|
Jan Czyński
Jan Kazimierz Czyński (1801–1867) was a Polish independence activist, lawyer by education, writer and publicist, fighter for the Jewish emancipation, emancipation of the Jews, trade supporter, utopian socialist, and Polish Jacobins, radical democrat. He went into exile after the Russian government issued a bounty for his capture. Czyński was one of the most vocal supporters of the Uprising and founded the first daily newspaper in Lublin, ''Kurier Lubelski.'' In his later life, he moved to Paris, France, where he was an advocate for Polish emigrants. Czyński served on the Polish National Committee. He authored multiple publications and edited several newspapers. Biography He was born on 20 January 1801 in Warsaw, partitions of Poland, Prussian partition of Poland, South Prussia province of the Kingdom of Prussia, in a Polish Jewish family of Frankists (Judaism), Frankists (Jews who converted to Roman Catholicism). After finishing his studies at the University of Warsaw, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
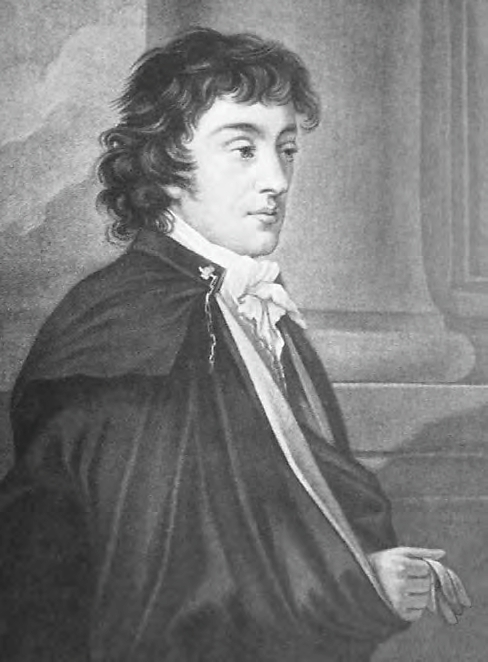
Jan Czyński, Portrait
Jan, JaN or JAN may refer to: Acronyms * Jackson, Mississippi (Amtrak station), US, Amtrak station code JAN * Jackson-Evers International Airport, Mississippi, US, IATA code * Jabhat al-Nusra (JaN), a Syrian militant group * Japanese Article Number, a barcode standard compatible with EAN * Japanese Accepted Name, a Japanese nonproprietary drug name * Job Accommodation Network, US, for people with disabilities * ''Joint Army-Navy'', US standards for electronic color codes, etc. * ''Journal of Advanced Nursing'' Personal name * Jan (name), male variant of ''John'', female shortened form of ''Janet'' and ''Janice'' * Jan (Persian name), Persian word meaning 'life', 'soul', 'dear'; also used as a name * Ran (surname), romanized from Mandarin as Jan in Wade–Giles * Ján, Slovak name Other uses * January, as an abbreviation for the first month of the year in the Gregorian calendar * Jan (cards), a term in some card games when a player loses without taking any tricks or scoring a minim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daily Newspaper
A newspaper is a Periodical literature, periodical publication containing written News, information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background. Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as politics, business, sports, art, and science. They often include materials such as opinion columns, weather forecasts, reviews of local services, Obituary, obituaries, birth notices, crosswords, editorial cartoons, comic strips, and advice columns. Most newspapers are businesses, and they pay their expenses with a mixture of Subscription business model, subscription revenue, Newsagent's shop, newsstand sales, and advertising revenue. The journalism organizations that publish newspapers are themselves often Metonymy, metonymically called newspapers. Newspapers have traditionally been published Printing, in print (usually on cheap, low-grade paper called newsprint). However, today most newspapers are also Electronic publishing, published on webs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Mickiewicz
Adam Bernard Mickiewicz (24 December 179826 November 1855) was a Polish poet, dramatist, essayist, publicist, translator and political activist. He is regarded as national poet in Poland, Lithuania and Belarus. He also largely influenced Ukrainian literature. A principal figure in Polish Romanticism, he is one of Poland's " Three Bards" () and is widely regarded as Poland's greatest poet. He is also considered one of the greatest Slavic and European poets and has been dubbed a "Slavic bard". A leading Romantic dramatist, he has been compared in Poland and Europe to Byron and Goethe. He is known chiefly for the poetic drama '' Dziady'' (''Forefathers' Eve'') and the national epic poem '' Pan Tadeusz''. His other influential works include '' Konrad Wallenrod'' and '' Grażyna''. All these served as inspiration for uprisings against the three imperial powers that had partitioned the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth out of existence. Mickiewicz was born in the Russian-parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messianism
Messianism is the belief in the advent of a messiah who acts as the savior of a group of people. Some religions also have messianism-related concepts. Religions with a messiah concept include Hinduism (Kalki), Judaism ( Mashiach), Christianity (Christ), Islam (Mahdi and Isa Masih), Druze faith ( Hamza ibn Ali), Zoroastrianism ( Saoshyant), Buddhism (Maitreya), Taoism ( Li Hong), and Bábism ( He whom God shall make manifest). In Judaism, the messiah will be a future Jewish king from the line of David and redeemer of the Jewish people and humanity. In Christianity, Jesus is the messiah, the savior, the redeemer, and God. In Islam, Jesus was a prophet and the messiah of the Jewish people who will return in the end times. Abrahamic religions Judaism Messiah (; ''mashiah'', ''moshiah'', ''mashiach'', or ''moshiach'', ("anointed ne) is a term used in the Hebrew Bible to describe priests and kings, who were traditionally anointed. For example, Cyrus the Great, the King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Jerzy Czartoryski
Adam Jerzy Czartoryski (14 January 1770 – 15 July 1861), also known as Adam George Czartoryski, was a Polish szlachta, nobleman, statesman, diplomat and author who served as Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Russian SFSR, Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire. The son of a wealthy prince, he began his political career as a foreign minister to Emperor Alexander I of Russia after Poland was Partitions of Poland, partitioned by Russia, Prussia and Austria. He later became a leader of the Polish government in exile during and after the failed November Uprising (1830–1831) and a bitter opponent of Alexander's successor, Nicholas I of Russia, Nicholas I. In exile, he advocated for the reestablishment of a sovereign Polish state, which also stimulated early Balkan and Belgium, Belgian nationalism, and intensified their desire for independence. Czartoryski was a dedicated patron of arts and greatly contributed to the Czartoryski Museum, Czartorys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Democratic Society
The Polish Democratic Society ( or TDP) was a radical constitutionalist political organization established in Paris by émigrés from the Kingdom of Poland in 1832. While not explicitly socialist with respect to their political program, the Democratic Society nonetheless was influenced by French Utopian socialist thinking of the era and advocated the right of citizens to own land or other means of production. The Polish Democratic Society continued in existence into the decade of the 1840s, when it was a leading voice for revolution in Galicia. It is recognized as a forerunner of the Polish socialist movement which culminated in the establishment of the Polish Socialist Party. Organizational history Establishment The Polish Democratic Society (TDP) was established in the Kingdom of Poland in March 1832.M.K. Dziewanowski, ''The Communist Party of Poland.'' Second edition. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1976; pg. 3. The first program of the TDP, a so-called "Small Mani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish National Committee (1831-1832)
{{Disambig ...
Polish National Committee (''Komitet Narodowy Polski'') can refer to several Polish organizations: ;Historical: *Polish National Committee (1831–1832) in Paris *Polish National Committee (1848) during the Spring of Nations *Polish National Committee (1834–1838) in the United States *Polish National Committee (1914–1917) pro-Russian *Polish National Committee (1917–1919) in Paris ;Modern: *Polish National Committee (2004), minor political coalition See also *Polish Committee of National Liberation The Polish Committee of National Liberation ( Polish: ''Polski Komitet Wyzwolenia Narodowego'', ''PKWN''), also known as the Lublin Committee, was an executive governing authority established by the Soviet-backed communists in Poland at the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joachim Lelewel
Joachim Lelewel (22 March 1786 – 29 May 1861) was a Polish historian, geographer, bibliographer, polyglot and politician. Life Born in Warsaw to a Polonized Prussian family, Lelewel was educated at the Imperial University of Vilna, where in 1814 he became a lecturer in history, with a brief sojourn at Warsaw, 1818–1821, where he joined the Warsaw Society of Friends of Learning. His lectures on Polish history created great enthusiasm, as shown in some lines addressed to him by Adam Mickiewicz that led to Lelewel's removal by the Russians in 1824. Five years later, Lelewel returned to Warsaw, where he was elected a deputy to the Sejm of Congress Poland. He joined the November 1830 Uprising with more enthusiasm than energy, though Tsar Nicholas I identified him as one of the most dangerous rebels. He is considered the author of the motto: "For our freedom and yours". On the suppression of the rebellion, Lelewel made his way in disguise to Germany and subsequently reached Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utopian Socialism
Utopian socialism is the term often used to describe the first current of modern socialism and socialist thought as exemplified by the work of Henri de Saint-Simon, Charles Fourier, Étienne Cabet, and Robert Owen. Utopian socialism is often described as the presentation of visions and outlines for imaginary or futuristic ideal and socialist societies that pursue ideals of positive inter-personal relationships separate from capitalist mechanisms. However, later socialists such as the Marxists and the critics of socialism both disparaged utopian socialism as not being grounded in actual material conditions of existing society. Utopian socialist visions of ideal societies compete with Revolutionary socialism, revolutionary and social democratic movements. Later socialists have applied the term ''utopian socialism'' to socialists who lived in the first quarter of the 19th century. They used the term as a pejorative in order to dismiss the ideas of the earlier thinkers as fanciful a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Fourier
François Marie Charles Fourier (; ; 7 April 1772 – 10 October 1837) was a French philosopher, an influential early socialist thinker, and one of the founders of utopian socialism. Some of his views, held to be radical in his lifetime, have become mainstream in modern society. For instance, Fourier is credited with having originated the word ''feminism'' in 1837. Fourier's social views and proposals inspired a whole movement of intentional communities. Among them in the United States were the community of Utopia, Ohio; La Reunion near present-day Dallas, Texas; Lake Zurich, Illinois; the North American Phalanx in Red Bank, New Jersey; Brook Farm in West Roxbury, Massachusetts; the Community Place and Sodus Bay Phalanx in New York State; Silkville, Kansas, and several others. In Guise, France, he influenced the . Fourier later inspired a diverse array of revolutionary thinkers and writers. Life Fourier was born in Besançon, France, on 7 April 1772. Serenyi 1967, p. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Emigration
The Great Emigration () was the emigration of thousands of Poles and Lithuanians, particularly from the political and cultural élites, from 1831 to 1870, after the failure of the November Uprising of 1830–1831 and of other uprisings such as the Kraków uprising of 1846 and the January Uprising of 1863–1864. The emigration affected almost the entirety of political elite in Congress Poland. The exiles included artists, soldiers and officers of the uprising, members of the Sejm of Congress Poland of 1830–1831 and several prisoners-of-war who escaped from captivity. Polish emigration after the partitions From the end of the 18th century, a large portion of the Polish political landscape was dominated by those who carried out their activities outside of the country as émigrés. Their exile was the result of the Partitions of Poland, which completely divided the lands of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth between the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia and the Hab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, History of Berlin, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. Prussia formed the German Empire when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by 1932 Prussian coup d'état, an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by Abolition of Prussia, an Allied decree in 1947. The name ''Prussia'' derives from the Old Prussians who were conquered by the Teutonic Knightsan organized Catholic medieval Military order (religious society), military order of Pru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |