|
JCOM América Latina
The International School for Advanced Studies (Italian: ''Scuola Internazionale Superiore di Studi Avanzati''; SISSA) is an international, state-supported, post-graduate-education and research institute in Trieste, Italy. SISSA is active in the fields of mathematics, physics and neuroscience, offering both undergraduate and post-graduate courses. Each year, about 70 PhD students are admitted to SISSA based on their scientific qualifications. SISSA also runs master's programs in the same areas, in collaboration with both Italian and other European universities. History SISSA was founded in 1978, as a part of the reconstruction following the Friuli earthquake of 1976. Although the city of Trieste itself did not suffer any damage, physicist Paolo Budinich asked and obtained from the Italian government to include in the interventions the institution of a new, post-graduate teaching and research institute, modeled on the Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa. The school became operative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, regional decentralization entity of Trieste. Trieste is located at the head of the Gulf of Trieste, on a narrow strip of Italian territory lying between the Adriatic Sea and Slovenia; Slovenia lies close, at approximately east and southeast of the city, while Croatia is about to the south of the city. The city has a long coastline and is surrounded by grassland, forest, and karstic areas. As of 2025, it has a population of 198,668. Trieste belonged, as Triest, to the Habsburg monarchy from 1382 until 1918. In the 19th century, the monarchy was one of the Great Powers of Europe and Trieste was its most important seaport. As a prosperous trading hub in the Mediterranean region, Trieste grew to become the fourth largest city of the Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International School For Advanced Studies 2
International is an adjective (also used as a noun) meaning "between nations". International may also refer to: Music Albums * ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011 * ''International'' (New Order album), 2002 * ''International'' (The Three Degrees album), 1975 *''International'', 2018 album by L'Algérino Songs * The Internationale, the left-wing anthem * "International" (Chase & Status song), 2014 * "International", by Adventures in Stereo from ''Monomania'', 2000 * "International", by Brass Construction from ''Renegades'', 1984 * "International", by Thomas Leer from ''The Scale of Ten'', 1985 * "International", by Kevin Michael from ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011 * "International", by McGuinness Flint from ''McGuinness Flint'', 1970 * "International", by Orchestral Manoeuvres in the Dark from '' Dazzle Ships'', 1983 * "International (Serious)", by Estelle from '' All of Me'', 2012 Politics * Internationalism (politics) * Political international, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confocal Microscopy
Confocal microscopy, most frequently confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) or laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM), is an optical imaging technique for increasing optical resolution and contrast (vision), contrast of a micrograph by means of using a Spatial filter, spatial pinhole to block out-of-focus light in image formation. Capturing multiple two-dimensional images at different depths in a sample enables the reconstruction of three-dimensional structures (a process known as optical sectioning) within an object. This technique is used extensively in the scientific and industrial communities and typical applications are in life sciences, semiconductor inspection and materials science. Light travels through the sample under a conventional microscope as far into the specimen as it can penetrate, while a confocal microscope only focuses a smaller beam of light at one narrow depth level at a time. The CLSM achieves a controlled and highly limited depth of field. Basic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercomputer
A supercomputer is a type of computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS). Since 2022, supercomputers have existed which can perform over 1018 FLOPS, so called Exascale computing, exascale supercomputers. For comparison, a desktop computer has performance in the range of hundreds of gigaFLOPS (1011) to tens of teraFLOPS (1013). Since November 2017, all of the TOP500, world's fastest 500 supercomputers run on Linux-based operating systems. Additional research is being conducted in the United States, the European Union, Taiwan, Japan, and China to build faster, more powerful and technologically superior exascale supercomputers. Supercomputers play an important role in the field of computational science, and are used for a wide range of computationally intensive tasks in various fields, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLOPS
Floating point operations per second (FLOPS, flops or flop/s) is a measure of computer performance in computing, useful in fields of scientific computations that require floating-point calculations. For such cases, it is a more accurate measure than measuring instructions per second. Floating-point arithmetic Floating-point arithmetic is needed for very large or very small real numbers, or computations that require a large dynamic range. Floating-point representation is similar to scientific notation, except computers use base two (with rare exceptions), rather than base ten. The encoding scheme stores the sign, the exponent (in base two for Cray and VAX, base two or ten for IEEE floating point formats, and base 16 for IBM Floating Point Architecture) and the significand (number after the radix point). While several similar formats are in use, the most common is ANSI/IEEE Std. 754-1985. This standard defines the format for 32-bit numbers called ''single precision'', a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tera-
A metric prefix is a unit prefix that precedes a basic unit of measure to indicate a multiple or submultiple of the unit. All metric prefixes used today are decadic. Each prefix has a unique symbol that is prepended to any unit symbol. The prefix '' kilo'', for example, may be added to ''gram'' to indicate ''multiplication'' by one thousand: one kilogram is equal to one thousand grams. The prefix '' milli'', likewise, may be added to ''metre'' to indicate ''division'' by one thousand; one millimetre is equal to one thousandth of a metre. Decimal multiplicative prefixes have been a feature of all forms of the metric system, with six of these dating back to the system's introduction in the 1790s. Metric prefixes have also been used with some non-metric units. The SI prefixes are metric prefixes that were standardised for use in the International System of Units (SI) by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) in resolutions dating from 1960 to 2022. Since 2009, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. Though cells and other microscopic structures had been observed in living organisms as early as the 18th century, a detailed understanding of the mechanisms and interactions governing their behavior did not emerge until the 20th century, when technologies used in physics and chemistry had advanced sufficiently to permit their application in the biological sciences. The term 'molecular biology' was first used in 1945 by the English physicist William Astbury, who described it as an approach focused on discerning the underpinnings of biological phenomena—i.e. uncovering the physical and chemical structures and properties of biological molecules, as well as their interactions with other molecules and how these interactions explain observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Centre For Genetic Engineering And Biotechnology
The International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB) was established as a project of the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) in 1983. The Organisation has three Component laboratories with over 45 ongoing research projects in Infectious and Non-communicable diseases, Medical, Industrial and Plant Biology Biotechnology in: Trieste, Italy, New Delhi, India and Cape Town, South Africa Cape Town is the legislature, legislative capital city, capital of South Africa. It is the country's oldest city and the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. Cape Town is the country's List of municipalities in South Africa, second-largest .... On February 3, 1994, under the direction of Arturo Falaschi the ICGEB became an autonomous International Organisation and now has over 65 Member States across world regions. Its main pillars of action comprise: Research, Advanced Education through PhD and Postdoctoral Fellowships, International Scientific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Journalism
Science journalism conveys reporting about science to the public. The field typically involves interactions between scientists, journalists and the public. Origins Modern science journalism originated in weather and other natural history observations, as well as reports of new scientific findings, reported by almanacs and other news writing in the centuries following the advent of the printing press. One early example dates back to '' Digdarshan'' (means showing the direction), which was an educational monthly magazine that started publication in 1818 from Srirampore, Bengal, India. ''Digdarshan'' carried articles on different aspects of science, such as plants, steam boat, etc. It was available in Bengali, Hindi and English languages. In the U.S., ''Scientific American'' was founded in 1845, in another early example. One of the occasions an article was attributed to a 'scientific correspondent' was "A Gale in the Bay of Biscay" by William Crookes which appeared in ''The Ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
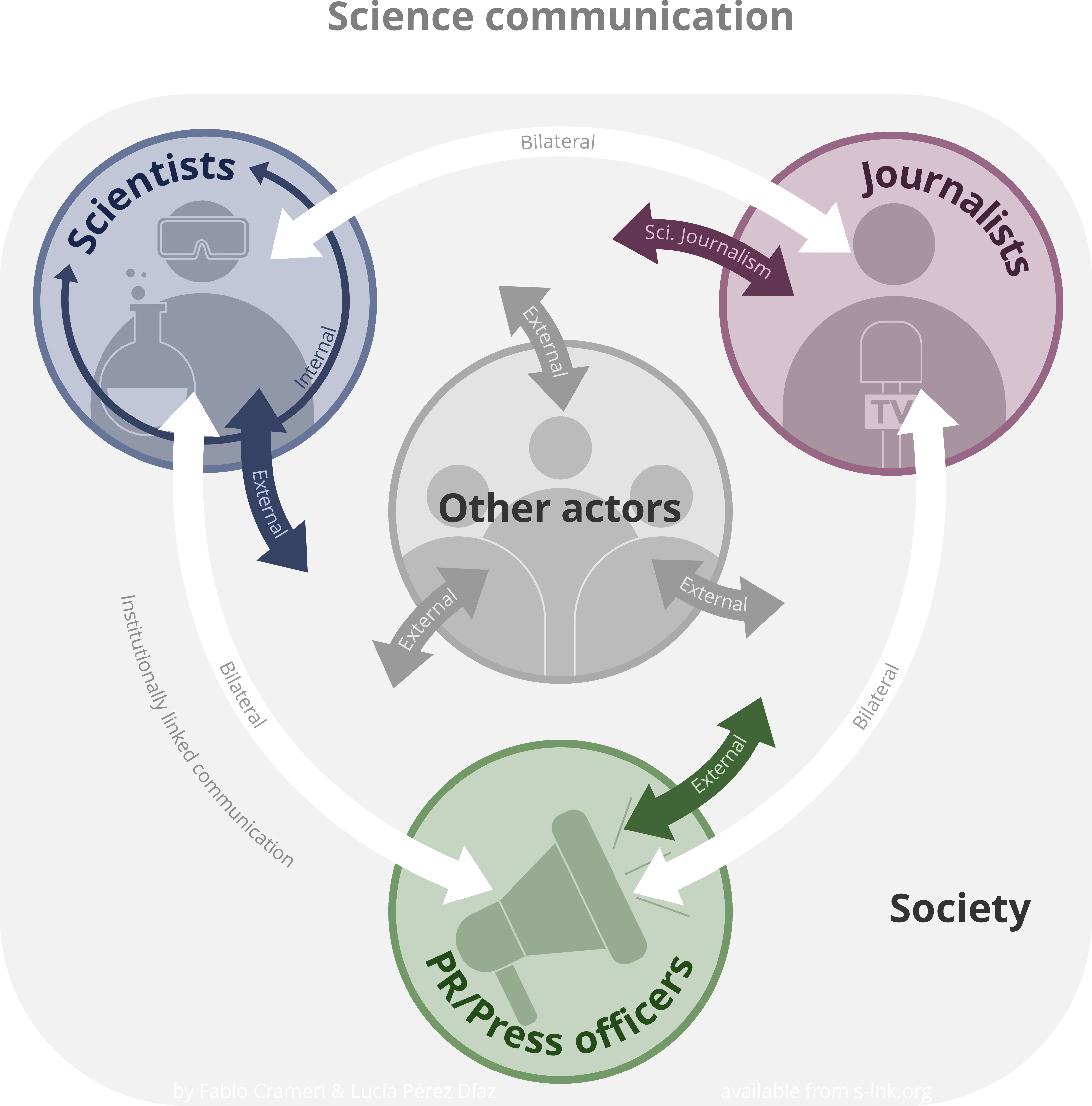
Science Communication
Science communication encompasses a wide range of activities that connect science and society. Common goals of science communication include informing non-experts about scientific findings, raising the Public awareness of science, public awareness of and interest in science, influencing people's attitudes and behaviors, informing public policy, and Public engagement, engaging with diverse communities to address societal problems. The term "science communication" generally refers to settings in which audiences are not experts on the scientific topic being discussed (Science outreach, outreach), though some authors categorize expert-to-expert communication ("inreach" such as publication in scientific journals) as a type of science communication. Examples of outreach include science journalism and health communication. Since science has political, moral, and legal implications, science communication can help bridge gaps between different stakeholders in public policy, industry, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphitheatre
An amphitheatre (American English, U.S. English: amphitheater) is an open-air venue used for entertainment, performances, and sports. The term derives from the ancient Greek ('), from ('), meaning "on both sides" or "around" and ('), meaning "place for viewing". Ancient Greek Theater (structure), theatres were typically built on hillsides and semi-circular in design. The first amphitheatre may have been built at Pompeii around 70 BC. Ancient Roman amphitheatres were oval or circular in plan, with seating tiers that surrounded the central performance area, like a modern open-air stadium. In contrast, both ancient Greek and ancient Roman theatre (structure), Roman theatres were built in a semicircle, with tiered seating rising on one side of the performance area. Modern English parlance uses "amphitheatre" for any structure with sloping seating, including theater (structure), theatre-style stages with spectator seating on only one side, Theatre in the round, theatres in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opicina
Opicina (), formerly Poggioreale del Carso in Italian, is a town in northeastern Italy, close to the Slovenian border at Fernetti (). Opicina is a ''frazione'' of the ''comune'' of Trieste, the provincial and regional capital. The town has a large Slovene population, with Slovenian being widely used alongside Italian in private and public institutions. The first town near Opicina is Sežana in Slovenia, there is also the next railway station. Geography It is located on the Karst Plateau, 3 miles north of Trieste, a seaport on the Adriatic Sea. Name The name Opicina is of Slovene origin. It derives from "ob p'čine" ("ob pečini" in modern standard Slovene), meaning "by the cliff". Thus, it is among the Italian towns and villages in Friuli-Venezia Giulia with a name of Slavic origin. Before World War I, it used to be known in Italian as Opcina, a name still used in the local Triestine dialect. During the Fascist regime, the name was first Italianized into Villa Opicina, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |