|
James Inman
James Inman (1776–1859), an English mathematician and astronomer, was professor of mathematics at the Royal Naval College, Portsmouth, and author of ''Inman's Nautical Tables''. Early years Inman was born at Tod Hole in Garsdale, then in the West Riding of Yorkshire, the younger son of Richard Inman and Jane Hutchinson. He was educated at Sedbergh and St John's College, Cambridge, graduating as first Smith's prizeman and Senior Wrangler for 1800. Among his close college friends was Henry Martyn. After graduating with first class honours in 1800, Inman intended to undertake missionary work in the Middle East, in Syria, but due to a declaration of war could travel no further than Malta, where he continued to study Arabic. Astronomer for Matthew Flinders, 1803–04 Returning to England, the Board of Longitude appointed him as replacement astronomer (the original astronomer, suffering from severe seasickness, was discharged en route to Australia) on the expedition of under M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. Astronomers observe astronomical objects, such as stars, planets, natural satellite, moons, comets and galaxy, galaxies – in either observational astronomy, observational (by analyzing the data) or theoretical astronomy. Examples of topics or fields astronomers study include planetary science, Sun, solar astronomy, the Star formation, origin or stellar evolution, evolution of stars, or the galaxy formation and evolution, formation of galaxies. A related but distinct subject is physical cosmology, which studies the Universe as a whole. Types Astronomers typically fall under either of two main types: observational astronomy, observational and theoretical astronomy, theoretical. Observational astronomers make direct observations of Astronomical object, celestial objects and analyze the data. In contrast, theoretical astronomers create and investigate Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warley (1796 Ship)
Warley may refer to: Places in the United Kingdom * Warley, Essex, a suburb of Brentwood * Warley, West Midlands, a neighbourhood centred on the towns of Oldbury and Smethwick **Warley (UK Parliament constituency), a current constituency **County Borough of Warley, a former district * Warley Town, West Yorkshire Schools * Warley College, a former college of further and higher education in the West Midlands of England * Warley High School, a former comprehensive school in the West Midlands Ships * HMS ''Calcutta'', the East Indiaman ''Warley'', built in 1788 and sold to the Royal Navy in 1795 * ''Warley'' (1796 ship), an East Indiaman, launched in 1795, participated in Nathaniel Dance's victory at the Battle of Pulo Aura People * Warley (footballer, born 1978), Brazilian football forward Warley Silva dos Santos * Warley (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian football wing-back Warley Leandro da Silva * Warley Oliveira (born 1989), Brazilian football forward * Ben Warley (1936–2002) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All Saints' Church, Oakham
All Saints' Church, Oakham is a parish church in the Church of England in Oakham, Rutland. It is Grade I listed. History The spire of Oakham parish church dominates distant views of the town for several miles in all directions. The impressive west tower and spire, built during the 14th century in the Decorated Period, Decorated Gothic style, are slightly earlier in date than most of the rest of the exterior of the building, which (apart from some Victorian restoration) is in the Perpendicular Period, Perpendicular style. Oddly, the south doorway and its porch seem to be the oldest parts of the church, the doorway probably dating from the early 13th century with the porch having been added later that century. In the light, spacious interior there is more evidence of the mature Decorated style of the 14th century. The tall, slender columns of the nave have intricately carved capital (architecture), capitals showing animals, birds, figures, foliage and scenes from the Bible in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Astronomical Society
The Royal Astronomical Society (RAS) is a learned society and charitable organisation, charity that encourages and promotes the study of astronomy, planetary science, solar-system science, geophysics and closely related branches of science. Its headquarters are in Burlington House, on Piccadilly in London. The society has over 4,000 members, known as fellows, most of whom are professional researchers or postgraduate students. Around a quarter of Fellows live outside the UK. The society holds monthly scientific meetings in London, and the annual National Astronomy Meeting at varying locations in the British Isles. The RAS publishes the scientific journals ''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'', ''Geophysical Journal International'' and ''RAS Techniques and Instruments'', along with the trade magazine ''Astronomy & Geophysics''. The RAS maintains an astronomy research library, engages in public outreach and advises the UK government on astronomy education. The socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
School Of Naval Architecture
A school is the educational institution (and, in the case of in-person learning, the building) designed to provide learning environments for the teaching of students, usually under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes compulsory. In these systems, students progress through a series of schools that can be built and operated by both government and private organization. The names for these schools vary by country (discussed in the '' Regional terms'' section below) but generally include primary school for young children and secondary school for teenagers who have completed primary education. An institution where higher education is taught is commonly called a university college or university. In addition to these core schools, students in a given country may also attend schools before and after primary (elementary in the U.S.) and secondary (middle school in the U.S.) education. Kindergarten or preschool provide some sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Admiralty
The Admiralty was a Departments of the Government of the United Kingdom, department of the Government of the United Kingdom that was responsible for the command of the Royal Navy. Historically, its titular head was the Lord High Admiral of the United Kingdom, Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of its history, from the early Admiralty in the 18th century, 18th century until its abolition, the role of the Lord High Admiral was almost invariably put "in commission" and exercised by the Lords Commissioner of the Admiralty, who sat on the governing Board of Admiralty, rather than by a single person. The Admiralty was replaced by the Admiralty Board (United Kingdom), Admiralty Board in 1964, as part of the reforms that created the Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), Ministry of Defence and its Navy Department (Ministry of Defence), Navy Department (later Navy Command (Ministry of Defence), Navy Command). Before the Acts of Union 1707, the Office of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haversine Formula
The haversine formula determines the great-circle distance between two points on a sphere given their longitudes and latitudes. Important in navigation, it is a special case of a more general formula in spherical trigonometry, the law of haversines, that relates the sides and angles of spherical triangles. The first table of haversines in English was published by James Andrew in 1805, but Florian Cajori credits an earlier use by José de Mendoza y Ríos in 1801. (NB. ISBN and link for reprint of second edition by Cosimo, Inc., New York, 2013.) The term ''haversine'' was coined in 1835 by James Inman. (Fourth edition) These names follow from the fact that they are customarily written in terms of the haversine function, given by . The formulas could equally be written in terms of any multiple of the haversine, such as the older versine function (twice the haversine). Prior to the advent of computers, the elimination of division and multiplication by factors of two proved convenient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
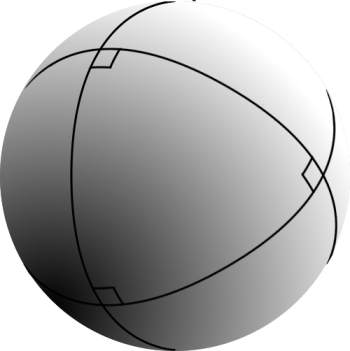
Spherical Trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the edge (geometry), sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, geodesics are great circles. Spherical trigonometry is of great importance for calculations in astronomy, geodesy, and navigation. The origins of spherical trigonometry in Greek mathematics and the major developments in Islamic mathematics are discussed fully in History of trigonometry and Mathematics in medieval Islam. The subject came to fruition in Early Modern times with important developments by John Napier, Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre, Delambre and others, and attained an essentially complete form by the end of the nineteenth century with the publication of Todhunter's textbook ''Spherical trigonometry for the use of colleges and Schools''. Since then, significant developments have been the application of vector methods, quaternion m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haversine
The versine or versed sine is a trigonometric function found in some of the earliest (Sanskrit ''Aryabhatia'', Section I) trigonometric tables. The versine of an angle is 1 minus its . There are several related functions, most notably the coversine and haversine. The latter, half a versine, is of particular importance in the haversine formula of navigation. Overview The versine[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Tables
Mathematical tables are lists of numbers showing the results of a calculation with varying arguments. Trigonometric tables were used in ancient Greece and India for applications to astronomy and celestial navigation, and continued to be widely used until electronic calculators became cheap and plentiful in the 1970s, in order to simplify and drastically speed up computation. Tables of logarithms and trigonometric functions were common in math and science textbooks, and specialized tables were published for numerous applications. History and use The first tables of trigonometric functions known to be made were by Hipparchus (c.190 – c.120 BCE) and Menelaus (c.70–140 CE), but both have been lost. Along with the surviving table of Ptolemy (c. 90 – c.168 CE), they were all tables of chords and not of half-chords, that is, the sine function. The table produced by the Indian mathematician Āryabhaṭa (476–550 CE) is considered the first sine table ever constructed. � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Naval College (Portsmouth)
The Royal Naval Academy was a facility established in 1733 in Portsmouth Dockyard to train officers for the Royal Navy. The founders' intentions were to provide an alternative means to recruit officers and to provide standardised training, education and admission. In 1806 it was renamed the Royal Naval College and in 1816 became the Royal Naval College and the School for Naval Architecture. It was closed as a training establishment for officer entrants in 1837. Training In 1733, a shoreside facility was established in the dockyard for 40 recruits. A comprehensive syllabus provided theoretical and practical experience in the dockyard and at sea. Graduates of the Academy could earn two years of sea time as part of their studies, and would be able to take the lieutenant's examination after four years at sea instead of six. The Academy did not, however, achieve the objective of becoming the preferred path to becoming a naval officer; the traditional means of a sea-going "apprentices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |