|
Jan Marek Marci
Jan Marek Marci (; June 13, 1595April 10, 1667), or Johannes Marcus Marci, was a Bohemian doctor and scientist, rector of the Charles University in Prague, University of Prague, and official physician to the Holy Roman Emperors. The crater Marci (crater), Marci on the Far side (Moon), far side of the Moon is named after him. Career Marci was born in Lanškroun, near the border between Czech lands, historical lands Bohemia and Moravia (presently parts of the Czech Republic). He studied under Athanasius Kircher, and spent most of his career as a professor of Charles University in Prague, where he served for over thirty years as a professor of medicine, eight times as Dean of the medical school and once as Rector in 1662. He was also the personal doctor of Emperors Ferdinand III, Holy Roman Emperor, Ferdinand III and Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, Leopold I, and distinguished himself in the defense of Prague against the Sweden, Swedish armies in 1648. In October 1654 he was given t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanškroun
Lanškroun (; ) is a town in Ústí nad Orlicí District in the Pardubice Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 9,800 inhabitants. It lies on the border of the historical lands of Bohemia and Moravia. The historic town centre is well preserved and is protected as an Cultural monument (Czech Republic)#Monument zones, urban monument zone. Administrative division Lanškroun consists of four municipal parts (in brackets population according to the 2021 census): *Lanškroun-Vnitřní Město (488) *Ostrovské Předměstí (2,670) *Žichlínské Předměstí (5,437) *Dolní Třešňovec (875) Etymology The original historic name of Lanškroun was ''Landeskrone'', meaning "Land's crown". It referred to its location on the border of the historical lands of Bohemia and Moravia. Geography Lanškroun is located about northeast of Ústí nad Orlicí and east of Pardubice. It lies in the Orlické Foothills. The highest point is at above sea level. The stream Třešňovský potok flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic country by both area and population, and is the List of European countries by area, fifth-largest country in Europe. Its capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a population of 10.6 million, and a low population density of ; 88% of Swedes reside in urban areas. They are mostly in the central and southern half of the country. Sweden's urban areas together cover 1.5% of its land area. Sweden has a diverse Climate of Sweden, climate owing to the length of the country, which ranges from 55th parallel north, 55°N to 69th parallel north, 69°N. Sweden has been inhabited since Prehistoric Sweden, prehistoric times around 12,000 BC. The inhabitants emerged as the Geats () and Swedes (tribe), Swedes (), who formed part of the sea-faring peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linda Hall Library
The Linda Hall Library is a privately endowed American library of science, engineering and technology located in Kansas City, Missouri, on the grounds of a urban arboretum. It claims to be the "largest independently funded public library of science, engineering and technology in North America" and "among the largest science libraries in the world." Description Established in 1946 through the philanthropy of Linda and Herbert F. Hall of the Hall-Bartlett Grain Co., the library is open to the public, and invites individual researchers, academic institutions, and companies from Kansas City and around the world to use the library's research-level collection. Its mission is to act as "guardian of the collective intellectual heritage with regard to the science, technology, and engineering disciplines." The library's William N. Deramus III Cosmology Theater, temporarily closed since 2020, shows images of the cosmos from the Hubble Space Telescope and NASA science missions. These imag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilfrid Voynich
Wilfrid Voynich (born Michał Habdank-Wojnicz; Деятели революционного движения в России: Био-библиографический словарь: От предшественников декабристов до падения царизма: � 5 т. - М.: Изд-во Всесоюзного общества политических каторжан и ссыльно-поселенцев, 1927-1934Entry on Voynich – 19 March 1930) was a Polish revolutionary, antiquarian and bibliophile. Voynich operated one of the largest rare book businesses in the world. He is remembered as the eponym of the Voynich manuscript. Life Michał Habdank-Wojnicz was born in the town of Telšiai in present-day Lithuania, then part of the Russian Empire, into a Polish noble family. The " Habdank" part of his surname is the name of a Polish heraldic clan. He was the son of a Polish petty official ( titular counsellor). He attended a ''gimnazjum'' in Suwałki ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Baresch
Georg Baresch, (15851662), was a Bohemian antique collector and alchemist from Prague known for his connection to the Voynich manuscript. Biography Baresch received his baccalaureate in 1602. He studied at the Jesuit College of Clementinum. Connection with the Voynich Manuscript Georg Baresch was the earliest confirmed owner of the Voynich manuscript. He was apparently just as puzzled as modern cryptologists about this "Sphinx" that had been in his library for many years. On learning that Athanasius Kircher, a Jesuit scholar from the Collegio Romano, had published a Coptic dictionary and "deciphered" Egyptian hieroglyphs, he sent a sample copy of the script to Kircher in Rome, asking for clues. His 1639 letter to Kircher, recently located by Rene Zandbergen, is the earliest known mention of the manuscript. In 1637, Baresch wrote his first letter to Kircher, and from his later reference to it we may conclude that he was familiar with Kircher's '' Prodromus Coptus'', which a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl B
Carl may refer to: *Carl, Georgia, city in USA *Carl, West Virginia, an unincorporated community *Carl (name), includes info about the name, variations of the name, and a list of people with the name *Carl², a TV series * "Carl", an episode of television series ''Aqua Teen Hunger Force'' * An informal nickname for a student or alum of Carleton College CARL may refer to: *Canadian Association of Research Libraries *Colorado Alliance of Research Libraries See also *Carle (other) *Charles *Carle, a surname *Karl (other) *Karle (other) Karle may refer to: Places * Karle (Svitavy District), a municipality and village in the Czech Republic * Karli, India, a town in Maharashtra, India ** Karla Caves, a complex of Buddhist cave shrines * Karle, Belgaum, a settlement in Belgaum ... {{disambig ja:カール zh:卡尔 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard S
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic language">Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include " Richie", " Dick", " Dickon", " Dickie", " Rich", " Rick", "Rico (name), Rico", " Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English (the name was introduced into England by the Normans), German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Portuguese and Spanish "Ricardo" and the Italian "Riccardo" (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Ander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment that followed. His book (''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy''), first published in 1687, achieved the Unification of theories in physics#Unification of gravity and astronomy, first great unification in physics and established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and Leibniz–Newton calculus controversy, shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for formulating calculus, infinitesimal calculus, though he developed calculus years before Leibniz. Newton contributed to and refined the scientific method, and his work is considered the most influential in bringing forth modern science. In the , Newton formulated the Newton's laws of motion, laws of motion and Newton's law of universal g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
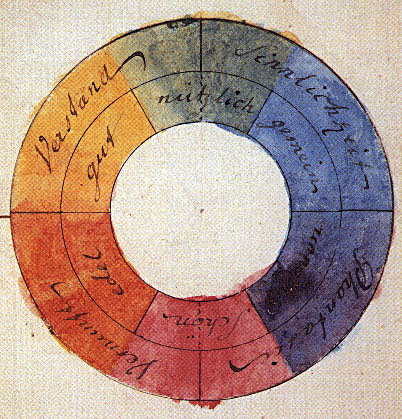
Color Theory
Color theory, or more specifically traditional color theory, is a historical body of knowledge describing the behavior of colors, namely in color mixing, color contrast effects, color harmony, color schemes and color symbolism. Modern color theory is generally referred to as color science. While there is no clear distinction in scope, traditional color theory tends to be more subjective and have artistic applications, while color science tends to be more objective and have functional applications, such as in chemistry, astronomy or color reproduction. Color theory dates back at least as far as Aristotle's treatise ''On Colors'' and Bharata_(sage), Bharata's Natya_Shastra, Nāṭya Shāstra. A formalization of "color theory" began in the 18th century, initially within a partisan controversy over Isaac Newton's theory of color (''Opticks'', 1704) and the nature of primary colors. By the end of the 19th century, a schism had formed between traditional color theory and color science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesuit
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rome. It was founded in 1540 by Ignatius of Loyola and six companions, with the approval of Pope Paul III. The Society of Jesus is the largest religious order in the Catholic Church and has played significant role in education, charity, humanitarian acts and global policies. The Society of Jesus is engaged in evangelization and apostolic ministry in 112 countries. Jesuits work in education, research, and cultural pursuits. They also conduct retreats, minister in hospitals and parishes, sponsor direct social and humanitarian works, and promote Ecumenism, ecumenical dialogue. The Society of Jesus is consecrated under the patron saint, patronage of Madonna della Strada, a title of the Blessed Virgin Mary, and it is led by a Superior General of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, recognising excellence in science, supporting outstanding science, providing scientific advice for policy, education and public engagement and fostering international and global co-operation. Founded on 28 November 1660, it was granted a royal charter by Charles II of England, King Charles II and is the oldest continuously existing scientific academy in the world. The society is governed by its Council, which is chaired by the society's president, according to a set of statutes and standing orders. The members of Council and the president are elected from and by its Fellows, the basic members of the society, who are themselves elected by existing Fellows. , there are about 1,700 fellows, allowed to use the postnominal title FRS (Fellow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |