|
James Flint (merchant)
James Flint (Chinese name: 洪任輝, ''Hóng Rènhuī'', 1720 – unknown) was a British merchant and diplomat employed by the East India Company and noted for his role in precipitating the Canton System of Chinese trade with the West. One of the first English people to learn the Chinese language, Flint broke Qing dynasty court protocol through a direct complaint to the Qianlong Emperor, which led to three years of detention in the Portuguese colony of Macau. In later life, he was jointly responsible for the introduction of the soybean to North America. Biography Early life Left in China as a teenage boy by Captain Rigby of the East India Company, Honourable East India Company ship ''Normanton'' in 1736, Flint grew to adulthood speaking Mandarin Chinese. For reasons unknown, he adopted or was given the Chinese name Hóng Rènhuī (洪任辉) and in 1739 departed for Bombay and other East India Company run locations. Three years later he returned to China to continue his language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Name
Chinese may refer to: * Something related to China * Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity **Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China. **'' Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation ** List of ethnic groups in China, people of various ethnicities in contemporary China ** Ethnic minorities in China, people of non-Han Chinese ethnicities in modern China ** Ethnic groups in Chinese history, people of various ethnicities in historical China ** Nationals of the People's Republic of China ** Nationals of the Republic of China ** Overseas Chinese, Chinese people residing outside the territories of mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan * Sinitic languages, the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family ** Chinese language, a group of related languages spoken predominantly in China, sharing a written script (Chinese characters in traditional and simplified forms) *** Standar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Culture Of The People's Republic Of China
The Ministry of Culture (MOC) was a ministry of the government of the People's Republic of China which was dissolved on 19 March 2018. The responsibilities of the MOC, which were assumed by the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, encompassed cultural policy and activities in the country, including managing national museums and monuments; promoting and protecting the arts (including censorship of visual, folk, theatrical, musical, dance, architectural, literary, televisual and cinematographic works); and managing the national archives and regional culture centers. Its headquarters were in Chaoyang District, Beijing. History The ministry was dissolved on 19 March 2018 and replaced by the Ministry of Culture and Tourism as part of the deepening the reform of the Party and state institutions. Duties In 1955, the Ministry of Culture sought to develop rural cultural networks to distribute media like other performances, lantern slides, books, cinema, radio, books, and to establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macartney Embassy
The Macartney Embassy ( zh, t=馬加爾尼使團), also called the Macartney Mission, was the first British diplomatic mission to China, which took place in 1793. It is named for its leader, George Macartney, Great Britain's first envoy to China. The goals of the mission included the opening of new ports for British trade in China, the establishment of a permanent embassy in Beijing, the cession of a small island for British use along China's coast, and the relaxation of trade restrictions on British merchants in Guangzhou (Canton). Macartney's delegation met with the Qianlong Emperor, who rejected all of the mission's requests. Although the mission failed to achieve its official objectives, it was later noted for the extensive cultural, political, and geographical observations its participants recorded in China and brought back to Europe. It came to light in 1796 that a Chinese court official, Heshen, was embezzling state funds and frustrated the mission. Background Foreign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jakarta
Jakarta (; , Betawi language, Betawi: ''Jakartè''), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta (; ''DKI Jakarta'') and formerly known as Batavia, Dutch East Indies, Batavia until 1949, is the capital and largest city of Indonesia and an autonomous region at the provincial level. Lying on the northwest coast of Java, the world's List of islands by population, most populous island, Jakarta is the List of cities in ASEAN by population, largest metropole in Southeast Asia and serves as the diplomatic capital of ASEAN. The Special Region has a status equivalent to that of a Provinces of Indonesia, province and is bordered by two other provinces: West Java to the south and east; and Banten to the west. Its coastline faces the Java Sea to the north, and it shares a maritime border with Lampung to the west. Jakarta metropolitan area, Jakarta's metropolitan area is List of ASEAN country subdivisions by GDP, ASEAN's second largest economy after Singapore. In 2023, the city's Gros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fujian
Fujian is a provinces of China, province in East China, southeastern China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its capital is Fuzhou and its largest prefecture city by population is Quanzhou, with other notable cities including the port city of Xiamen and Zhangzhou. Fujian is located on the west coast of the Taiwan Strait as the closest province geographically and culturally to Taiwan; as a result of the Chinese Civil War, a small portion of historical Fujian is administered by Taiwan, romanized as Fuchien Province, Republic of China, Fuchien. While the population predominantly identifies as Han Chinese, Han, it is one of China's most culturally and linguistically diverse provinces. The dialects of the language group Min Chinese are most commonly spoken within the province, including the Fuzhou dialect and Eastern Min of Northeastern Fujian province and various Southern Min and Hokkien dial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuan
Sichuan is a province in Southwestern China, occupying the Sichuan Basin and Tibetan Plateau—between the Jinsha River to the west, the Daba Mountains to the north, and the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau to the south. Its capital city is Chengdu, and its population stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors Qinghai and Gansu to the north, Shaanxi and Chongqing to the east, Guizhou and Yunnan to the south, and Tibet to the west. During antiquity, Sichuan was home to the kingdoms of Ba and Shu until their incorporation by the Qin. During the Three Kingdoms era (220–280), Liu Bei's state of Shu was based in Sichuan. The area was devastated in the 17th century by Zhang Xianzhong's rebellion and the area's subsequent Manchu conquest, but recovered to become one of China's most productive areas by the 19th century. During World War II, Chongqing served as the temporary capital of the Republic of China, and was heavily bombed. It was one of the last mainland areas captured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroy Of Zhili
The Viceroy of Zhili, officially in Chinese as the Governor-General of the Directly Subordinate Province and Other Local Areas, in Charge of Military Affairs, Food and Wages, Management of Rivers and Governor Affairs, was one of eight regional Viceroys in China#Qing dynasty, Viceroys during the Qing dynasty. The Viceroy of Zhili had jurisdiction of military, civil, and political affairs over then Zhili, Zhili Province (nowadays approx. Hebei, Beijing suburban, Tianjin). The Governor's Office sat in then Zhili Province's Baoding Prefecture City (nowadays Baoding, Baoding City's Lianchi District). The Viceroy of Zhili was an important post because the province of Zhili, which literally means "directly ruled," was the area surrounding the imperial capital, Beijing. The administrative centre was in Tianjin even though the provincial capital was in Baoding. The Viceroy's duties as well as responsibilities have never been defined entirely. Generally speaking, the Viceroy oversaw the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroy Of Liangguang
The Viceroy of Liangguang, fully in Chinese as the Governor-General of Two Guang Provinces and Other Local Areas, in Charge of Military Affairs, Food and Wages and Governor Affairs, was one of eight regional Viceroys during the Ming and Qing dynasties of China. The Viceroy of Liangguang had jurisdiction of military, civil, and political affairs over then Guangdong Province and then Guangxi Province (approx. nowadays Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Hong Kong, and Macau). History Ming dynasty The office of the Viceroy of Liangguang originated in 1452 during the Ming dynasty. The Jingtai Emperor accepted Yu Qian's proposal to create the office and appointed Wang Ao (王翱) as the first viceroy. In 1465, the Chenghua Emperor appointed Han Yong (韓雍) as Left Censor-in-Chief and Viceroy of Liangguang. The office was formalised in 1469, with the administrative headquarters fixed in Wuzhou, Guangxi. In 1536, during the reign of the Jiajing Emperor, the viceroy Qian Rujing (錢� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoppo (Qing Dynasty Official)
Hoppo or Administrator of the Canton Customs ( zh, t=粵海關部, s=粤海关部, p=Yuèhǎi Guānbù), was the Qing dynasty official at Guangzhou (Canton) given responsibility by the emperor for controlling shipping, collecting tariffs, and maintaining order among traders in and around the Pearl River Delta from 1685 to 1904. Initially, the Hoppo was always a Manchu and a bondservant of the imperial family, appointed personally by the emperor, not a scholar-official chosen through the exams, but after the mid-18th century this expectation was relaxed. Since he depended on the good will of emperor and the Imperial Household Department, the Hoppo could be trusted to send revenues directly to the court rather than through the normal bureaucratic channels. In the mid-18th century the Qianlong emperor approved the Canton system, which restricted the burgeoning overseas trade with Europeans to Canton and granted a monopoly on that trade to Chinese merchants, who formed the Thirteen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianjin
Tianjin is a direct-administered municipality in North China, northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the National Central City, nine national central cities, with a total population of 13,866,009 inhabitants at the time of the 2020 Chinese census. Its metropolitan area, which is made up of 12 central districts (other than Baodi District, Baodi, Jizhou District, Tianjin, Jizhou, Jinghai District, Jinghai and Ninghe District, Ninghe), was home to 11,165,706 inhabitants and is also the world's 29th-largest agglomeration (between Chengdu and Rio de Janeiro) and 11th-List of cities proper by population, most populous city proper. Tianjin is governed as one of the four municipalities (alongside Beijing, Shanghai, and Chongqing) under the direct-administered municipalities of China, direct administration of the State Council of the People's Republic of China, State Council of Government of China, China. The city borders Hebei Province and Beijing Municipality, bounded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
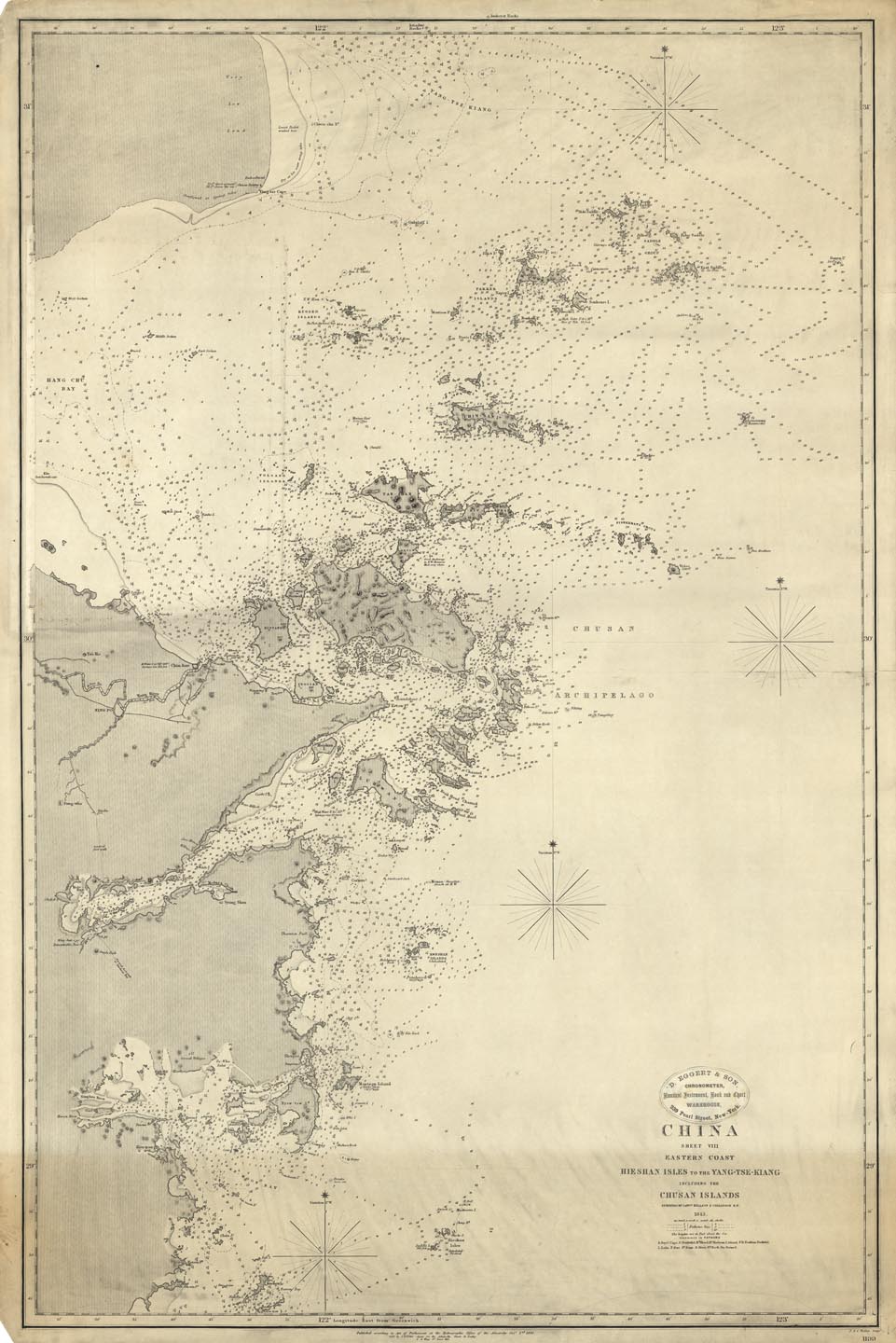
Zhoushan
Zhoushan is an urbanized archipelago with the administrative status of a prefecture-level city in the eastern Chinese province of Zhejiang. It consists of an archipelago of islands at the southern mouth of Hangzhou Bay off the mainland city of Ningbo. The prefecture's city proper is Dinghai on Zhoushan Island, now administered as the prefecture's Dinghai District. During the 2020 census, Zhoushan Prefecture's population was 1,157,817, out of whom 882,932 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of two urban districts of Dinghai and Putuo. On 8 July 2011, the central government approved Zhoushan as Zhoushan Archipelago New Area, a state-level new area. History The archipelago was inhabited 6,000 years ago, during the Neolithic by people of the Hemudu culture. During the Spring and Autumn period, Zhoushan was called Yongdong, referring to its location east of the Yong River. At the time, it belonged to the state of Yue. The fishermen and sailors who inhabit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |