadirid princess. He spent his early childhood in Amasya. In 1410, Murad came along with his father to the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman capital, Edirne. After his father ascended to the Ottoman throne, he made Murad governor of the Amasya Sanjak. Murad remained at Amasya until the death of Mehmed I in 1421. He was solemnly recognized as sultan of the Ottoman Sultanate at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Siege Of Malta
The Great Siege of Malta (Maltese language, Maltese: ''L-Assedju l-Kbir'') occurred in 1565 when the Ottoman Empire attempted to conquer the island of Malta, then held by the Knights Hospitaller. The siege lasted nearly four months, from 18 May to 8 September 1565. The Knights Hospitaller had been Hospitaller Malta, headquartered in Malta since 1530, after being driven out of Rhodes, also by the Ottomans, in 1522, following the Siege of Rhodes (1522), siege of Rhodes. The Ottomans first attempted to take Malta in 1551 but failed. In 1565, Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Sultan, made a second attempt to take Malta. The Knights, who numbered around 500 together with approximately 6,000 footsoldiers, withstood the siege and repelled the invaders. This victory became one of the most celebrated events of sixteenth-century Europe, to the point that Voltaire said: "Nothing is better known than the siege of Malta." It undoubtedly contributed to the eventual erosion of the European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanham, Maryland
Lanham is an unincorporated community and census-designated place in Prince George's County, Maryland. As of the 2020 United States census, it has a population of 11,282. The New Carrollton station (the terminus of the Washington Metro's Orange Line) as well as an Amtrak station are across the Capital Beltway in New Carrollton, Maryland. Doctors Community Hospital is located in Lanham. History The Thomas J. Calloway House was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2005. Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, Lanham has a total area of , of which is land and , or 0.54%, is water. Government and infrastructure Prince George's County Police Department District 2 Station in Brock Hall CDP, with a Bowie postal address, serves the community. The U.S. Postal Service operates the Lanham Seabrook Post Office in Lanham CDP. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standing Army
A standing army is a permanent, often professional, army. It is composed of full-time soldiers who may be either career soldiers or conscripts. It differs from army reserves, who are enrolled for the long term, but activated only during wars or natural disasters, and temporary armies, which are raised from the civilian population only during a war or threat of war, and disbanded once the war or threat is over. Standing armies tend to be better equipped, better trained, and better prepared for emergencies, defensive deterrence, and particularly, wars. Wills, Garry (1999). ''A Necessary Evil, A History of American Distrust of Government'' New York, N.Y.; Simon & Schuster. The term dates from approximately 1600, although the phenomenon it describes is much older. History Ancient history Mesopotamia Sargon of Akkad, the founder of the Akkadian Empire, is believed to have formed the first standing professional army. Tiglath-Pileser III of Assyria (ruled 745–727 BC) cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |