|
Isodar
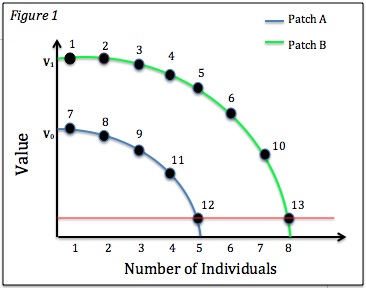
Isodar is a theory of habitat selection in population biology The term population biology has been used with different meanings. In 1971 Edward O. Wilson ''et al''. used the term in the sense of applying mathematical models to population genetics, community ecology, and population dynamics. Alan Hastings ... proposed by Douglas W. Morris. The theory underscores the importance of the abundance and thus competition between the members of the same species in selecting habitats. The name "isodar" stems from "iso" in Latin meaning same and "dar" from Darwin. Background and theory An isodar, or habitat isodar, is a theory in evolutionary ecology developed in the late 1980s by Douglas W. Morris. Isodars model density-dependent habitat selection for one or two species in two habitats according to the ideal free and ideal despotic distributions. Isodar is a two-part word: "iso" meaning equal in Latin; "dar" for Darwinian evolution, and is defined as ''all combinations of populati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat A~Habitat B
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate. The physical factors may include (for example): soil, moisture, range of temperature, and light intensity. Biotic factors will include the availability of food and the presence or absence of predators. Every species has particular habitat requirements, with habitat generalist species able to thrive in a wide array of environmental conditions while habitat specialist species requiring a very limited set of factors to survive. The habitat of a species is not necessarily found in a geographical area, it can be the interior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Biology
The term population biology has been used with different meanings. In 1971 Edward O. Wilson ''et al''. used the term in the sense of applying mathematical models to population genetics, community ecology, and population dynamics. Alan Hastings used the term in 1997 as the title of his book on the mathematics used in population dynamics. The name was also used for a course given at UC Davis in the late 2010s, which describes it as an interdisciplinary field combining the areas of ecology and evolutionary biology. The course includes mathematics, statistics, ecology, genetics, and systematics. Numerous types of organisms are studied. The journal ''Theoretical Population Biology ''Theoretical Population Biology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on theoretical aspects population biology in its widest sense, including mathematical modelling of populations, ecology, evolution, genetics, demography, ...'' is published. See also References External links ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas W
Douglas may refer to: People * Douglas (given name) * Douglas (surname) Animals *Douglas (parrot), macaw that starred as the parrot ''Rosalinda'' in Pippi Longstocking *Douglas the camel, a camel in the Confederate Army in the American Civil War Businesses * Douglas Aircraft Company * Douglas (cosmetics), German cosmetics retail chain in Europe * Douglas (motorcycles), British motorcycle manufacturer Peerage and Baronetage * Duke of Douglas * Earl of Douglas, or any holder of the title * Marquess of Douglas, or any holder of the title * Douglas Baronets Peoples * Clan Douglas, a Scottish kindred * Dougla people, West Indians of both African and East Indian heritage Places Australia * Douglas, Queensland, a suburb of Townsville * Douglas, Queensland (Toowoomba Region), a locality * Port Douglas, North Queensland, Australia * Shire of Douglas, in northern Queensland Belize * Douglas, Belize Canada * Douglas, New Brunswick * Douglas Parish, New Brunswick * Douglas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Ecology
Evolutionary ecology lies at the intersection of ecology and evolutionary biology. It approaches the study of ecology in a way that explicitly considers the evolutionary histories of species and the interactions between them. Conversely, it can be seen as an approach to the study of evolution that incorporates an understanding of the interactions between the species under consideration. The main subfields of evolutionary ecology are life history evolution, sociobiology (the evolution of social behavior), the evolution of interspecific interactions (e.g. cooperation, predator–prey interactions, parasitism, mutualism) and the evolution of biodiversity and of ecological communities. Evolutionary ecology mostly considers two things: how interactions (both among species and between species and their physical environment) shape species through selection and adaptation, and the consequences of the resulting evolutionary change. Evolutionary models A large part of evolutionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Free Distribution
In ecology, an ideal free distribution (IFD) is a theoretical way in which a populations individuals distribute themselves among several patches of resources within their environment, in order to minimize resource competition and maximize fitness.Fretwell, S. D. 1972. ''Populations in a Seasonal Environment''. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.Fretwell, S. D. & Lucas, H. L., Jr. 1970. On territorial behavior and other factors influencing habitat distribution in birds. I. Theoretical Development. ''Acta Biotheoretica'' 19: 16–36. The theory states that the number of individual animals that will aggregate in various patches is proportional to the amount of resources available in each. For example, if patch A contains twice as many resources as patch B, there will be twice as many individuals foraging in patch A as in patch B. The term "ideal" implies that animals are aware of each patch's quality, and they choose to forage in the patch with the highest quality. The ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Free Distribution
In ecology, an ideal free distribution (IFD) is a theoretical way in which a populations individuals distribute themselves among several patches of resources within their environment, in order to minimize resource competition and maximize fitness.Fretwell, S. D. 1972. ''Populations in a Seasonal Environment''. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.Fretwell, S. D. & Lucas, H. L., Jr. 1970. On territorial behavior and other factors influencing habitat distribution in birds. I. Theoretical Development. ''Acta Biotheoretica'' 19: 16–36. The theory states that the number of individual animals that will aggregate in various patches is proportional to the amount of resources available in each. For example, if patch A contains twice as many resources as patch B, there will be twice as many individuals foraging in patch A as in patch B. The term "ideal" implies that animals are aware of each patch's quality, and they choose to forage in the patch with the highest quality. The ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Ecology
Population ecology is a sub-field of ecology that deals with the dynamics of species populations and how these populations interact with the environment, such as birth and death rates, and by immigration and emigration. The discipline is important in conservation biology, especially in the development of population viability analysis which makes it possible to predict the long-term probability of a species persisting in a given patch of habitat. Although population ecology is a subfield of biology, it provides interesting problems for mathematicians and statisticians who work in population dynamics. History In the 1940s ecology was divided into autecology—the study of individual species in relation to the environment—and synecology—the study of groups of species in relation to the environment. The term autecology (from Ancient Greek: αὐτο, ''aúto'', "self"; οίκος, ''oíkos'', "household"; and λόγος, ''lógos'', "knowledge"), refers to roughly the same fie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |