|
Integrated Nuclear Fuel Cycle Information System
Integrated Nuclear Fuel Cycle Information System (iNFCIS) is a set of databases related to the nuclear fuel cycle maintained by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). The main objective of iNFCIS is to provide information on all aspects of nuclear fuel cycle to various researchers, analysts, energy planners, academicians, students and the general public. Presently iNFCIS includes several modules. iNFCIS requires free registration for on-line access. Background Nuclear fuel cycle consists of a number of steps which are critical in supporting a nuclear power programme. This included fuel supply-related activities in the front end and used or spent fuel-related activities in the back end. Reliable and accurate statistical data on worldwide nuclear fuel cycle activities is desired by the nuclear community for national policy making, international co-operation and studies pertaining to sustainable global energy futures. The IAEA provides up-to-date fuel cycle information to M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Fuel Cycle
The nuclear fuel cycle, also called nuclear fuel chain, is the progression of nuclear fuel through a series of differing stages. It consists of steps in the ''front end'', which are the preparation of the fuel, steps in the ''service period'' in which the fuel is used during reactor operation, and steps in the ''back end'', which are necessary to safely manage, contain, and either reprocess or dispose of spent nuclear fuel. If spent fuel is not reprocessed, the fuel cycle is referred to as an ''open fuel cycle'' (or a ''once-through fuel cycle''); if the spent fuel is reprocessed, it is referred to as a ''closed fuel cycle''. Basic concepts Nuclear power relies on fissionable material that can sustain a chain reaction with neutrons. Examples of such materials include uranium and plutonium. Most nuclear reactors use a moderator to lower the kinetic energy of the neutrons and increase the probability that fission will occur. This allows reactors to use material with far lower c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOX Fuel
Mixed oxide fuel, commonly referred to as MOX fuel, is nuclear fuel that contains more than one oxide of fissile material, usually consisting of plutonium blended with natural uranium, reprocessed uranium, or depleted uranium. MOX fuel is an alternative to the low-enriched uranium (LEU) fuel used in the light-water reactors that predominate nuclear power generation. For example, a mixture of 7% plutonium and 93% natural uranium reacts similarly, although not identically, to LEU fuel (3 to 5% uranium-235). MOX usually consists of two phases, UO2 and PuO2, and/or a single phase solid solution (U,Pu)O2. The content of PuO2 may vary from 1.5 wt.% to 25–30 wt.% depending on the type of nuclear reactor. One attraction of MOX fuel is that it is a way of utilizing surplus weapons-grade plutonium, an alternative to storage of surplus plutonium, which would need to be secured against the risk of theft for use in nuclear weapons. On the other hand, some studies warned that normalisin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NFCIS
The Nuclear Fuel Cycle Information System (NFCIS) is an international database of civilian and commercial nuclear fuel cycles maintained by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). The NFCIS is one of the five databases that comprise the Integrated Nuclear Fuel Cycle Information System. The NFCIS is a database that is housed by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). According to the IAEA website, on Jun 14, 2016, the NFCIS held information pertaining to 650 different facilities, located in 54 countries throughout the world. The Nuclear Fuel Cycle Information System's information comes from countries that are members of the IAEA and other public information sources. The IAEA's Nuclear Fuel Cycle Information System is considered a nuclear safeguard. The NFC Information System database has evolved since its original development during the 1980s. The current layout of the database provides information on the types of facilities currently monitored and facilities that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spent Nuclear Fuel Shipping Cask
A nuclear flask is a shipping container that is used to transport active nuclear materials between nuclear power station and spent fuel reprocessing facilities. Each shipping container is designed to maintain its integrity under normal transportation conditions and during hypothetical accident conditions. They must protect their contents against damage from the outside world, such as impact or fire. They must also contain their contents from leakage, both for physical leakage and for radiological shielding. Spent nuclear fuel shipping casks are used to transport spent nuclear fuel used in nuclear power plants and research reactors to disposal sites such as the nuclear reprocessing center at COGEMA La Hague site. International United Kingdom Railway-carried flasks are used to transport spent fuel from nuclear power stations in the UK and the Sellafield spent nuclear fuel reprocessing facility. Each flask weighs more than 50 tonnes, and transports usually not more than 2.5 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spent Nuclear Fuel
Spent nuclear fuel, occasionally called used nuclear fuel, is nuclear fuel that has been irradiated in a nuclear reactor (usually at a nuclear power plant). It is no longer useful in sustaining a nuclear reaction in an ordinary thermal reactor and depending on its point along the nuclear fuel cycle, it may have considerably different isotopic constituents. The term "fuel" is slightly confusing, as it implies a combustion of some type, which does not occur in a nuclear power plant. Nevertheless, this term is generally accepted. Nature of spent fuel Nanomaterial properties In the oxide fuel, intense temperature gradients exist that cause fission products to migrate. The zirconium tends to move to the centre of the fuel pellet where the temperature is highest, while the lower-boiling fission products move to the edge of the pellet. The pellet is likely to contain many small bubble-like pores that form during use; the fission product xenon migrates to these voids. Some of this xen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post Irradiation Examination
Post Irradiation Examination (PIE) is the study of used nuclear materials such as nuclear fuel. It has several purposes. It is known that by examination of used fuel that the failure modes which occur during normal use (and the manner in which the fuel will behave during an accident) can be studied. In addition information is gained which enables the users of fuel to assure themselves of its quality and it also assists in the development of new fuels. After major accidents the core (or what is left of it) is normally subject to PIE in order to find out what happened. One site where PIE is done is the ITU which is the EU centre for the study of highly radioactive materials. Materials in a high radiation environment (such as a reactor) can undergo unique behaviors such as swelling and non-thermal creep. If there are nuclear reactions within the material (such as what happens in the fuel), the stoichiometry will also change slowly over time. These behaviors can lead to new materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enriched Uranium
Enriched uranium is a type of uranium in which the percent composition of uranium-235 (written 235U) has been increased through the process of isotope separation. Naturally occurring uranium is composed of three major isotopes: uranium-238 (238U with 99.2739–99.2752% natural abundance), uranium-235 (235U, 0.7198–0.7202%), and uranium-234 (234U, 0.0050–0.0059%). 235U is the only nuclide existing in nature (in any appreciable amount) that is fissile with thermal neutrons. Enriched uranium is a critical component for both civil nuclear power generation and military nuclear weapons. The International Atomic Energy Agency attempts to monitor and control enriched uranium supplies and processes in its efforts to ensure nuclear power generation safety and curb nuclear weapons proliferation. There are about 2,000 tonnes of highly enriched uranium in the world, produced mostly for nuclear power, nuclear weapons, naval propulsion, and smaller quantities for research reactors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
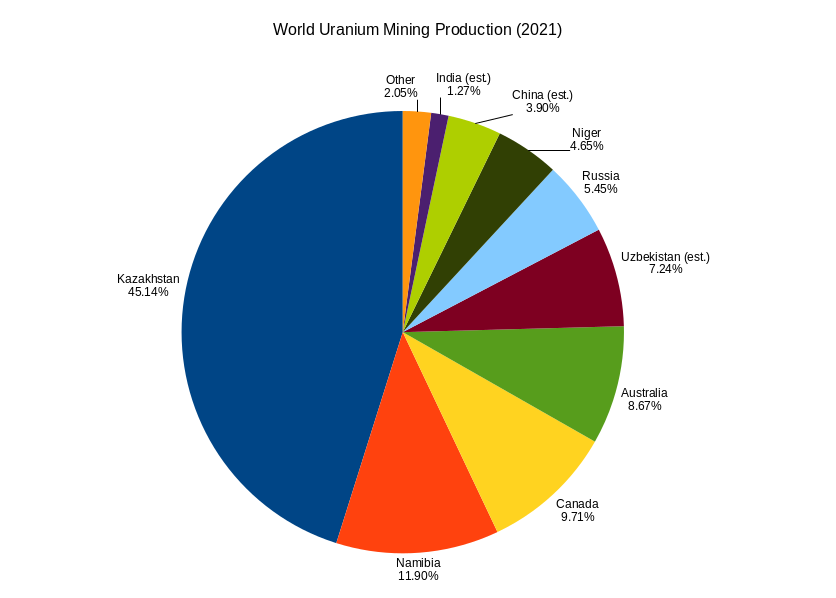
Uranium Mining
Uranium mining is the process of extraction of uranium ore from the ground. Over 50 thousand tons of uranium were produced in 2019. Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia were the top three uranium producers, respectively, and together account for 68% of world production. Other countries producing more than 1,000 tons per year included Namibia, Niger, Russia, Uzbekistan, the United States, and China. Nearly all of the world's mined uranium is used to power nuclear power plants. Historically uranium was also used in applications such as uranium glass or ferrouranium but those applications have declined due to the radioactivity of uranium and are nowadays mostly supplied with a plentiful cheap supply of depleted uranium which is also used in uranium ammunition. In addition to being cheaper, depleted uranium is also less radioactive due to a lower content of short-lived and than natural uranium. Uranium is mined by in-situ leaching (57% of world production) or by conventional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation states. It reacts with carbon, halogens, nitrogen, silicon, and hydrogen. When exposed to moist air, it forms oxides and hydrides that can expand the sample up to 70% in volume, which in turn flake off as a powder that is pyrophoric. It is radioactive and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of plutonium dangerous. Plutonium was first synthetically produced and isolated in late 1940 and early 1941, by a deuteron bombardment of uranium-238 in the cyclotron at the University of California, Berkeley. First, neptunium-238 ( half-life 2.1 days) was synthesized, which subsequently beta-decayed to form the new element with atomic number 94 and atomic weight 238 (half-life 88 years). Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 1957 as an autonomous organization within the United Nations system; though governed by its own founding treaty, the organization reports to both the General Assembly and the Security Council of the United Nations, and is headquartered at the UN Office at Vienna, Austria. The IAEA was created in response to growing international concern toward nuclear weapons, especially amid rising tensions between the foremost nuclear powers, the United States and the Soviet Union. U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower's " Atoms for Peace" speech, which called for the creation of an international organization to monitor the global proliferation of nuclear resources and technology, is credited with catalyzing the formation of the IAEA, whose treaty came i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reprocessed Uranium
Reprocessed uranium (RepU) is the uranium recovered from nuclear reprocessing, as done commercially in France, the UK and Japan and by nuclear weapons states' military plutonium production programs. This uranium makes up the bulk of the material separated during reprocessing. Commercial LWR spent nuclear fuel contains on average (excluding cladding) only four percent plutonium, minor actinides and fission products by weight. Despite it often containing more fissile material than natural uranium, reuse of reprocessed uranium has not been common because of low prices in the uranium market of recent decades, and because it contains undesirable isotopes of uranium. Given sufficiently high uranium prices, it is feasible for reprocessed uranium to be re- enriched and reused. A higher enrichment level is required to compensate for the 236U which is lighter than 238U and therefore concentrates in the enriched product. As enrichment concentrates lighter isotopes on the "enriched" side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activation Product
Activation products are materials made radioactive by neutron activation. Fission products and actinides produced by neutron absorption of nuclear fuel itself are normally referred to by those specific names, and ''activation product'' reserved for products of neutron capture by other materials, such as structural components of the nuclear reactor or nuclear bomb, the reactor coolant, control rods or other neutron poisons, or materials in the environment. All of these, however, need to be handled as radioactive waste. Some nuclides originate in more than one way, as activation products or fission products. Activation products in a reactor's primary coolant loop are a main reason reactors use a chain of two or even three coolant loops linked by heat exchangers. Fusion reactors will not produce radioactive waste from the fusion product nuclei themselves, which are normally just helium-4, but generate high neutron fluxes, so activation products are a particular concern. Activatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(cropped).jpg)