|
Irwin Barracks
Irwin Barracks is an Australian Army military base located in , a suburb of , Western Australia. It occupies a site on the western side of the Fremantle railway line. It was previously known as Karrakatta Camp and Irwin Training Centre. History The barracks were originally named the ''Irwin Training Centre'' on 5 December 1948 in honour of Lieutenant-Colonel Frederick Chidley Irwin, the first military commandant of Western Australia (1829–1833). Prior to this the area was known as ''Karrakatta Camp'' and was set-aside as a military training area by the Western Australian Colonial Government in 1895. The site was used for short camps (in tented accommodation) and courses for Militia and School Cadet units until the beginning of World War II. In 1896 a rifle range was constructed at Karrakatta and equipped with seven sets of Jeffries patented "Wimbledon" targetsonly the fourth range in the world so equipped. The range replaced the original rifle range located at Mount Eliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Australia is Australia's largest state, with a total land area of . It is the List of country subdivisions by area, second-largest country subdivision in the world, surpassed only by Russia's Sakha, Sakha Republic. the state has 2.76 million inhabitants percent of the national total. The vast majority (92 percent) live in the South-West Land Division, south-west corner; 79 percent of the population lives in the Perth area, leaving the remainder of the state sparsely populated. The first Europeans to visit Western Australia belonged to the Dutch Dirk Hartog expedition, who visited the Western Australian coast in 1616. The first pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Eliza (Western Australia)
Mount Eliza is a hill that overlooks the city of Perth, Western Australia and forms part of Kings Park. It is known as nys , Kaarta Gar-up , label=none , italic=unset and nys , Mooro Katta , label=none , italic=unset in the local Noongar dialect. As part of Kings Park, Mount Eliza has received more than 5 million visitors each year (2019), due to events such as; the Anzac Day Memorial service, the Australia Day fireworks and the Kings Park festival. In addition to these events, Mount Eliza attracts visitors and interest with its ecosystems, indigenous and colonial history, landmarks and other activities. Naming The local Noongar people refer to the peak of Mount Eliza as nys , Mooro Katta , label=none , italic=unset and nys , Kaarta Gar-up , label=none , italic=unset. The southern base of Mount Eliza is known as nys , Gooninup , label=none , italic=unset and is considered a significant site for ceremonies and dreaming for Aboriginal males. In 1827, James Stirling o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citizen Military Forces
The Australian Army Reserve is a collective name given to the reserve units of the Australian Army. Since the Federation of Australia in 1901, the reserve military force has been known by many names, including the Citizens Forces, the Citizen Military Forces, the Militia and, unofficially, the Australian Military Forces. In 1980, however, the current name—Australian Army Reserve—was officially adopted, and it now consists of a number of components based around the level of commitment and training obligation that its members are required to meet. Overview For the first half of the 20th century, due to a widespread distrust of permanent military forces in Australia, the reserve military forces were the primary focus of Australian military planning.Grey 2008, pp. 66–83. Following the end of World War II, however, this focus gradually shifted due to the changing strategic environment, and the requirement for a higher readiness force available to support collective security go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Armed Forces In The West
The Polish Armed Forces in the West () refers to the Polish military formations formed to fight alongside the Western Allies against Nazi Germany and its allies during World War II. Polish forces were also raised within Soviet territories; these were the Polish Armed Forces in the East. The formations, loyal to the Polish government-in-exile, were first formed in France and its Middle East territories following the defeat and occupation of Poland by Germany and the Soviet Union in September 1939. After the fall of France in June 1940, the formations were recreated in the United Kingdom. Making a large contribution to the war effort, the Polish Armed Forces in the West was composed of army, air and naval forces. The Poles soon became shock troops in Allied service, most notably in the Battle of Monte Cassino during the Italian Campaign, where the Polish flag was raised on the ruined abbey on 18 May 1944, as well as in the Battle of Bologna and the Battle of Ancona (bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisoner Of War
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610. Belligerents hold prisoners of war in custody for a range of legitimate and illegitimate reasons, such as isolating them from the enemy combatants still in the field (releasing and repatriating them in an orderly manner after hostilities), demonstrating military victory, punishing them, prosecuting them for war crimes, exploiting them for their labour, recruiting or even conscripting them as their own combatants, collecting military and political intelligence from them, or indoctrinating them in new political or religious beliefs. Ancient times For most of human history, depending on the culture of the victors, enemy fighters on the losing side in a battle who had surrendered and been taken as prisoners of war could expect to be either slaughtered or enslaved. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campbell Barracks (Australia)
Campbell Barracks is an Australian Army base located in Swanbourne, a coastal suburb of Perth, Western Australia. It is named after Lieutenant Colonel Campbell (1842–1924), former commandant of the Commonwealth Military Forces in Western Australia. The Special Air Service Regiment (SASR) has been based at Campbell Barracks since the regiment was first established as an independent company in 1957. Although Campbell Barracks is the home of the SASR, most of the training and selection for the regiment takes place in Bindoon, Western Australia. The SASR is a special forces regiment of the Australian Army and is modelled on the original British SAS, while also drawing on the traditions of the Australian Z Special Force Z Special Unit () was a joint Allied special forces unit formed during the Second World War to operate behind Japanese lines in South East Asia. Predominantly Australian, Z Special Unit was a specialist reconnaissance and sabotage unit that in ... commando ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
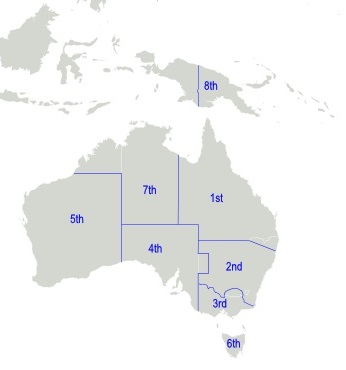
5th Military District (Australia)
The 5th Military District was an administrative district of the Australian Army. Formed shortly after the Federation of Australia, the 5th Military District covered all of Western Australia except the Kimberley region, with its headquarters at Swan Barracks in Perth. Following the First World War, the area's designation was changed to the 5th District Base. In October 1939, it was re-designated as Western Command when the Army moved towards a geographic command structure. In April 1942, the Army was reorganised and Western Command became III Corps in April 1942. Western Command was re-formed in June 1944 when the need for a corps-level headquarters passed. Then-Captain William Henderson, later promoted to Major General, served on the command's staff soon after the Second World War ended. The 13th Infantry Brigade was re-raised in 1948, once again headquartered in Western Australia, and assigned to Western Command. Upon formation, it consisted of two infantry battalions: th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Pound
The pound ( Sign: £, £A for distinction) was the currency of Australia from 1910 until 14 February 1966, when it was replaced by the Australian dollar. As with other £sd currencies, it was subdivided into 20 shillings (denoted by the symbol s or /–), each of 12 pence (denoted by the symbol d). History The establishment of a separate Australian currency was contemplated by section 51(xii) of the Constitution of Australia, which gave Federal Parliament the right to legislate with respect to "currency, coinage, and legal tender". Establishment Coinage The Deakin Government's ''Coinage Act 1909'' distinguished between "British coin" and "Australian coin", giving both status as legal tender of equal value. The Act gave the Treasurer the power to issue silver, bronze and nickel coins, with the dimensions, size, denominations, weight and fineness to be determined by proclamation of the Governor-General. The first coins were issued in 1910, produced by the Royal Mint in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Australia
The Australian Government, also known as the Commonwealth Government, is the national government of Australia, a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy. Like other Westminster-style systems of government, the Australian Government is made up of three branches: the executive (the prime minister, the ministers, and government departments), the legislative (the Parliament of Australia), and the judicial. The legislative branch, the federal Parliament, is made up of two chambers: the House of Representatives (lower house) and Senate (upper house). The House of Representatives has 151 members, each representing an individual electoral district of about 165,000 people. The Senate has 76 members: twelve from each of the six states and two each from Australia's internal territories, the Australian Capital Territory and Northern Territory. The Australian monarch, currently King Charles III, is represented by the governor-general. The Australian Government in its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federation Of Australia
The Federation of Australia was the process by which the six separate British self-governing colonies of Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania, South Australia (which also governed what is now the Northern Territory), and Western Australia agreed to unite and form the Commonwealth of Australia, establishing a system of federalism in Australia. The colonies of Fiji and New Zealand were originally part of this process, but they decided not to join the federation. Following federation, the six colonies that united to form the Commonwealth of Australia as states kept the systems of government (and the bicameral legislatures) that they had developed as separate colonies, but they also agreed to have a federal government that was responsible for matters concerning the whole nation. When the Constitution of Australia came into force, on 1 January 1901, the colonies collectively became states of the Commonwealth of Australia. The efforts to bring about federation in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Heritage Database
The Australian Heritage Database is a searchable online database of heritage sites in Australia. It is maintained by the Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment , in consultation with Australian Heritage Council. There are more than 20,000 entries in the database, which includes natural, historic and Indigenous heritage places, held in separately maintained lists. Description Included in the database are places or items: * the World Heritage List, places that are of outstanding universal value and have been included on this United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO) managed list; * the National Heritage List, a long list of natural, historic and Indigenous places that are of outstanding national heritage value to the Australian nation; * the Commonwealth Heritage List, a list of natural, historic and Indigenous places of heritage significance owned or controlled by the Australian Government; * the Register of the National Estate, a lis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Heritage List
The Commonwealth Heritage List is a heritage register established in 2003, which lists places under the control of the Australian government, on land or in waters directly owned by the Crown (in Australia, the Crown in right of the Commonwealth of Australia). Such places must have importance in relation to the natural or historic heritage of Australia, including those of cultural significance to Indigenous Australians. National heritage sites on the list are protected by the ''Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999'' (''EPBC Act''). The Commonwealth Heritage List, together with the Australian National Heritage List, replaced the former Register of the National Estate in 2003. Under the ''EPBC Act'', the National Heritage List includes places of outstanding heritage value to the nation, and the Commonwealth Heritage List includes heritage places owned or controlled by the Commonwealth. Places protected under the Act include federally owned telegraph statio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |