|
Jakar
Jakar () is a town in the central-eastern region of Bhutan. It is the district capital ( dzongkhag thromde) of Bumthang District and the location of Jakar Dzong, the regional dzong fortress. The name Jakar roughly translates as "white bird" in reference to its foundation myth, according to which a roosting white bird signalled the proper and auspicious location to found a monastery around 1549. History The town is the site of Chakhar Lhakhang, a small and unassuming temple which marks the site of the "Iron Palace" of Sindhu Raja, the Indian monarch who is believed to have first invited Guru Rinpoche to Bhutan in 746. The current building is said to have been constructed by Tertön Dorje Lingpa in the 14th century. According to the Jakar foundation myth, a roosting white bird signaled the proper and auspicious location to found a monastery around 1549. The settlement thus earned the moniker Jakar, meaning "white bird." There are many significant Buddhist sacred sites nea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jakar Dzong
Jakar Dzong or Jakar Yugyal Dzong is the ''dzong'' or fortress of the Bumthang District in central Bhutan. It is located on a ridge above Jakar town in the Chamkhar valley of Bumthang. It is built on the site of an earlier temple established by the Ralung hierarch Yongzin Ngagi Wangchuk (1517–1554) when he came to Bhutan. Jakar Dzong may be the largest dzong in Bhutan, with a circumference of more than . The name Jakar is derived from the word ''bjakhab'', meaning "white bird", in reference to Jakar's foundation myth, according to which a roosting white bird signaled the proper and auspicious location to found a monastery. Jakar Dzong, or the ''castle of the white bird',' dominates the Chamkhar valley and overlooks the town. Constructed in 1549, by the Tibetan lama Ngagi Wangchuk, who came to Bhutan to spread the Drukpa Kagyu The Drukpa or Drukpa Kagyu () lineage, sometimes called Dugpa in older sources, is a branch of the Kagyu school of Tibetan Buddhism. The Kagyu school ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
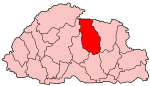
Bumthang District
Bumthang District (Dzongkha: བུམ་ཐང་རྫོང་ཁག་; Wylie: ''Bum-thang rzong-khag'') is one of the 20 dzongkhag (districts) comprising Bhutan. It contains numerous temples and Buddhist sacred sites. The district is divided into four '' gewogs'' (village blocks), each corresponding to a major glacial valley: Choekor, Tang, Ura, and Chhume. The latter valley is also called Bumthang, lending its name to the whole district. ''Bumthang'' directly translates as "beautiful field" – ''thang'' means field or flat place, and ''bum'' is said be an abbreviation of either ''bumpa'' (a vessel for holy water, thus describing the shape and nature of the valley), or simply ''bum'' ("girl", indicating this is the valley of beautiful girls). The name is said to have arisen after the construction of Jambay Lhakhang. Economy Bumthang's primary agricultural products are wheat, buckwheat, dairy, honey, apples, potatoes, rice, and wool. Bumthang is also nationally fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bhutan
Bhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia, in the Eastern Himalayas between China to the north and northwest and India to the south and southeast. With a population of over 727,145 and a territory of , Bhutan ranks List of countries and dependencies by area, 133rd in land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, 160th in population. Bhutan is a Democracy, democratic constitutional monarchy with a King of Bhutan, King as the head of state and a Prime Minister of Bhutan, prime minister as the head of government. The Je Khenpo is the head of the state religion, Vajrayana Buddhism. The Himalayas, Himalayan mountains in the north rise from the country's lush subtropical plains in the south. In the Mountains of Bhutan, Bhutanese Himalayas, there are peaks higher than above sea level. Gangkhar Puensum is Bhutan's highest peak and is the highest unclimbed mountain in the world. The wildlife of Bhutan is notable for its diversi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bumthang Valley
Bumthang Valley is the main inhabited valley in the Bumthang district of Bhutan. History Bumthang is one of the most beautiful and sacred valleys in Bhutan. The main town in the valley is Jakar. Bhutan's only brewery, brewing Red Panda wheat beer, is in Jakar. Bumthang is divided into four '' gewogs'', namely Chhoekhor, Tang, Chhume and Ura. The valley is broad with various habitats including coniferous woodland. The language spoken in Bumthang is known as Bumthang Kha, a Tibeto-Burman language. Each of the four valleys of Bumthang has its own dialect. Jampa Lhakhang The Jampa Lhakhang temple is located in the heart of Jakar Valley, it was built in the early 7th century by the dharma king Songtsen Gempo. He commissioned the creation of 108 temples at the same time to successive circles in order to pin down and evil demoness who was seen to be blocking the spread of Buddhism. This monastery is one of two such temples that survive in Bhutan. the other being Kichu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bathpalathang Airport
Bathpalathang Airport is a domestic Bhutanese airport in Jakar (Bjakar), Bumthang District. One of only four airports in the country, it opened on 17 December 2011 with flights to Paro. The airport suspended operations in July 2012 due to runway damage, but it has since reopened to limited service. Overview The airport was in development from the Royal Bhutanese Government's 10th Five Year Plan (2008). The airport was originally scheduled to open in October 2010, and then delayed to November 2010. By December 2010, operations were pushed back to March 2011, then April 2011. Shortages in the spring prompted a new target date of July 2011, however the airport had not yet opened for operations through late 2011. Airport construction at Bathpalathang met several delays, including soil instability under the runway, funding, labor and material shortages, and nearby river protection and diversion, each of which underpinned the ultimate success of any airport at the site. Despite a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
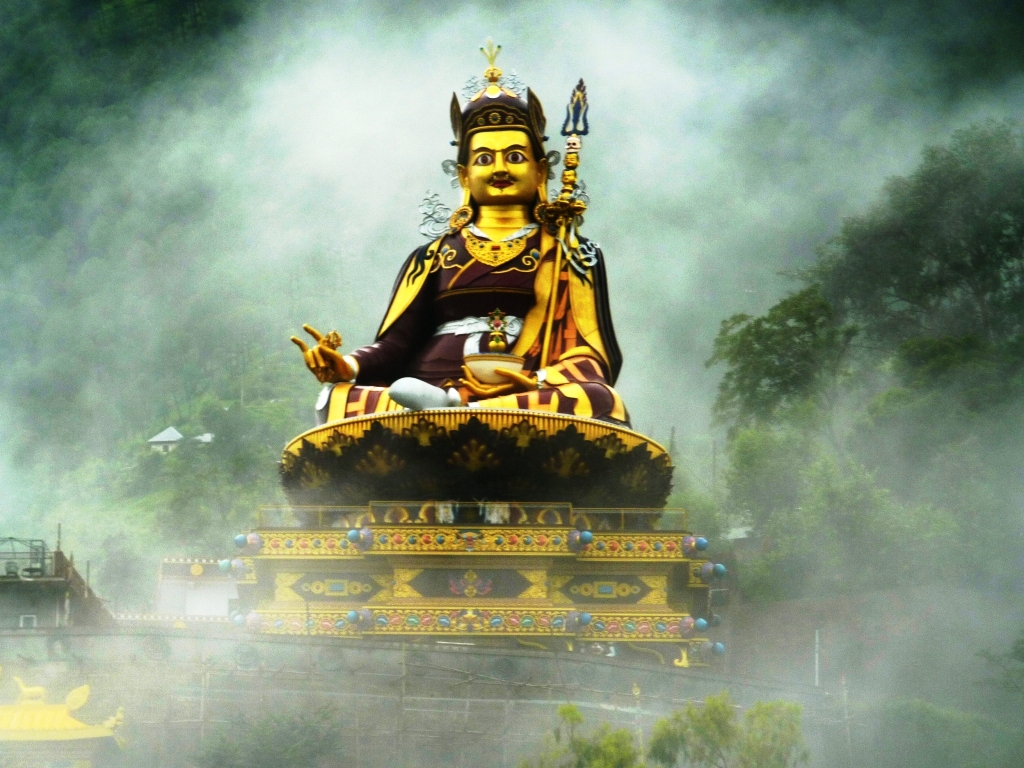
Guru Rinpoche
Padmasambhava ('Born from a Lotus'), also known as Guru Rinpoche ('Precious Guru'), was a legendary tantric Buddhist Vajra master from Oddiyana. who fully revealed the Vajrayana in Tibet, circa 8th – 9th centuries... He is considered an emanation or Nirmāṇakāya of Shakyamuni Buddha as foretold by the Buddha himself. According to early Tibetan sources including the '' Testament of Ba'', he came to Tibet in the 8th century and designed Samye Monastery, the first Buddhist monastery in Tibet during the reign of King Trisong Detsen. He, the king, and Khenpo Shantarakshita are also responsible for creating the Tibetan Canon through translating all of the Buddha's teachings and their commentaries into the Tibetan language. According to Lewis Doney, while his historical authenticity was questioned by earlier Tibetologists, it is now "cautiously accepted.” Padmasambhava himself was recorded as saying he was an historical person, and his footprints left in rocks are evid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thromde
A Thromde (Dzongkha: ཁྲོམ་སྡེ་; Wylie: ''khrom-sde'') is a second-level administrative division in Bhutan. The legal administrative status of thromdes was most recently codified under the Local Government Act of 2009, and the role of thromdes in elections in Bhutan was defined in the Election Act of 2008. Governance Thromde administration is a product of the Bhutanese program of decentralization and devolution of power and authority. Thromdes are administered independently by a Thromde Tshogde if sufficiently developed and populated (Class A Thromdes); or directly by Dzongkhag Administration or the Gewog Administration as decided by the Government (Class B Thromdes and Yenlag Thromdes). From time to time, Parliament decides the boundaries of Thromde in consultation with the National Land Commission Secretariat and local authorities. Each Thromde Tshogde is composed of seven to ten elected members and headed by a Thrompon. Thromde Tshogdes are empowered to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wangchuck Centennial Park
Wangchuck Centennial National Park in northern Bhutan is the kingdom's largest national park, spanning over five districts, occupying significant portions of northern Bumthang, Lhuntse, and Wangdue Phodrang Districts. It borders Tibet to the north and is bound by tributaries of the Wong Chhu (Raidāk) basin to the west. Wangchuck Centennial directly abuts Jigme Dorji National Park, Bumdeling Wildlife Sanctuary, and Phrumsengla National Park in northern Bhutan, and is further connected to Jigme Singye Wangchuck National Park in central Bhutan via biological corridors. Thus, most of northern Bhutan is part of these protected areas. Wangchuck Centennial was established on December 12, 2008 in honor of the Wangchuck dynasty, founded in 1907. It contains headwaters of four major river systems: Punatsang Chhu/Sankosh River, Mangde Chhu, Chamkhar Chhu, and Kuri Chhu. Wangchuck Centennial also contains the various middle-Himalayan ecological biomes, ranging from blue pine forests to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thromde
A Thromde (Dzongkha: ཁྲོམ་སྡེ་; Wylie: ''khrom-sde'') is a second-level administrative division in Bhutan. The legal administrative status of thromdes was most recently codified under the Local Government Act of 2009, and the role of thromdes in elections in Bhutan was defined in the Election Act of 2008. Governance Thromde administration is a product of the Bhutanese program of decentralization and devolution of power and authority. Thromdes are administered independently by a Thromde Tshogde if sufficiently developed and populated (Class A Thromdes); or directly by Dzongkhag Administration or the Gewog Administration as decided by the Government (Class B Thromdes and Yenlag Thromdes). From time to time, Parliament decides the boundaries of Thromde in consultation with the National Land Commission Secretariat and local authorities. Each Thromde Tshogde is composed of seven to ten elected members and headed by a Thrompon. Thromde Tshogdes are empowered to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kuensel
(; ) is the national newspaper of the Kingdom of Bhutan. It was the only local newspaper available in Bhutan until 2006 when two more newspapers were launched. The government of Bhutan owns 51% of while 49% is held by the public. is published in two language editions: Dzongkha (the national language) and English, everyday except Sunday with a total weekly circulation of more than 15,000 copies and an average weekly readership of 130,000. The paper is distributed throughout the country by a string of sales agents appointed in all the dzongkhags, dungkhags and towns, while subscribers overseas are fed through mail service/e-mail. Subscribers also get a PDF version of the paper. History was founded in 1965 and it used to be published by Mani printing press in Kalimpong as an internal government bulletin. Kinley Dorji, who graduated from Columbia University, New York with a master's degree in journalism, served as editor of , and later as both editor-in-chief and manag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Five-Year Plans Of Bhutan
The Five-Year Plans of Bhutan are a series of national economic development plans created by the government of Bhutan since 1961. The government of Bhutan has played a pervasive role in its economy and development. Since 1961 the economy has been guided through development plans, which the Development Secretariat and later the Planning Commission directed, subject to the National Assembly's approval. In the World Bank's 1989 appraisal, "Coming late to the development scene, Bhutan was eager to avoid mistakes committed elsewhere. Although strongly dependent on foreign aid, it was determined to follow its own set of priorities, keep public finance on an even keel, build up a well trained but lean bureaucracy, and prevent environmental damage from overexploitation of the forests or uncontrolled growth of tourism." To help avoid further mistakes, the government used traditional social institutions and involved people at the local level in planning and implementation for their own distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Royal Bhutanese Government
The government of Bhutan has been a constitutional monarchy since 18 July 2008. The King of Bhutan is the head of state. The executive power is exercised by the Lhengye Zhungtshog, or council of ministers, headed by the Prime Minister. Legislative power is vested in the bicameral Parliament, both the upper house, National Council, and the lower house, National Assembly. A royal edict issued on April 22, 2007 lifted the previous ban on political parties in anticipation of the National Assembly elections in the following year. In 2008, Bhutan adopted its first modern Constitution, codifying the institutions of government and the legal framework for a democratic multi-party system. Sovereignty Bhutanese external relations and foreign policies were put under British control following the 1910 Treaty of Punakha. However, due to the policy of self-imposed isolationism, the effect of the treaty was limited to an extent. After Indian independence in 1949, Bhutan and India agreed to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |