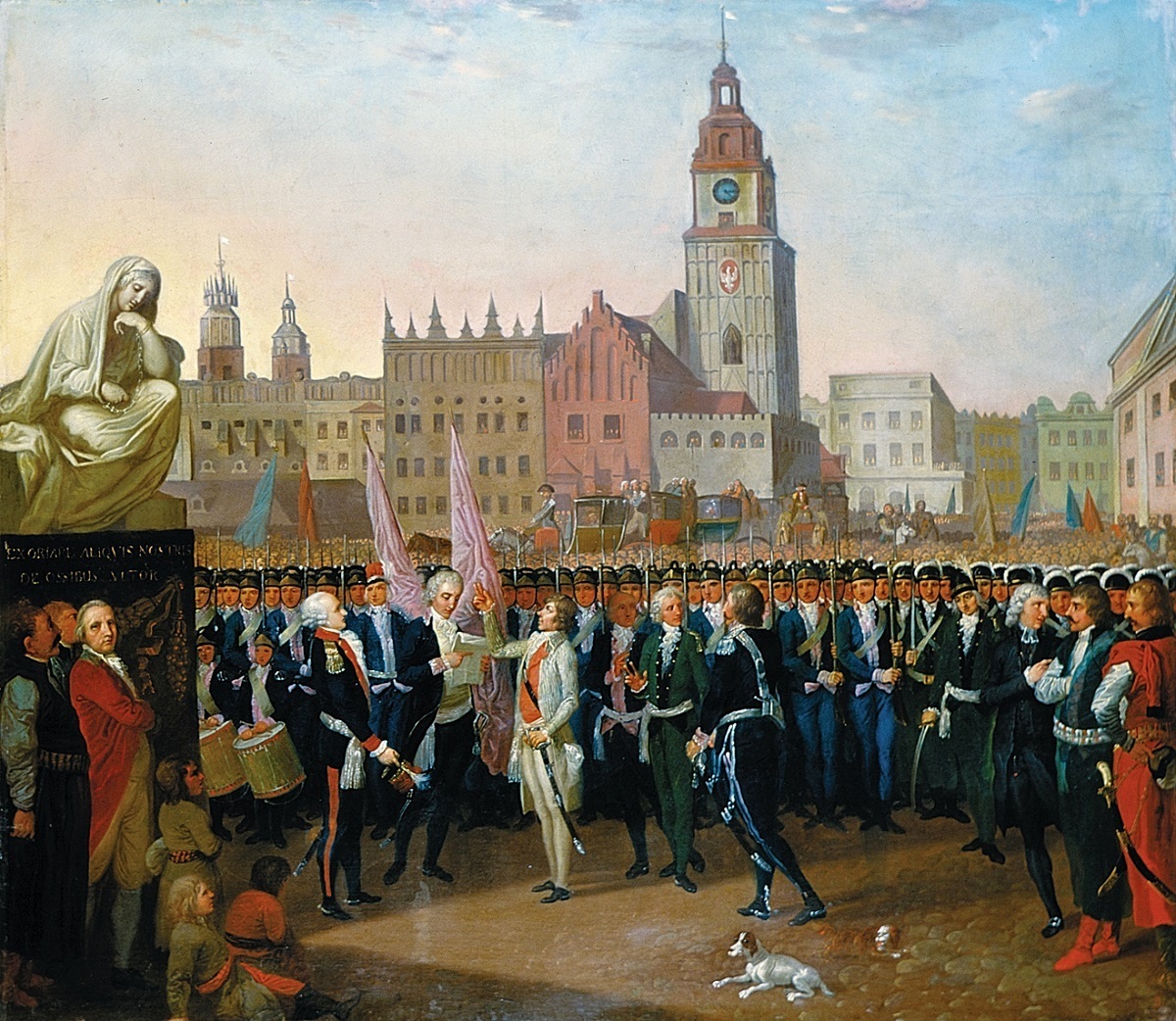|
Jan Paweł Woronicz
Jan Paweł Woronicz (1757 – 1829) was a Polish clergyman, orator, and poet. He lived through major periods such as the Partitions of Poland and Napoleonic Wars, and his work included themes from these events. At the time of his death, he was concurrently the Bishop of Kraków (1815-1829), Bishop of Warsaw (1827-1829), and Primate of Poland (1828-1829). Biography Jan Paweł Woronicz was born into the nobility near Tajkury. His early education was with the Jesuits in Ostróg, and he later entered a seminary in Warsaw to become a priest by 1784. According to writer Stanisław Baczyński, Woronicz's notoriety began to grow during his time as parish priest of Liw. During the Great Sejm (1788-1792), he became even more well known for his speeches. Woronicz eventually moved to a rectory in the Puławy region and became associated with the Czartoryski family. It was around this time that he produced his first notable work of poetry, ''Sybilli'', which was published much later in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Krakow
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of dioceses. The role or office of the bishop is called episcopacy or the episcopate. Organisationally, several Christian denominations utilise ecclesiastical structures that call for the position of bishops, while other denominations have dispensed with this office, seeing it as a symbol of power. Bishops have also exercised political authority within their dioceses. Traditionally, bishops claim apostolic succession, a direct historical lineage dating back to the original Twelve Apostles or Saint Paul. The bishops are by doctrine understood as those who possess the full priesthood given by Jesus Christ, and therefore may ordain other clergy, including other bishops. A person ordained as a deacon, priest (i.e. presbyter), and then bishop is understood to hold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liw, Poland
Liw is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Liw, within Węgrów County, Masovian Voivodeship, in east-central Poland. It lies on the river Liwiec (also sometimes called the Liw), approximately west of Węgrów and east of Warsaw. History Liw probably started as a gord guarding the ford across Liwiec river and the eastern borders of Duchy of Masovia, and the stronghold was moved from the original site to the area of the present castle, built in 1429, in the 13th century. First written document about Liw comes from 1304, during Masovian duke Bolesław II of Masovia rule. Liw received town rights in 1421 or earlier, and between 1493 and 1789 there were two separate towns, ''Liw Stary'' ("Old Liw") and ''Liw Nowy'' ("New Liw"), and this tradition survived in two ''Sołtys''(Schultheiß) offices in the present village. Under the Masovian dukes the town was developing rapidly lying on the border with Grand Duchy of Lithuania, it became the capital of ''ziemia liwska'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roland Greene
Roland Greene (born 1957) is a scholar of the early modern literature and culture of England, Latin Europe, and the colonial Americas; and of poetry and poetics from the sixteenth century to the present. He is the Mark Pigott KBE Professor in the School of Humanities and Sciences at Stanford University. He serves as Director of the Stanford Humanities Center. Education ''Greene'' attended Fairfax High School (Los Angeles). He obtained degrees at Princeton University (Ph.D.) and Brown University (A.B.), where he was a student of Earl Miner and Barbara Lewalski. Career He began his professorial career at Harvard University as an Assistant and Associate Professor from 1984 to 1992. He served for six years as the Director of the Program in Comparative Literature at the University of Oregon, where he was Professor of Comparative Literature and English. He joined Stanford in 2001. Greene served as president of the Modern Language Association in 2015-16, and is a member of the American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2,746,984 residents in , Rome is the list of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, third most populous city in the European Union by population within city limits. The Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, with a population of 4,223,885 residents, is the most populous metropolitan cities of Italy, metropolitan city in Italy. Rome metropolitan area, Its metropolitan area is the third-most populous within Italy. Rome is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, within Lazio (Latium), along the shores of the Tiber Valley. Vatican City (the smallest country in the world and headquarters of the worldwide Catholic Church under the governance of the Holy See) is an independent country inside the city boun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troy
Troy (/; ; ) or Ilion (; ) was an ancient city located in present-day Hisarlik, Turkey. It is best known as the setting for the Greek mythology, Greek myth of the Trojan War. The archaeological site is open to the public as a tourist destination, and was added to the List of World Heritage Sites in Turkey, UNESCO World Heritage list in 1998. Troy was repeatedly destroyed and rebuilt during its 4000 years of occupation. As a result, the site is divided into nine Stratigraphy (archaeology), archaeological layers, each corresponding to a city built on the ruins of the previous. Archaeologists refer to these layers using Roman numerals, Troy I being the earliest and Troy IX being the latest. Troy was first settled around 3600 BC and grew into a small fortified city around 3000 BC (Troy I). Among the early layers, Troy II is notable for its wealth and imposing architecture. During the Late Bronze Age, Troy was called Wilusa and was a vassal of the Hittite Empire. The final layer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kościuszko Uprising
The Kościuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794, Second Polish War, Polish Campaign of 1794, and the Polish Revolution of 1794, was an uprising against the Russian and Prussian influence on the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, led by Tadeusz Kościuszko in Poland-Lithuania and the Prussian partition in 1794. It was a failed attempt to liberate the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from external influence after the Second Partition of Poland (1793) and the creation of the Targowica Confederation. Background Decline of the Commonwealth By the early 18th century, the magnates of Poland and Lithuania controlled the state – or rather, they managed to ensure that no reforms would be carried out that might weaken their privileged status (the " Golden Freedoms"). Through the abuse of the '' liberum veto'' rule which enabled any deputy to paralyze the Sejm (Commonwealth's parliament) proceedings, deputies bribed by magnates or foreign powers or those sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Józef Poniatowski
Prince Józef Antoni Poniatowski (; 7 May 1763 – 19 October 1813) was a Polish general, minister of war and army chief, who became a Marshal of the French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars. A nephew of the King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania Stanisław II August (), Poniatowski began his military career in 1780 in the Austrian army, where he attained the rank of colonel. In 1789, after leaving Austrian service, he joined the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth army at the request of his uncle. Poniatowski, now in the rank of major general and commander of the Royal Guards, took part in the Polish–Russian War of 1792, leading the crown forces at the victorious Battle of Zieleńce. After the king's support for the Targowica Confederation of 1792, Poniatowski felt compelled to resign. In 1794 he participated in the Kościuszko Uprising and took charge of defending Warsaw - for which the Russian authorities subsequently exiled him until 1798. In 1807, after Napoleon Bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tadeusz Kościuszko
Andrzej Tadeusz Bonawentura Kościuszko (; 4 or 12 February 174615 October 1817) was a Polish Military engineering, military engineer, statesman, and military leader who then became a national hero in Poland, the United States, Lithuania, and Belarus. He fought in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth's struggles against Russian Empire, Russia and Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia, and on the U.S. side in the American Revolutionary War. As Supreme Commander of the Polish National Armed Forces, he led the 1794 Kościuszko Uprising. Kościuszko was born in February 1746, in a manor house on the Mieračoŭščyna, Mereczowszczyzna estate in Brest Litovsk Voivodeship, then Grand Duchy of Lithuania, a part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, now the Ivatsevichy District of Belarus. At age 20, he graduated from the Corps of Cadets (Warsaw), Corps of Cadets in Warsaw, Poland. After the start of the War of the Bar Confederation in 1768, Kościuszko moved to France in 1769 to study. He r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw (; ; ), also known as the Grand Duchy of Warsaw and Napoleonic Poland, was a First French Empire, French client state established by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807, during the Napoleonic Wars. It initially comprised the ethnically Polish lands ceded to France by Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia under the terms of the Treaties of Tilsit, and was augmented in 1809 with territory ceded by Austrian Empire, Austria in the Treaty of Schönbrunn. It was the first attempt to re-establish Poland as a sovereign state after the 18th-century partitions of Poland, partitions and covered the central and southeastern parts of present-day Poland. The duchy was held in personal union by Napoleon's ally, Frederick Augustus I of Saxony, who became the duke of Warsaw and remained a legitimate candidate for the List of Polish monarchs, Polish throne. Following Napoleon's invasion of Russia, Napoleon's failed invasion of Russia, Napoleon seemingly abandoned the duchy, and it was left to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czartoryski
The House of Czartoryski (feminine form: Czartoryska, plural: Czartoryscy; ) is a Princely Houses of Poland, Polish princely family of Lithuanian-Ruthenians, Ruthenian origin, also known as the Familia (political party), Familia. The family, which derived their kin from the Gediminids dynasty, by the mid-17th century had split into two branches, based in the Klevan Castle and the Korets Castle, respectively. They used the Czartoryski coat of arms and were a szlachta, noble family of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in the 18th century. The Czartoryski and the Potocki were the two most influential aristocratic families of the last decades of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1569–1795). History The Czartoryski family is of Lithuanian descent from Ruthenia. Their ancestor, a grandson of Gediminas, the List of rulers of Lithuania , Grand Duke of Lithuania, became known with his baptismal name Constantine ( 1330−1390) - he became a Prince of Staryi Chortoryisk, Chorto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puławy
Puławy (, also written Pulawy) is a city in eastern Poland, in Lesser Poland's Lublin Voivodeship, at the confluence of the Vistula and Kurówka River, Kurówka Rivers. Puławy is the capital of Puławy County. The city's 2019 population was Census in Poland, estimated at 47,417. Its coat of arms is based on Coat of arms of Lithuania, Pogonia. Puławy was first mentioned in documents of the 15th century. At that time it was spelled ''Pollavy'', its name probably coming from a Vistula River Ford (crossing), ford located nearby. The town is a local center of science, industry and tourism, together with nearby Nałęczów and Kazimierz Dolny. Puławy is home to Poland's first permanent museum and is a Vistula River port. The town has two bridges and four rail stations, and serves as a road junction. Nearby Dęblin has a military airport. Location and transport Puławy lies in the western part of Lublin Voivodeship, at the edge of the picturesque Lesser Polish Gorge of the Vistul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |